This document provides an introduction to HTML, including:
- HTML is a markup language used to describe web pages
- HTML tags are used to structure and layout content and are written with angle brackets
- The basic HTML page structure includes the <head> for metadata and <body> for visible content
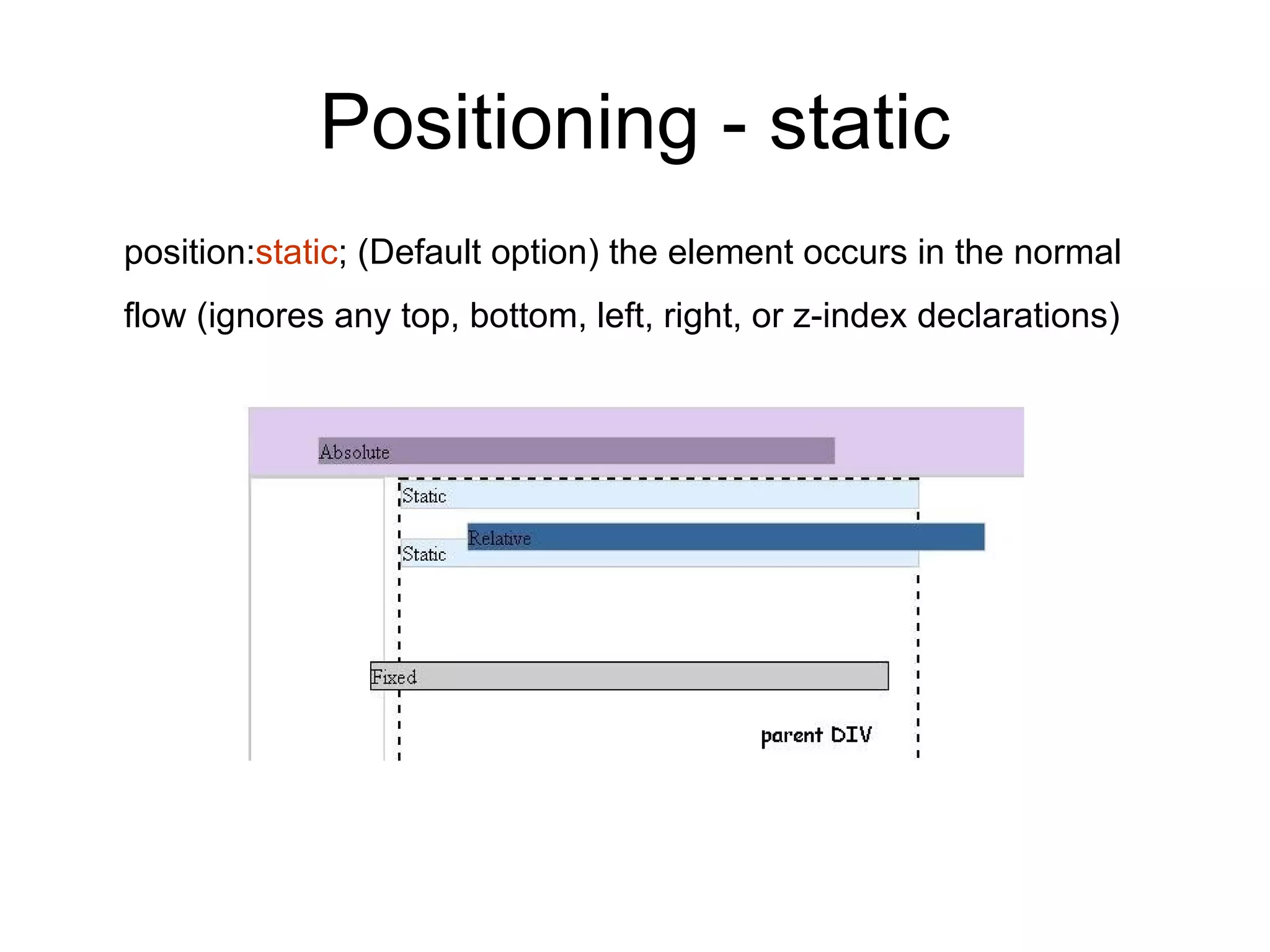
