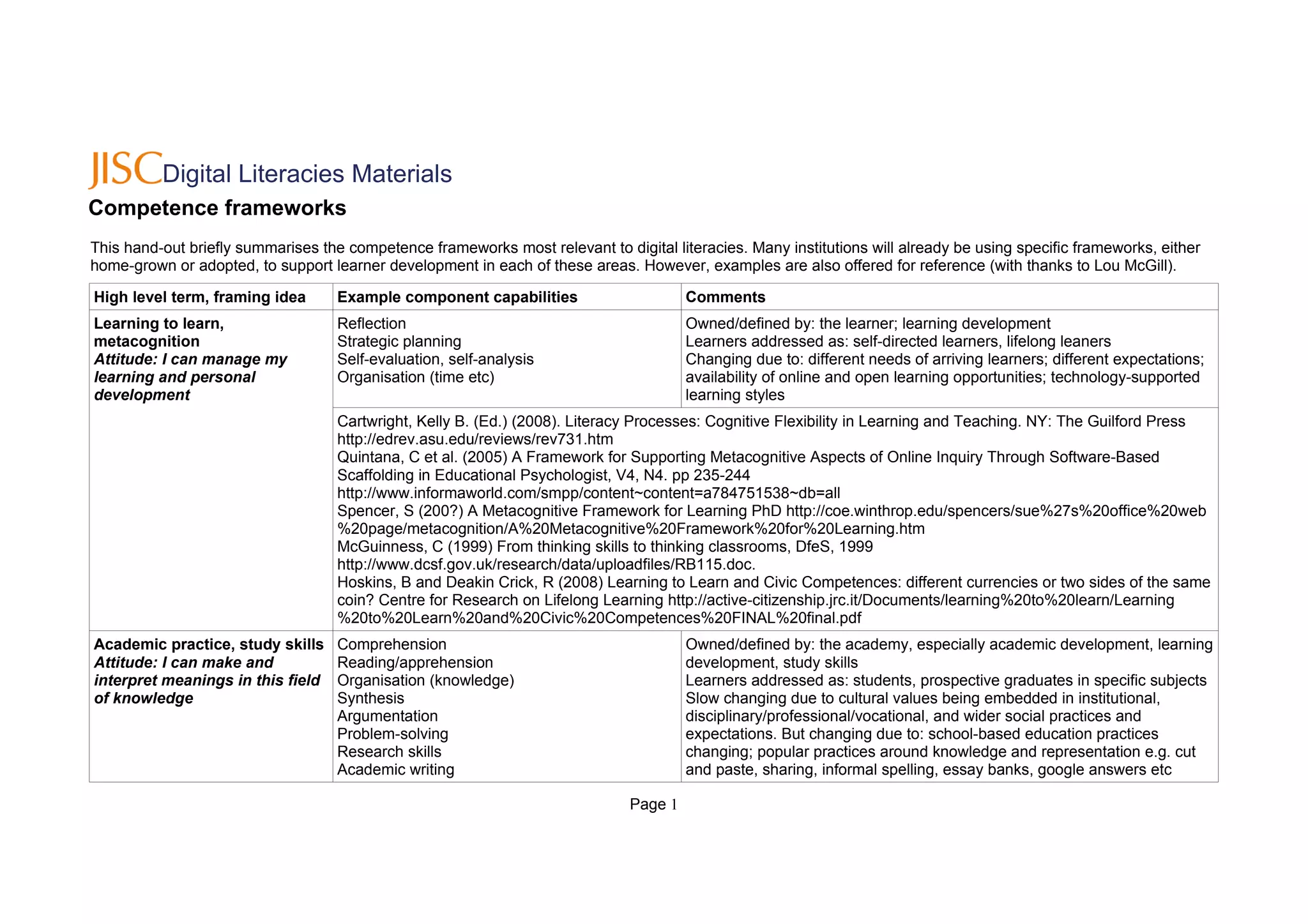
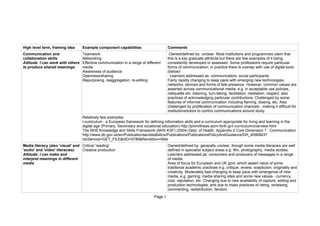
This document summarizes several competence frameworks relevant to digital literacies. It lists high-level terms for different competencies including learning to learn, academic practice, information literacy, communication skills, media literacy, ICT literacy, employability, and citizenship. For each competency, it provides examples of component capabilities and comments on how the frameworks are defined and changing over time.