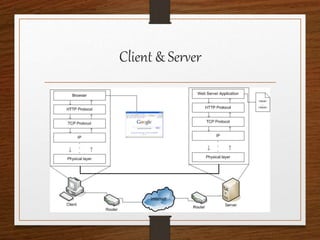
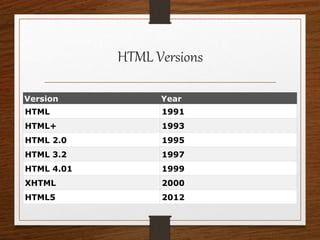
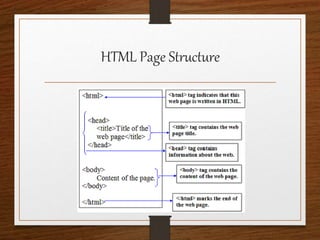
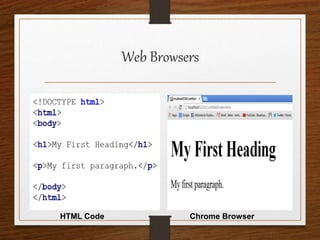
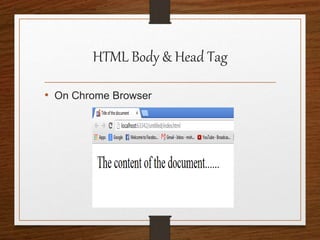
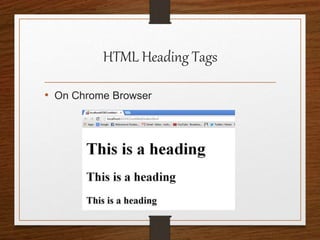
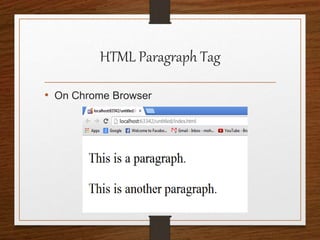
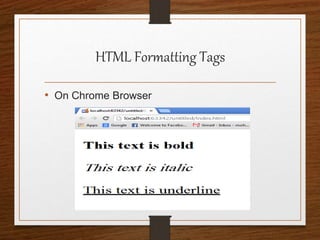
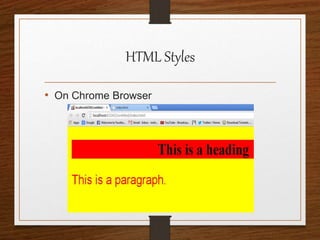
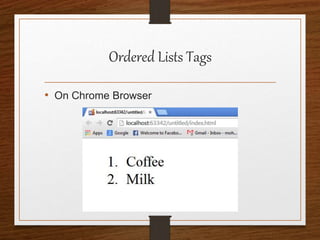
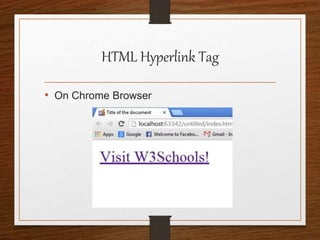
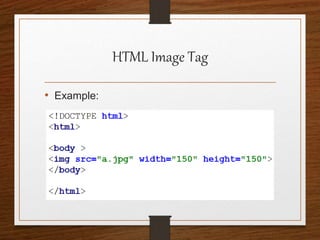
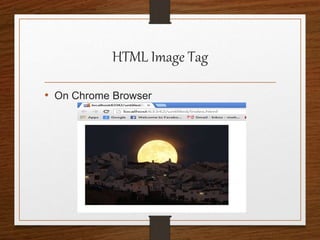
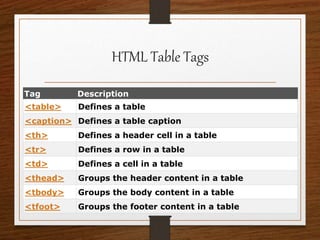
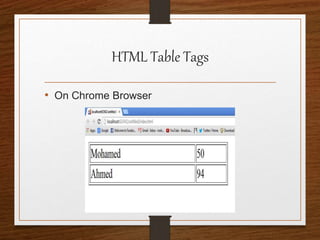
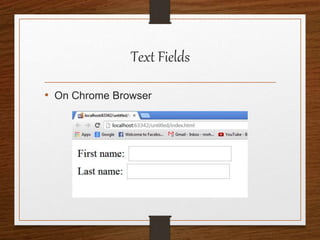
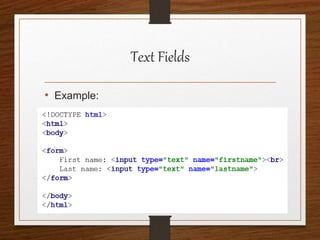
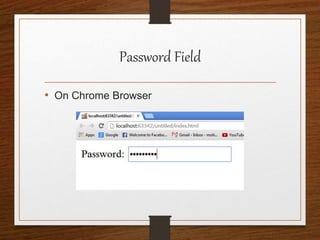
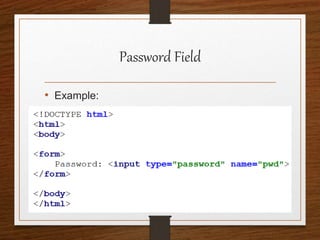
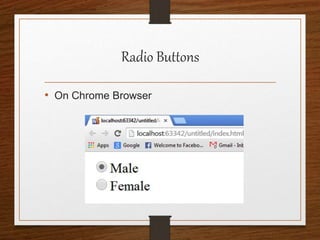
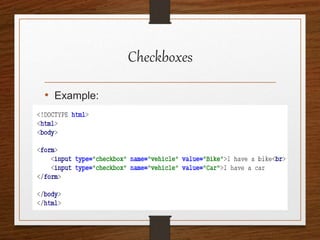
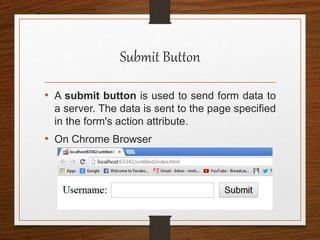
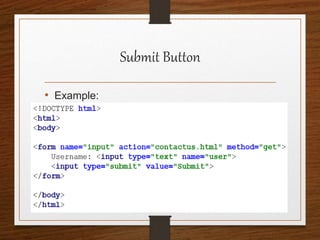
This document provides an agenda for an HTML tutorial. It begins with an introduction to HTML that defines it as a markup language and describes HTML tags, page structure, and web browsers. It then discusses HTML versions and editors. The agenda is divided into parts that cover basic HTML tags, forms, and other specific tags. It provides examples and screenshots of how tags appear in browsers. The document serves as a guide for teaching HTML basics and tags through an organized tutorial structure.