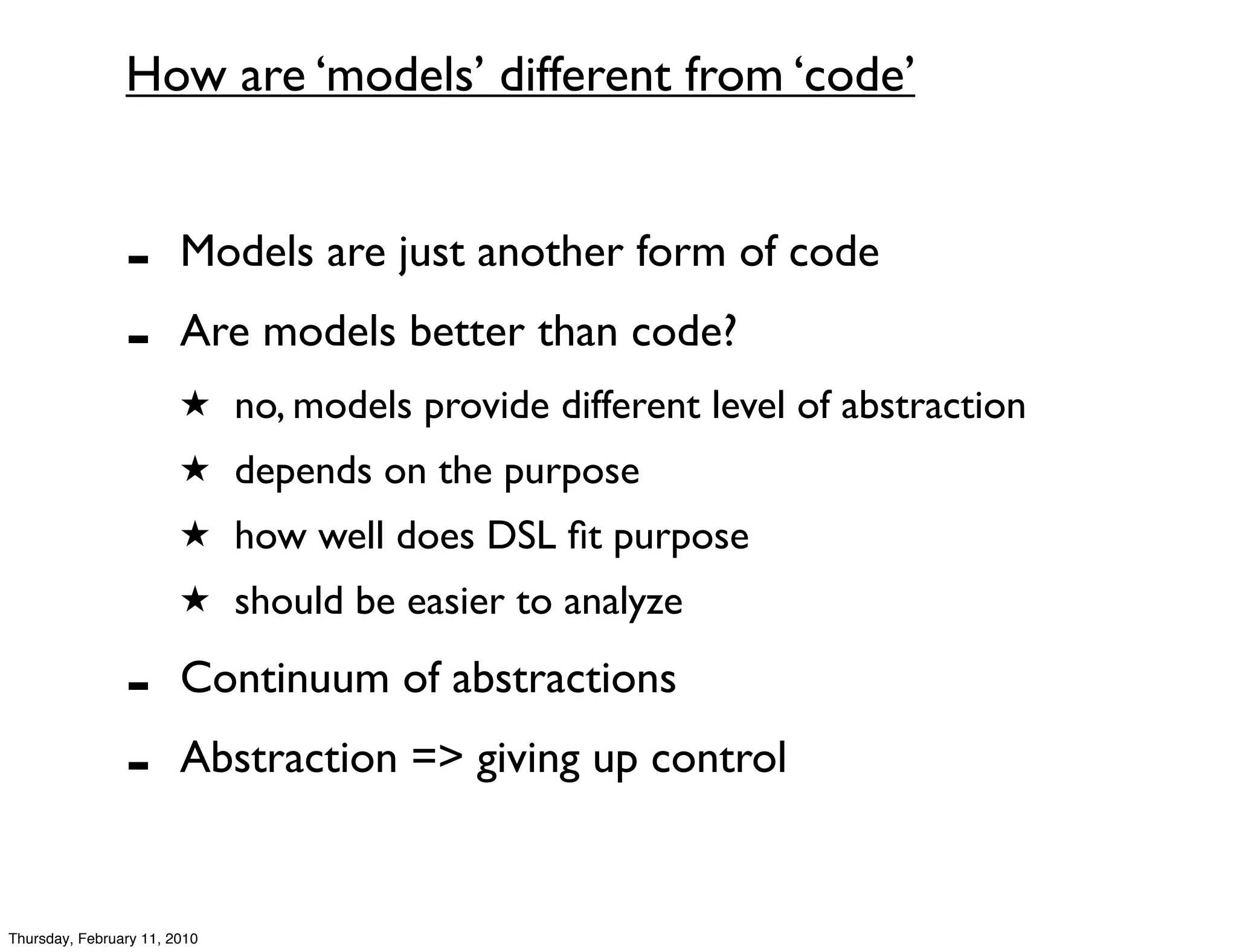
The document outlines a lecture on domain analysis and data modeling in the context of designing and implementing domain-specific languages (DSLs) within software development. It emphasizes the importance of models in understanding systems, domain engineering as a way to utilize reusable assets, and the integration of interaction design into software engineering practices. Key concepts like abstraction, user needs, and effective collaboration through DSLs are discussed throughout the lecture.

















































![[Course]-*[Student]
[Course]-*[Lecturer]
[Course]-*[Assistant]
[Course]-*[Lecture]
[Course]-*[Assignment]
[Assignment]-*[Submission]
[Submission]1-1..[Student]
[Lecture]-[Slides]
[Lecture]-[Notes]
http://yUML.me: a DSL for drawing UML diagrams
Thursday, February 11, 2010](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdsd02-100211154647-phpapp02/75/Domain-Analysis-Data-Modeling-52-2048.jpg)















