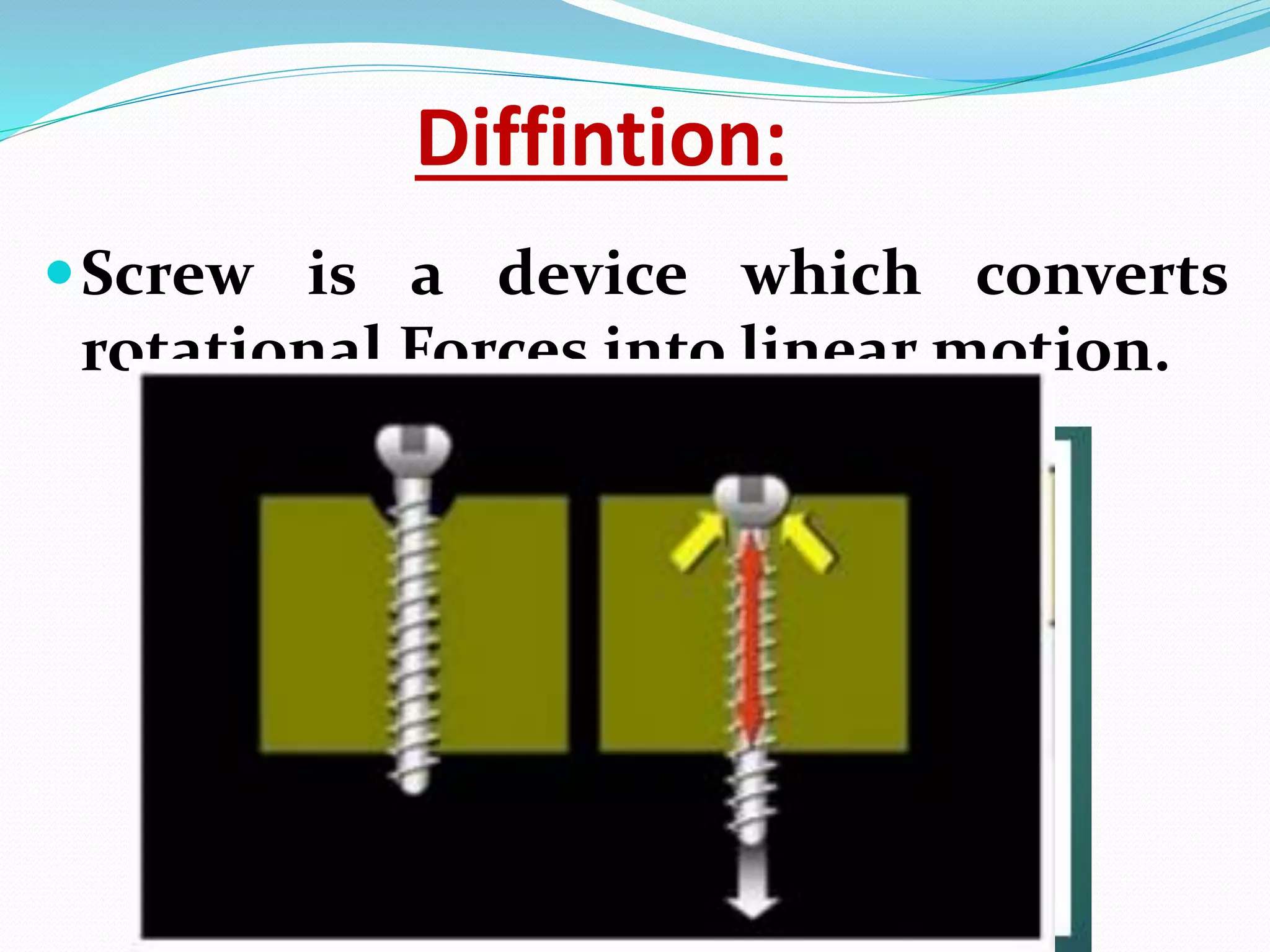
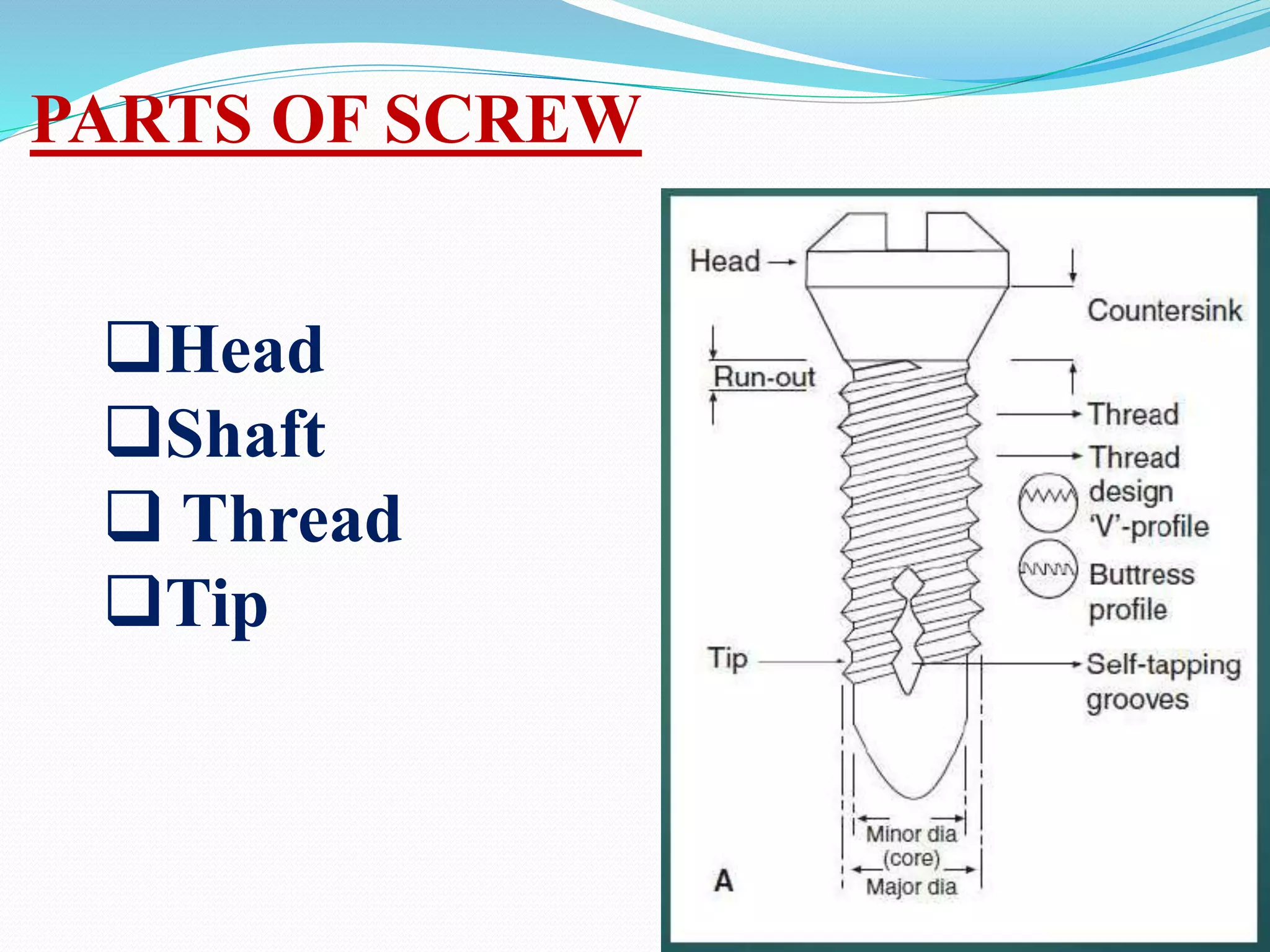
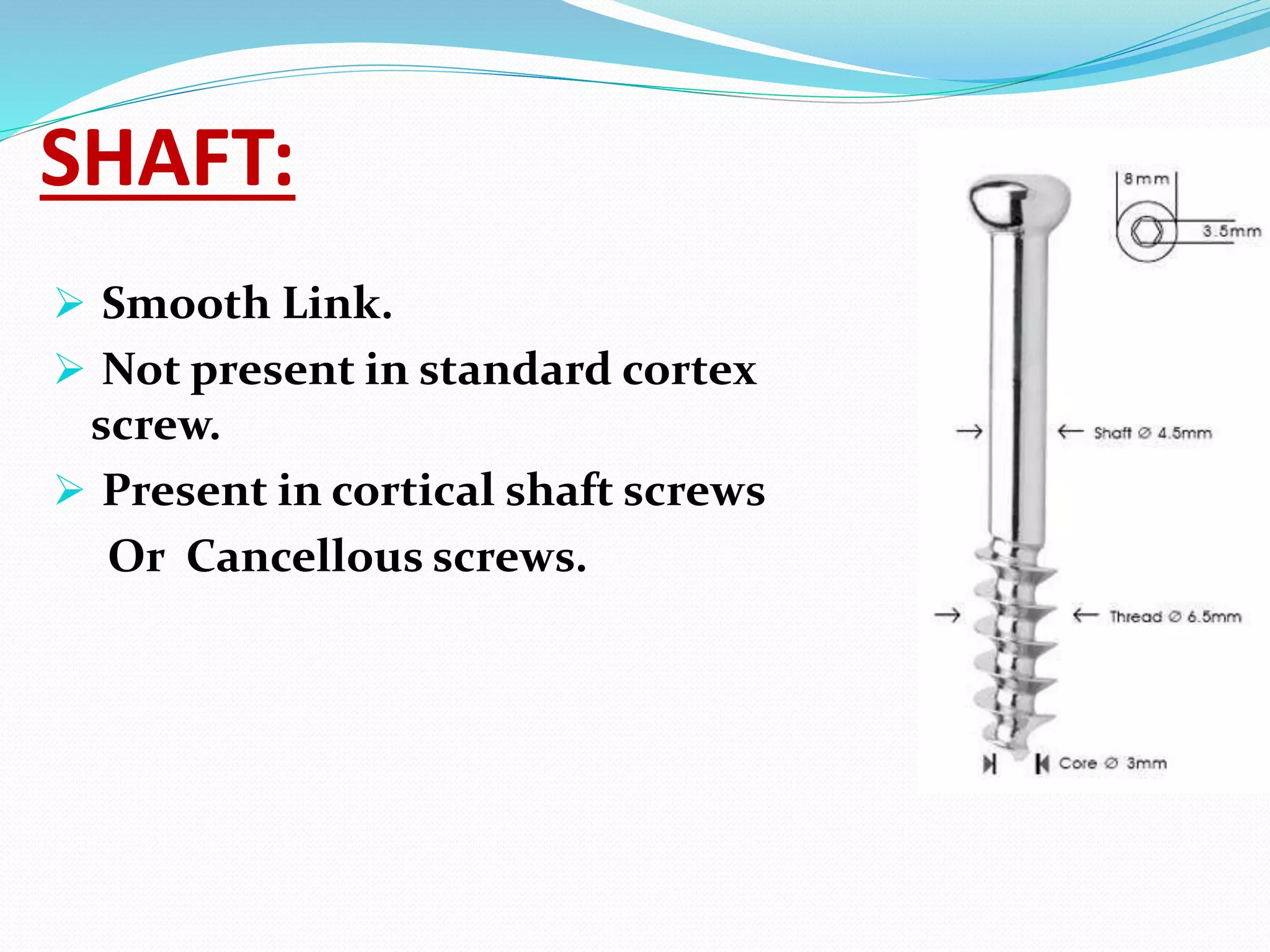
The document discusses the basic principles and parts of screws used in orthopedic surgery. It describes the four main parts of a screw - the head, shaft, thread, and tip. It discusses different types of screws including cortical, cancellous, and special screws like Herbert and variable angle locked screws. It also covers principles like lag screws and the benefits of far cortex locking screws which provide flexible fixation while promoting interfragmentary motion and secondary bone healing.





