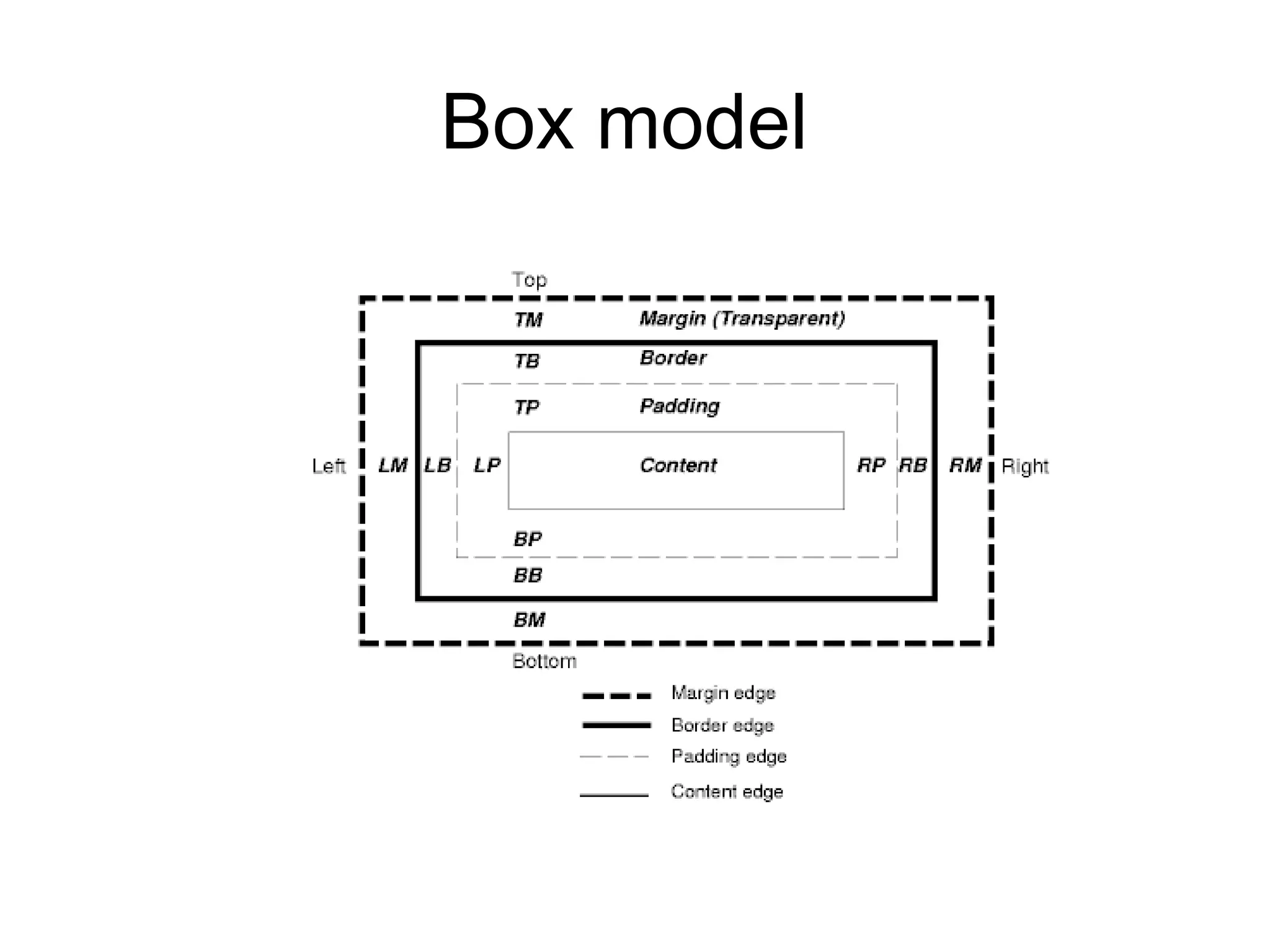
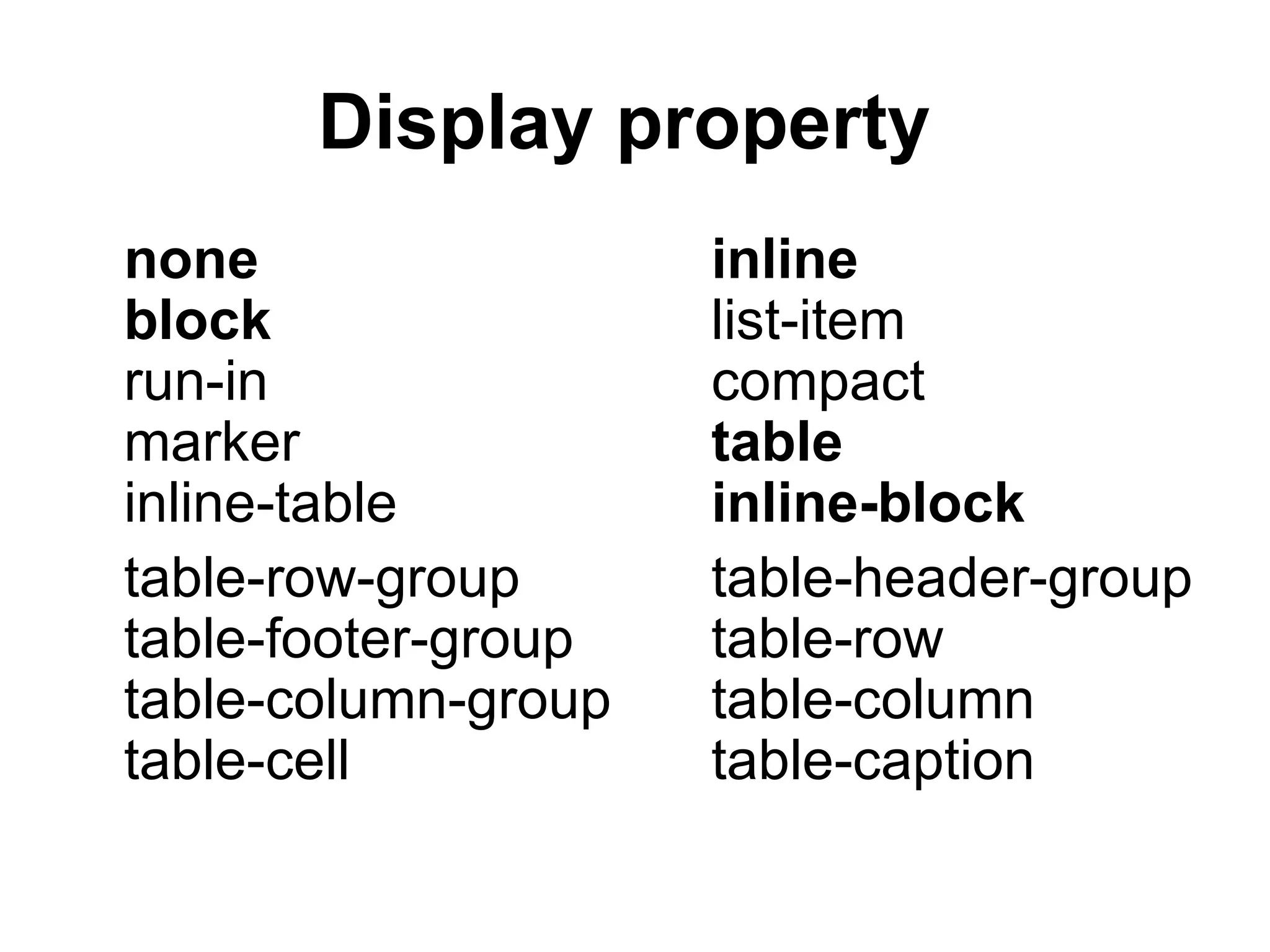
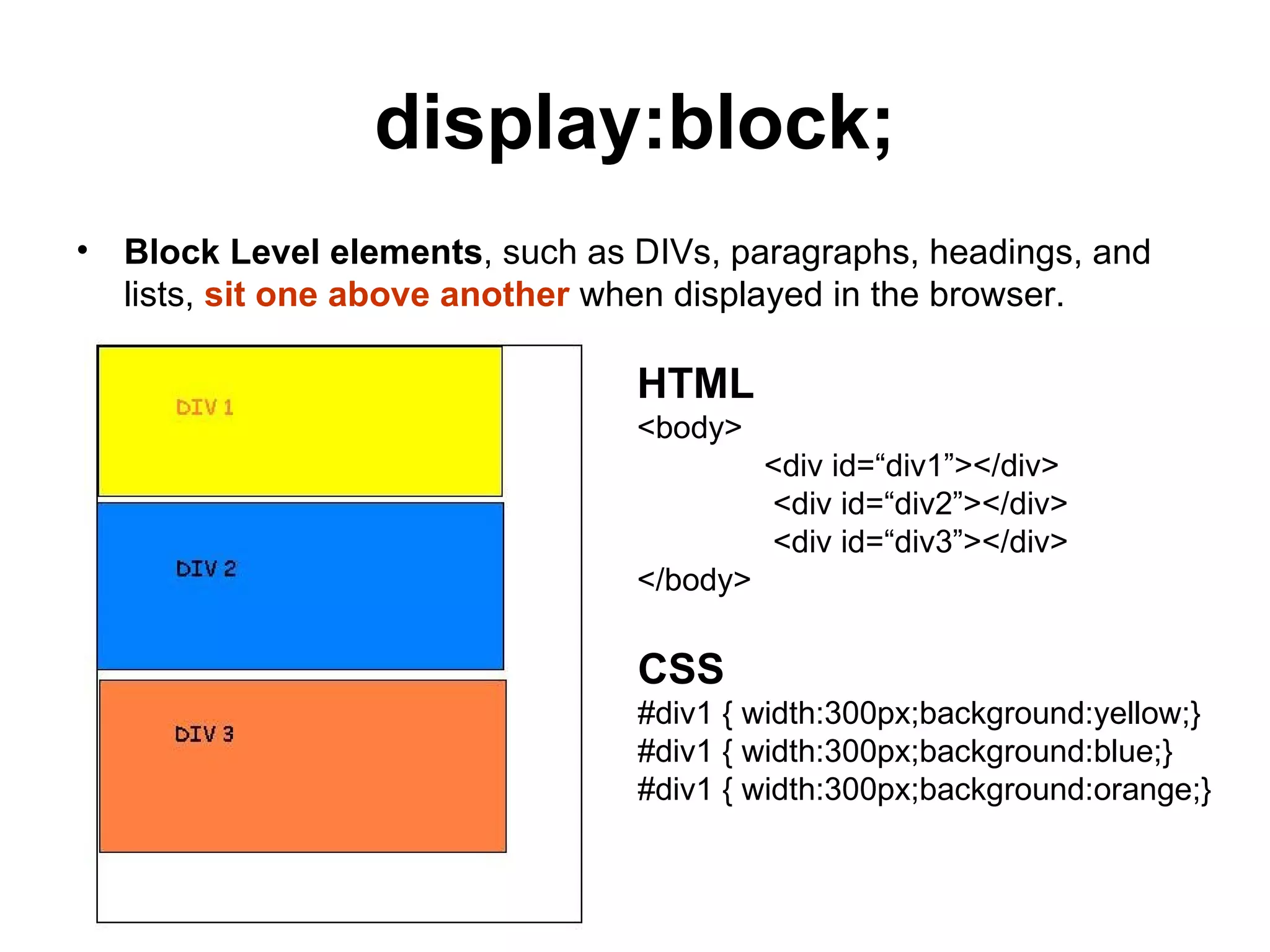
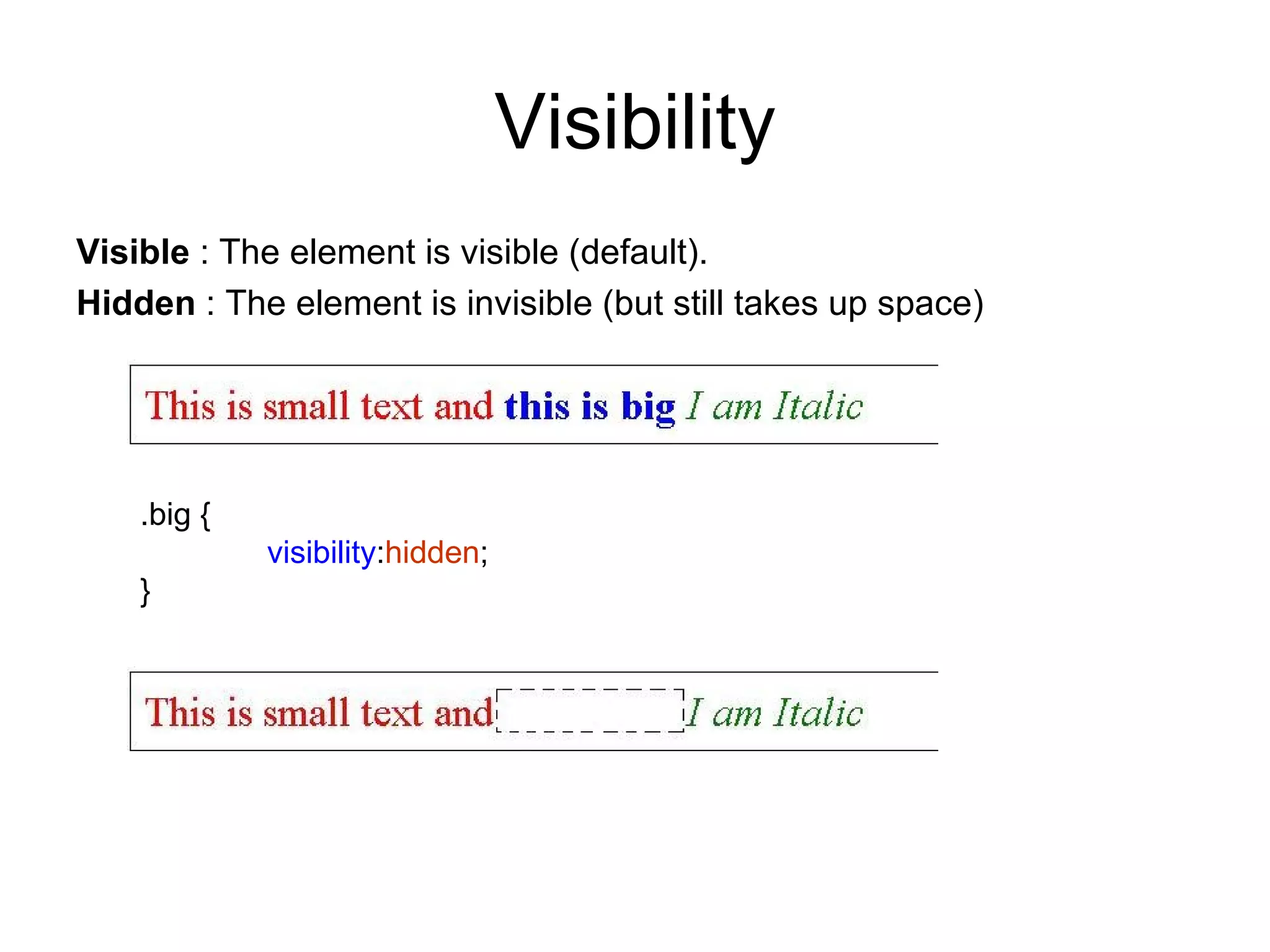
