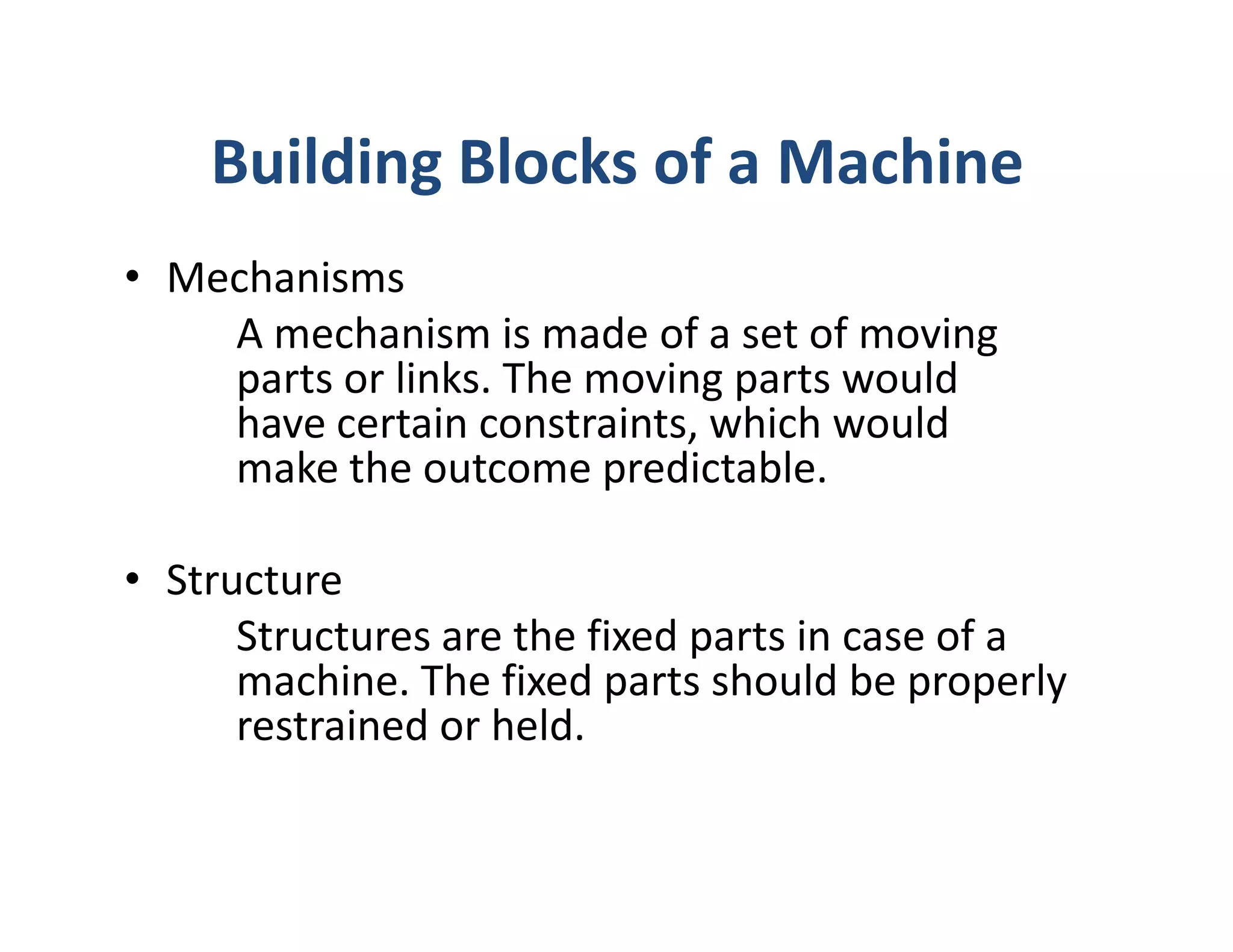
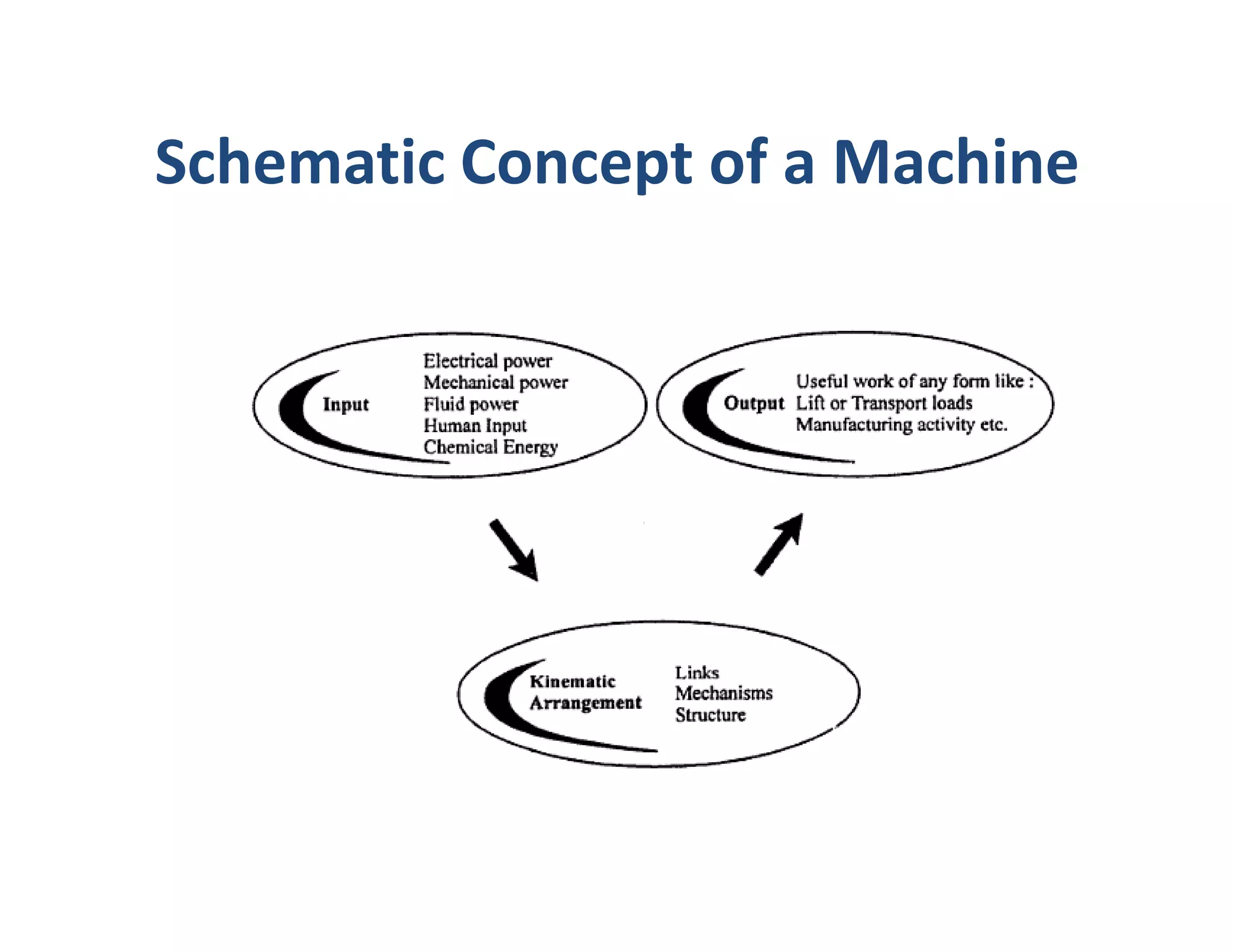
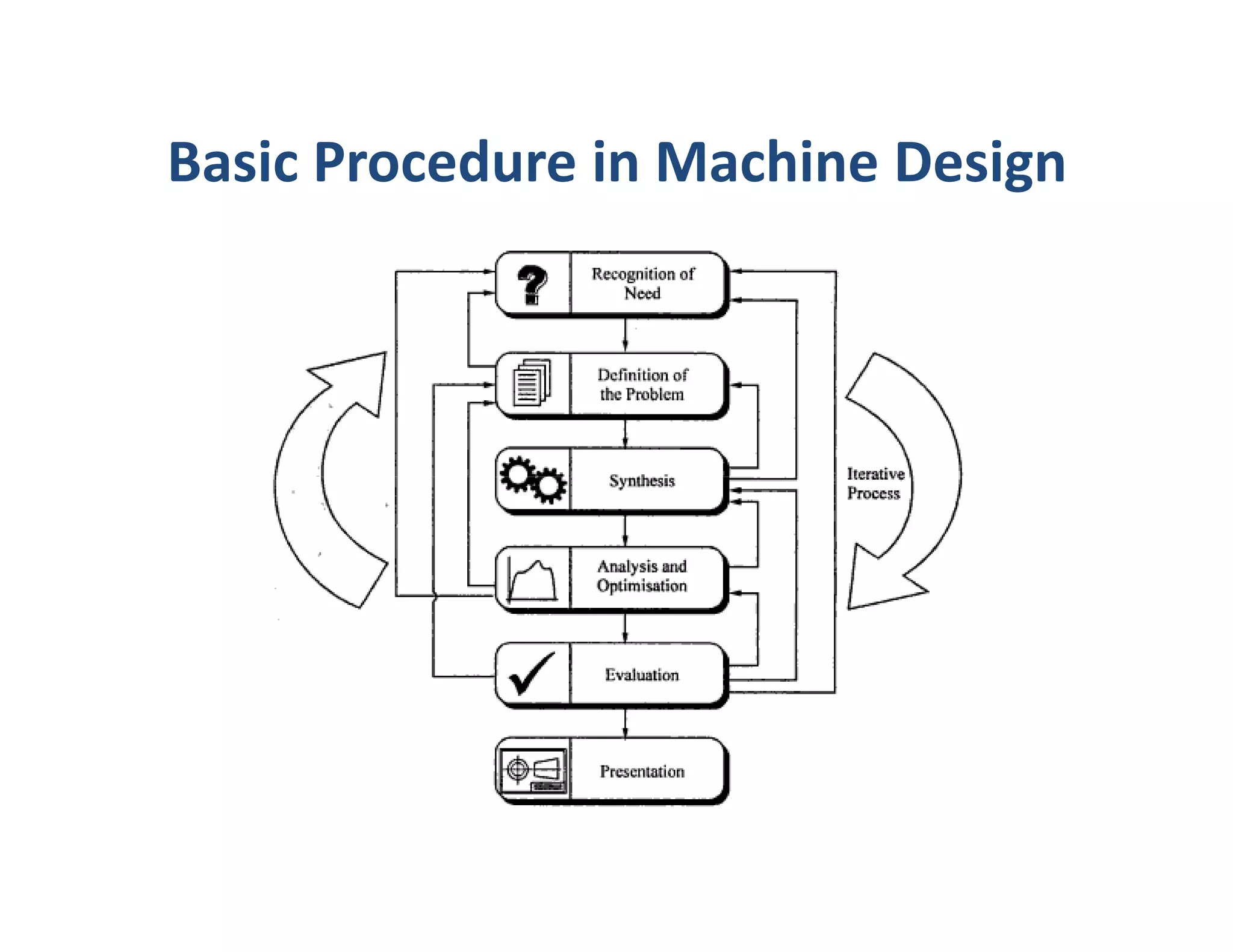
