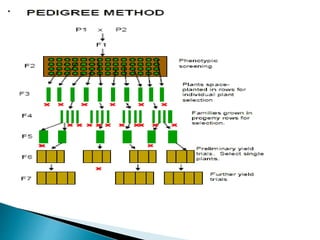
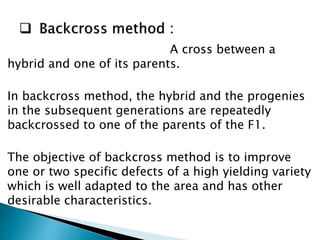
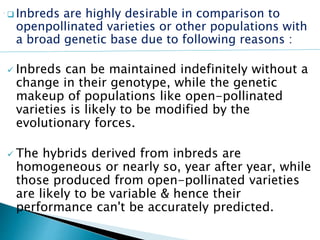
Inbred lines are developed through several generations of self-pollination to create genetically pure and homozygous breeding lines. There are two main methods for developing inbred lines - selfing of heterozygous populations using pedigree, bulk, or backcross methods, and doubling of haploids. Inbred lines are important for developing hybrid varieties in crops as they allow for the stable and uniform performance of hybrids from one generation to the next. Inbred lines are identified by numbers or letters and are important resources in crop breeding programs.