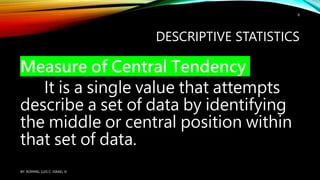
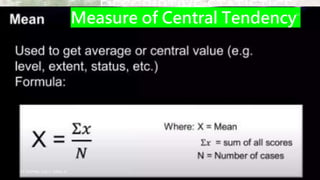
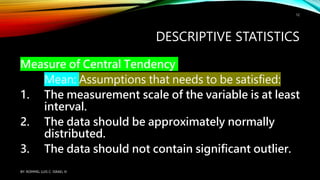
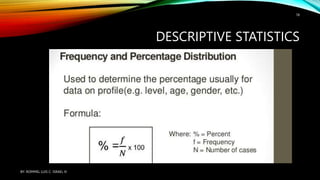
Statistical treatment of data involves applying statistical methods to transform raw data into meaningful outputs. There are two main types: descriptive statistics which describes and summarizes data through tables, charts and graphs; and inferential statistics which tests hypotheses and measures relationships in data. Some common statistical treatments include calculating measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode) and variability (standard deviation, variance), and conducting tests like t-tests, correlation analyses, and ANOVA.