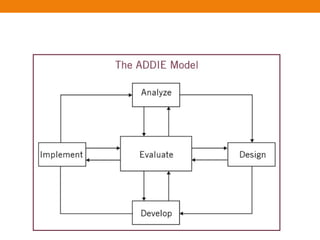
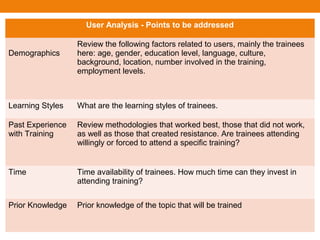
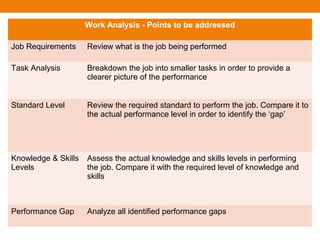
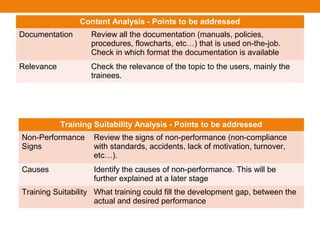
This document provides an overview of several instructional design models and processes for developing training programs. It describes the ASSURE instructional design model which involves analyzing learners, stating objectives, selecting methods/materials, utilizing technology, requiring participation, and evaluating. It also outlines the Dick and Carey instructional design model involving goal identification, analysis, objective writing, assessment development, strategy development, and evaluation. Additional models covered include the Jossey-Bass/Pfeiffer model involving context, user, work, content, suitability, and cost-benefit analyses. The document concludes with an overview of instructional design stages such as objective writing, developing an introduction-development-consolidation structure, writing introductory sessions, and