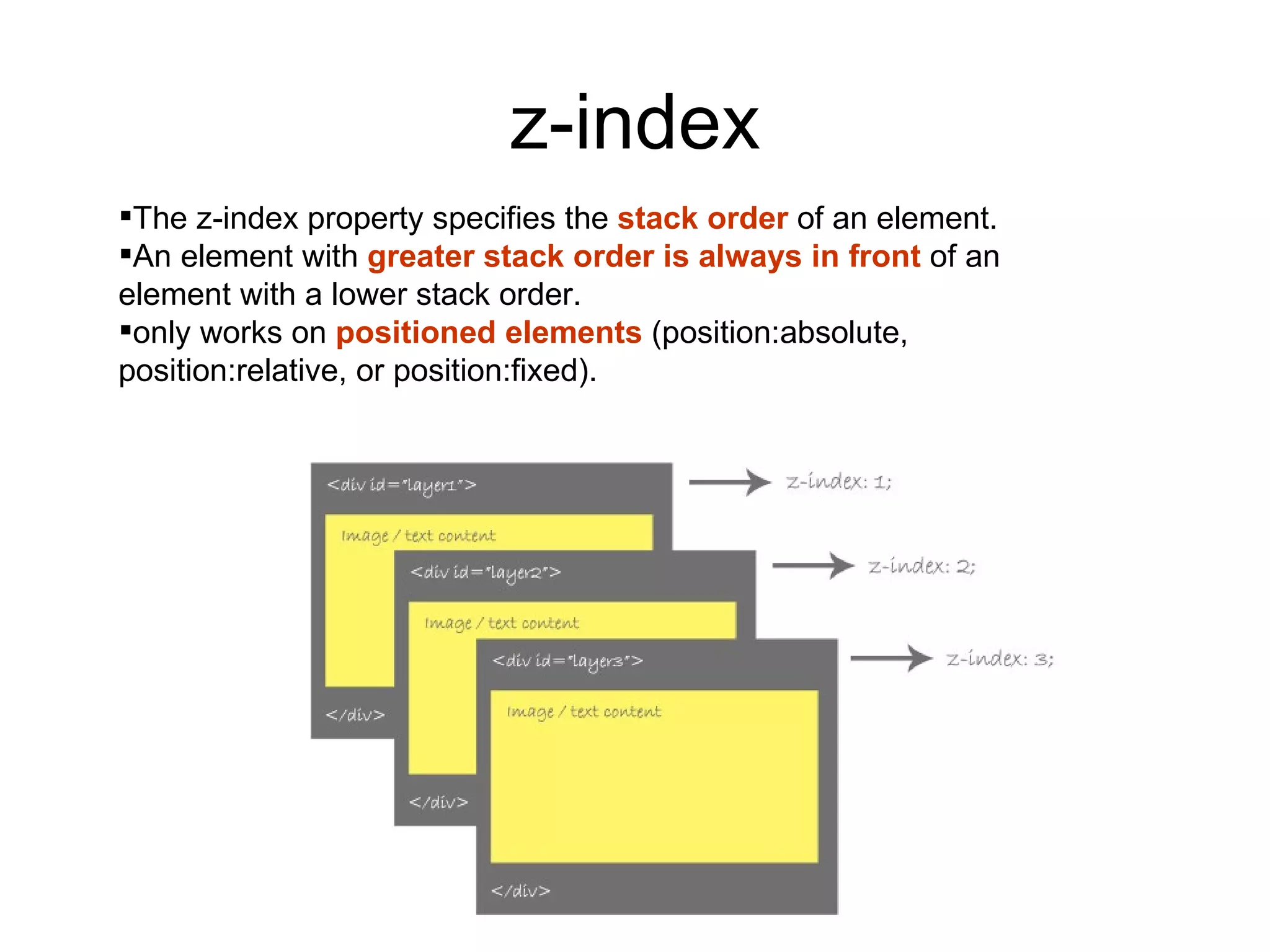
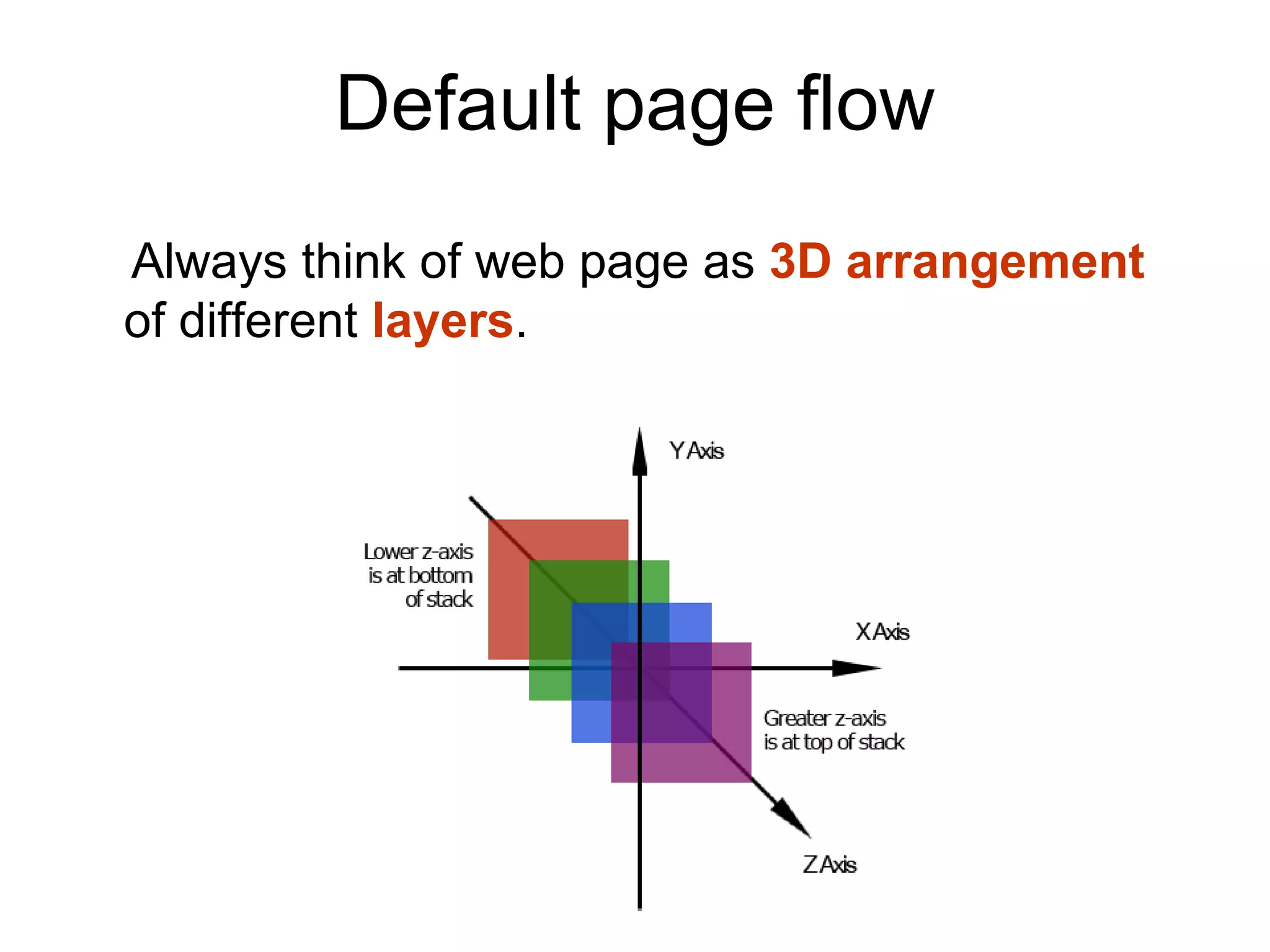
- HTML elements can be styled using CSS with properties like