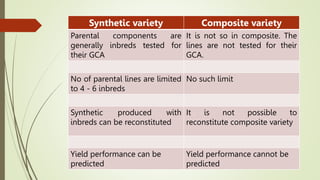
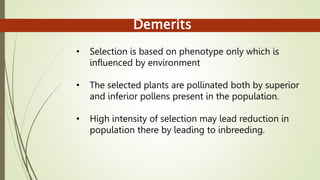
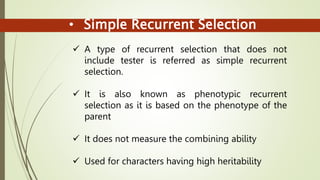
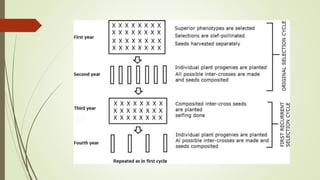
This document discusses breeding methods used in cross-pollinated crops. It describes several methods including mass selection, recurrent selection, progeny selection, and the development of hybrid and synthetic varieties. Mass selection involves selecting plants based on phenotype and bulking seed for the next generation. Recurrent selection involves selfing selected plants, intermating progeny, and repeating cycles of selection and intermating. Hybrid varieties are developed by crossing inbred lines to create uniform, high-yielding F1 hybrids. Synthetic varieties are produced by crossing multiple inbred lines and maintaining the population through open pollination.




















![ Prediction of double cross performance
The predicted performance of any double cross is the average
performance of the four non parental single crosses involving the
four parental inbreds. Inbreds: A, B, C, D.
6 possible single crosses = A x B, A x C, A x D, B x C, B x D, C x D.
From these 3 double crosses produced = (A x B) x (C x D), A x C) x
(B x D), (A x D) x (B x C)
The performance of these anyone double cross can be predicted
from performance of the four single crosses not involved in
producing that particular hybrid.
(A x B) x (C x D) = [(A x C) + (A x D) + (B x C) + (B x D)]/4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/breedingmethodincrosspollinatedcrops-231020133305-47b9b829/85/BREEDING-METHOD-IN-CROSS-POLLINATED-CROPS-pptx-24-320.jpg)