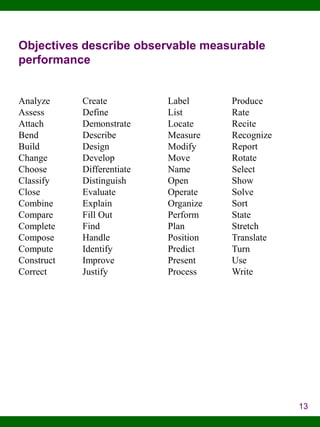
This document provides an overview of an 8-step process for developing and presenting effective safety training. The steps include: 1) assessing learner needs; 2) setting goals and objectives; 3) designing the curriculum; 4) selecting methods and media; 5) writing the course outline; 6) coordinating logistics; 7) presenting the training; and 8) documenting and evaluating the training. The overall goal is to help students improve their knowledge, skills, and ability to develop, present, and evaluate safety training outcomes.