display, position, float, and more
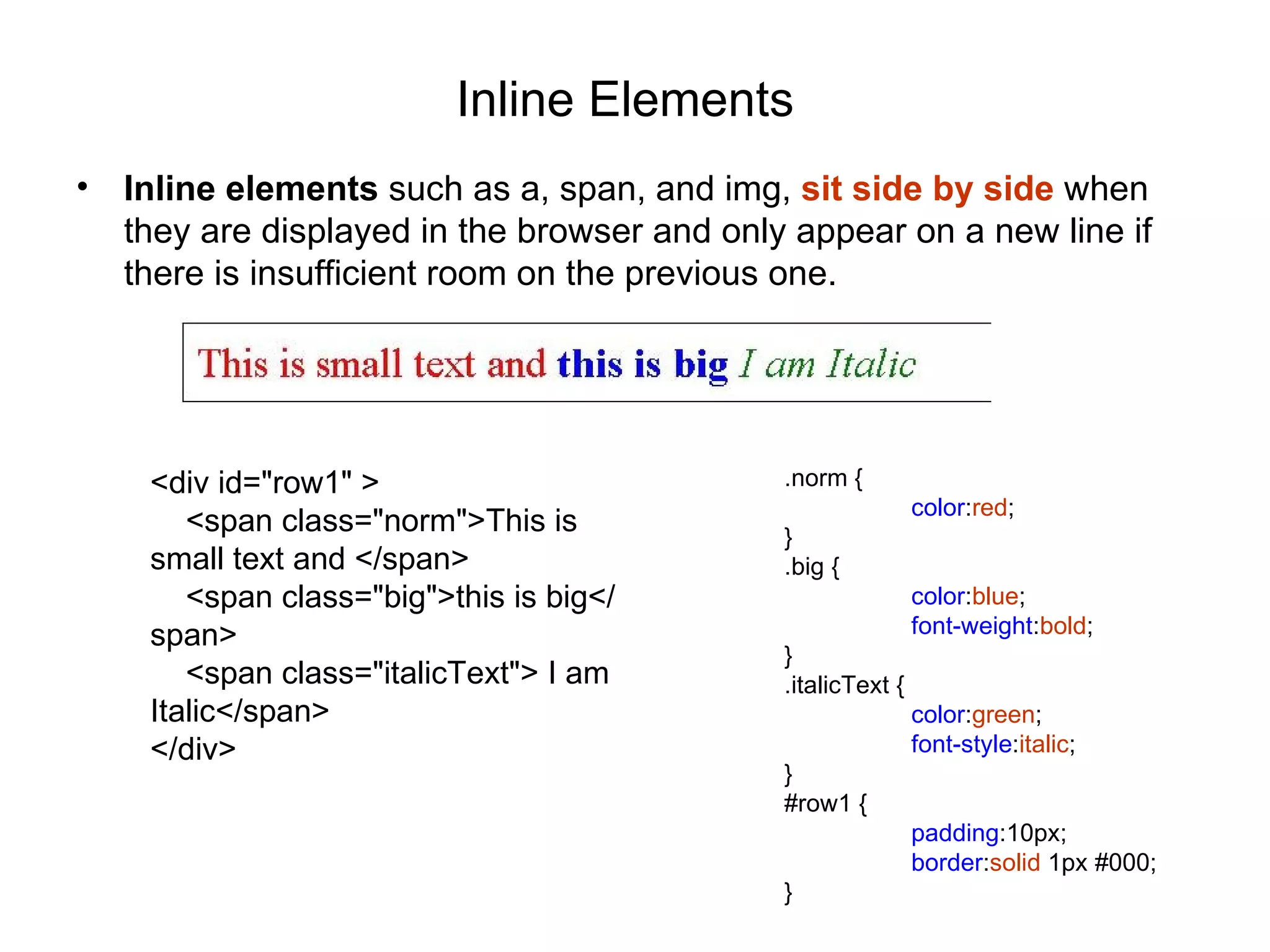
- Common tags include headings, paragraphs, lists, links, and div containers to group and style blocks of content





![Clearing Floats
Clear:both ;
Or
<style type="text/css">
.clearfix:after {
content: "."; display: block; height: 0; clear: both; visibility: hidden; }
.clearfix {display: inline-block;} /* for IE/Mac */
</style>
<!--[if IE]><style type="text/css">
.clearfix { zoom: 1; display: block; }
</style> <![endif]-->](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontohtmlcss-120711044236-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-HTML-14-2048.jpg)