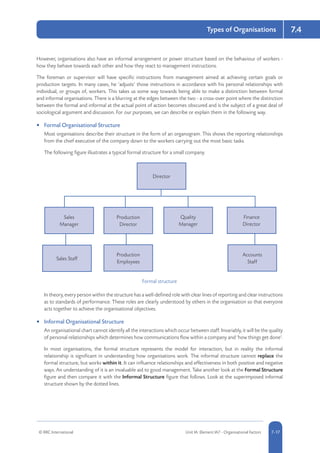
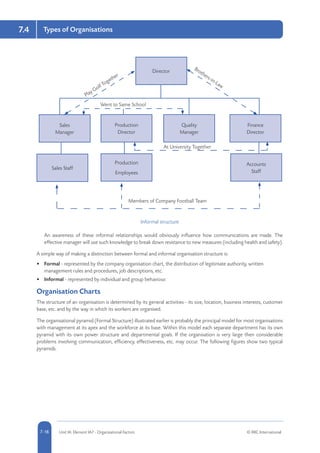
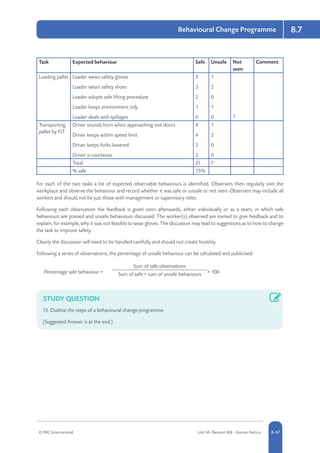
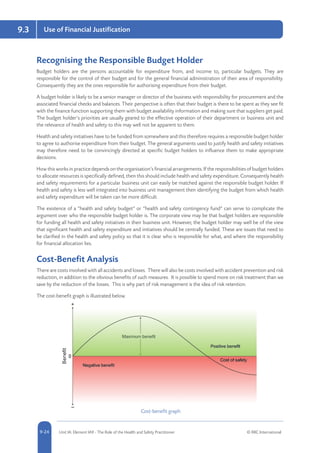
Common risk management strategies include risk avoidance or elimination (completely avoiding activities that pose risks), risk reduction (implementing controls to reduce the likelihood and severity of risks), risk transfer (shifting responsibility for risks to a third party such as through insurance), and risk retention (accepting responsibility for risks without transferring). The aim is to select controls appropriate to the risks identified in assessments, such as preventive measures to reduce risks, protective measures to mitigate harm, or procedural controls to manage risks. Factors like technical, financial, legal and social feasibility help determine suitable control measures.