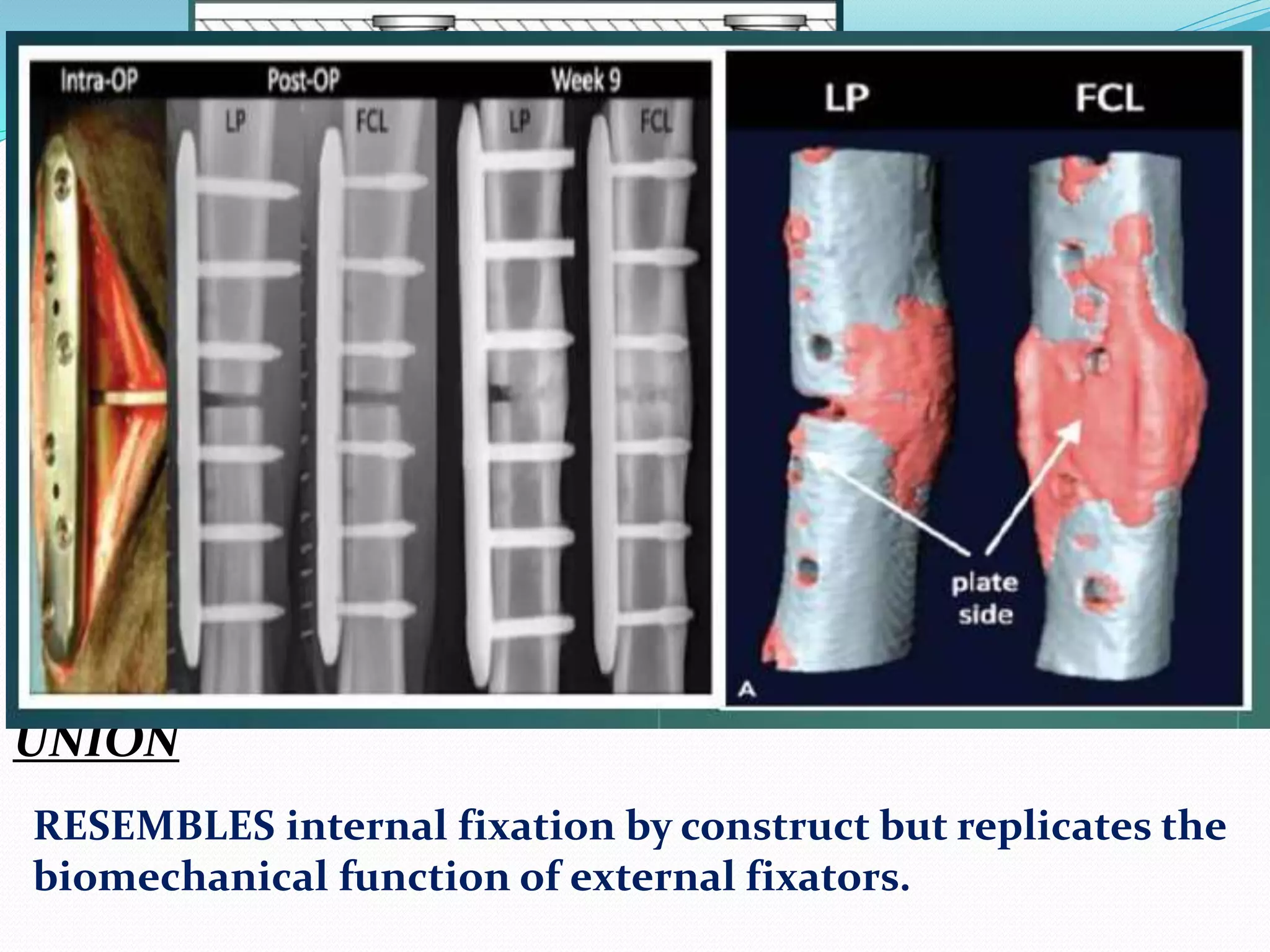
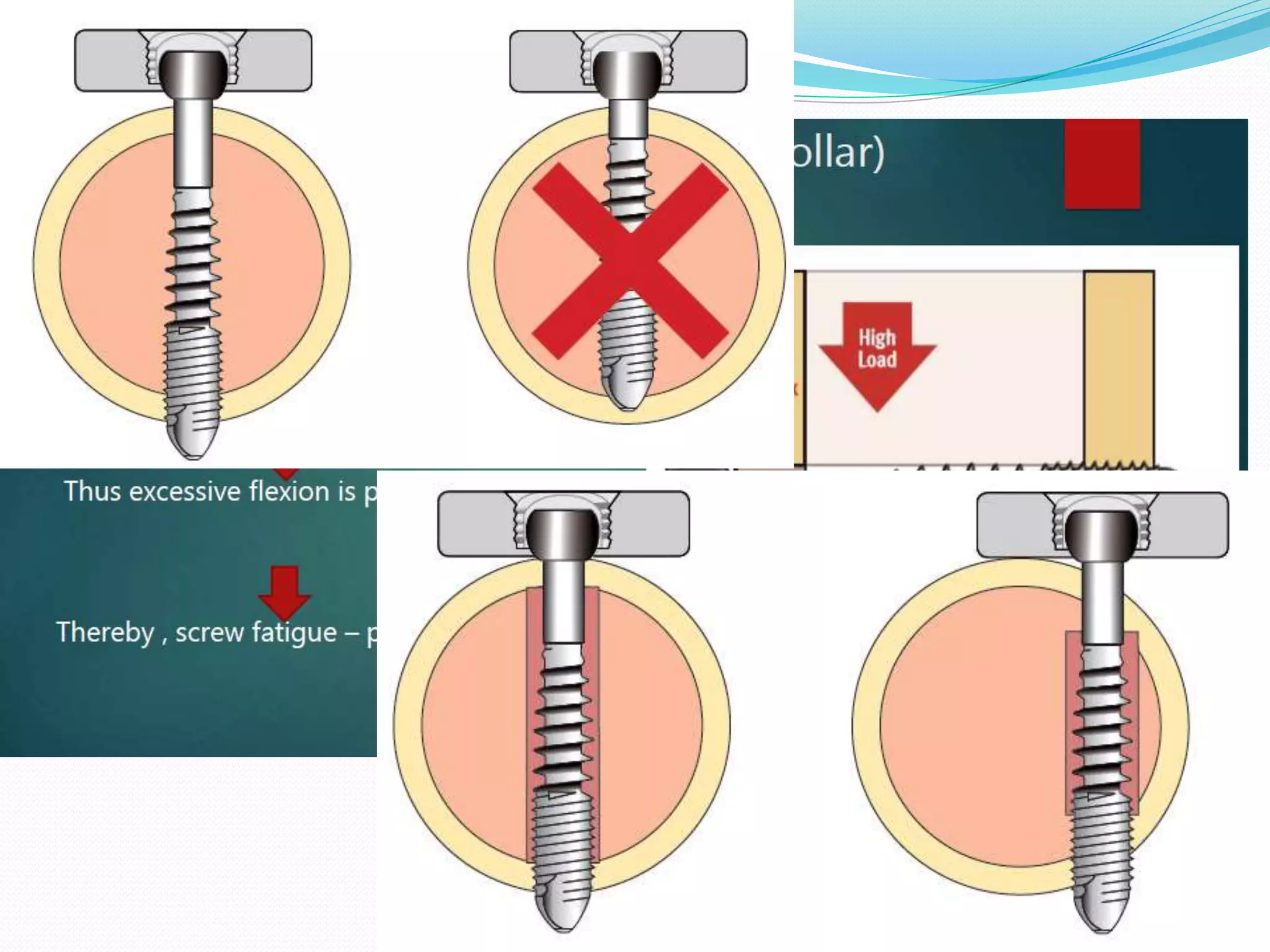
![Flexible Fixation : Flexibility is directly proportional -
working length of the screw.
Stiffness is reduced by screws – fixed in plate & far cortex, while retaining a
controlled motion envelope at near cortex.
Thereby promoting inter-fragmentary motion [ IDEAL: 0.2 – 1 mm ] to
produce secondary callus](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/screws-221008073056-0a6a465d/75/SCREWS-in-orthopaedic-surgery-pptx-26-2048.jpg)
![It has 4 Key Features:
1.Flexible fixation. ( reduces stiffness by 80- 88%)
actively promotes callus formation similar to
external fixator.
2.Uniform load distribution – mitigate stress
raisers.
3.Progressive stiffening – on increased loading.
4.Parallel inter-fragmentary motion – by ‘S’ shaped
flexion. [ FUNCTIONS AS EXTERNAL FIXATORS IN
BIOMECHANICAL BEHAVIOUR AND BIOLOGIC
HEALING ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/screws-221008073056-0a6a465d/75/SCREWS-in-orthopaedic-surgery-pptx-28-2048.jpg)