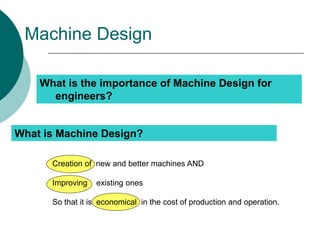
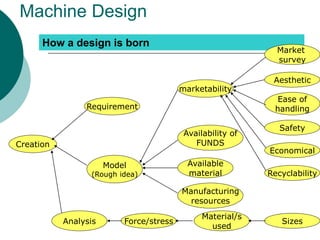
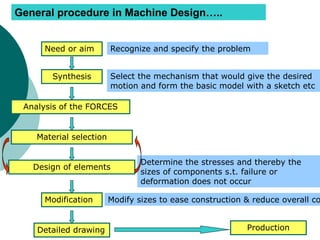
Machine design is the process of creating or improving machines. It requires consideration of factors like the type and stresses of loads on the machine, the kinematics or motion of parts, selection of suitable materials, and determining the proper form and size of parts. Successful machine design draws on knowledge of mathematics, engineering mechanics, strength of materials, manufacturing processes, and other disciplines. The general procedure involves recognizing a need, synthesizing a mechanism design, analyzing stresses, selecting materials, designing elements, and modifying the design as needed before production. The document outlines the content of a machine design course, including sessions on mechanism dynamics, failure analysis, design of elements like flywheels and joints, and a design project.