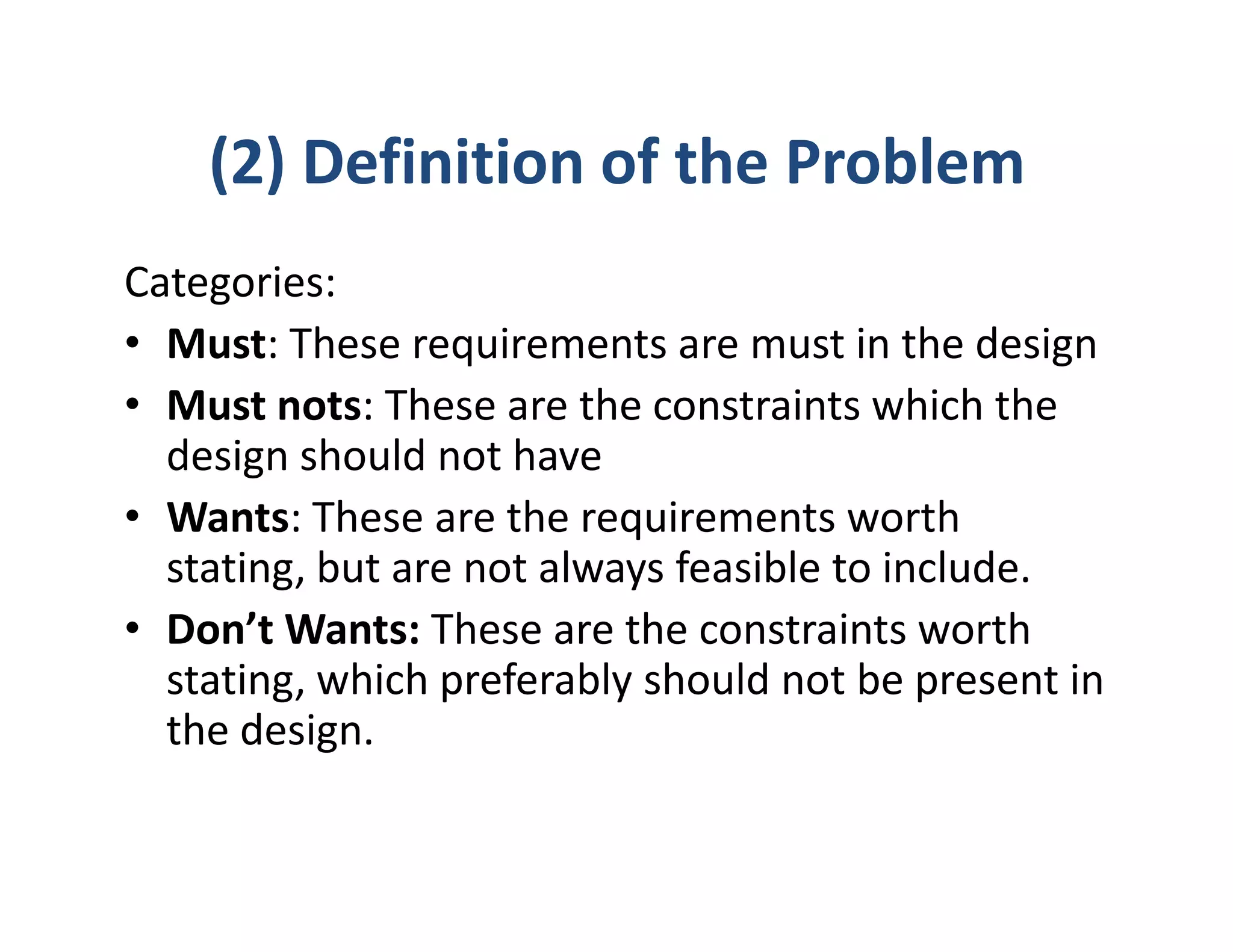
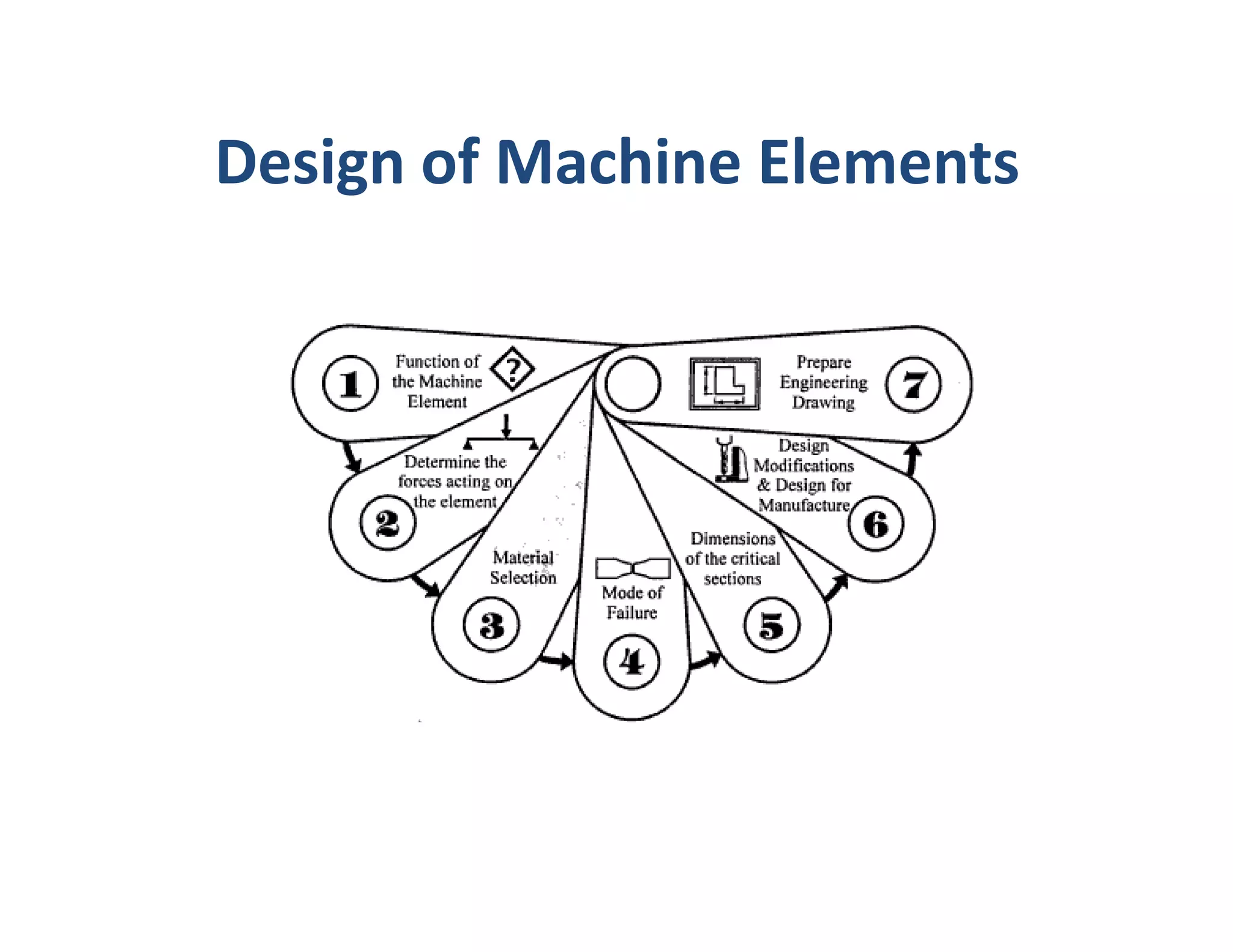
The document outlines the stages of machine design including problem recognition and definition, synthesis and analysis, evaluation, and presentation. It discusses the building blocks of machines as mechanisms with moving parts and fixed structures. The document also describes the abilities needed for a good designer such as communication skills, understanding of sciences and processes, and the use of standards to enable interchangeability and replacements.