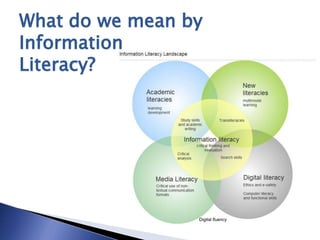
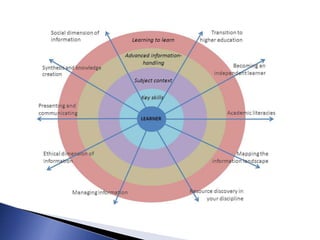
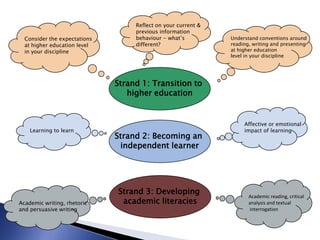
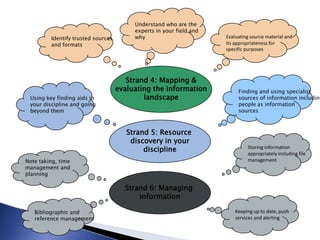
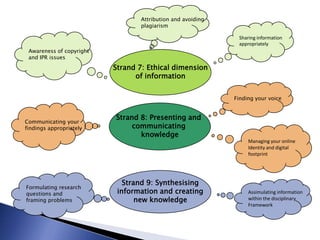
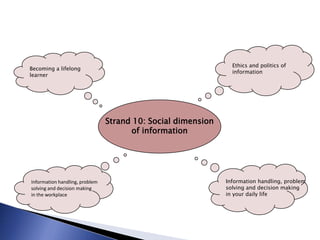
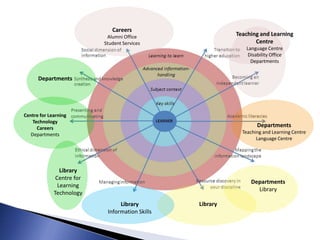
The document outlines the development of a new curriculum for information literacy led by Dr. Jane Secker at the London School of Economics, focusing on the needs of undergraduates in a digital age. It includes a detailed analysis of expert consultations, literature reviews, and frameworks for embedding information literacy into academic disciplines, while also addressing the importance of flexibility and holistic approaches to teaching. Additionally, it mentions collaborative efforts and resources for implementing this curriculum across various academic institutions.