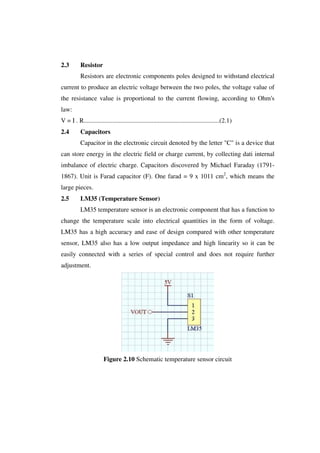
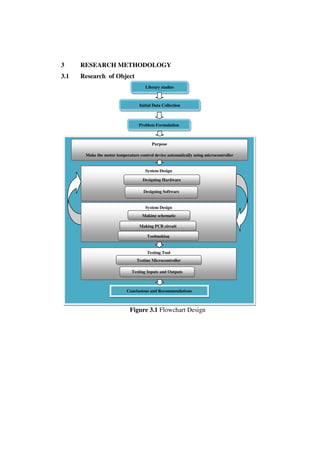
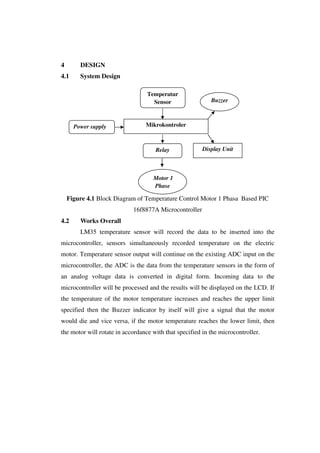
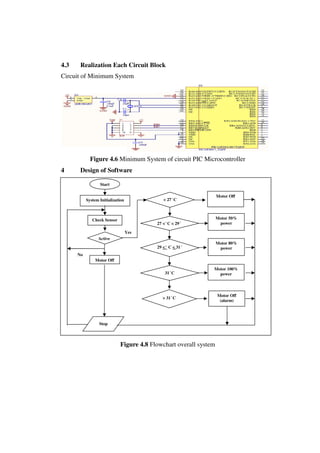
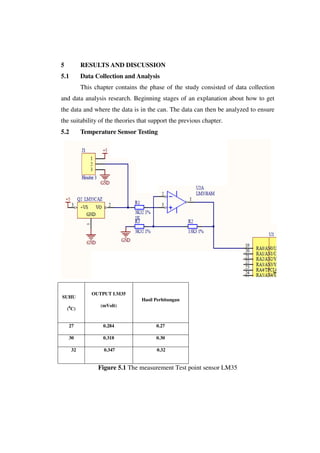
This document describes the design of a temperature control system for a single-phase motor using a PIC16f887A microcontroller. The system uses an LM35 temperature sensor to monitor the motor temperature and sends the data to the microcontroller. If the temperature reaches the upper limit, a buzzer will sound as a warning. The microcontroller can control the motor speed based on the temperature. Experimental results show the microcontroller can accurately adjust the motor speed according to temperature changes.