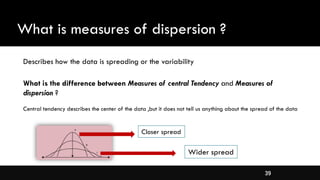
This document provides an outline and overview of descriptive statistics. It discusses the key concepts including:
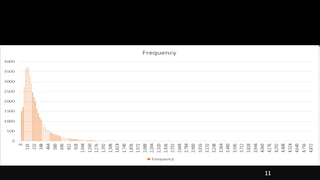
- Visualizing and understanding data through graphs and charts
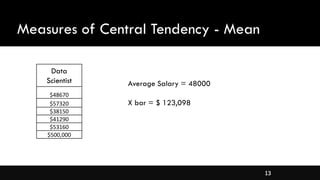
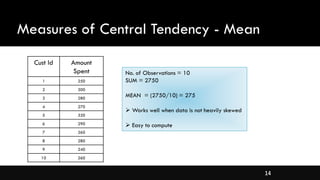
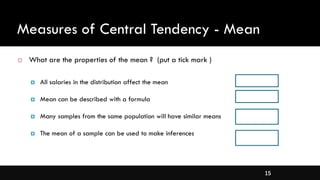
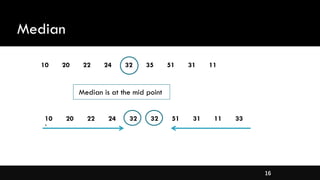
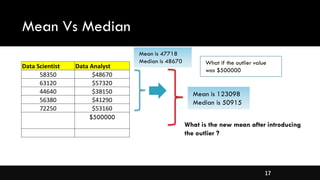
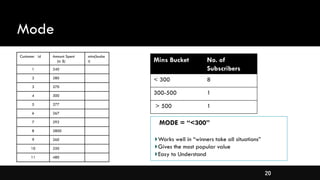
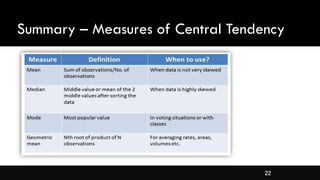
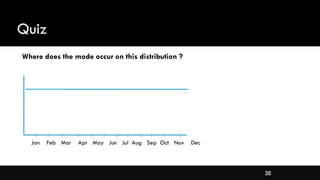
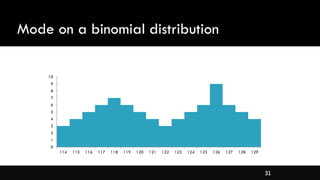
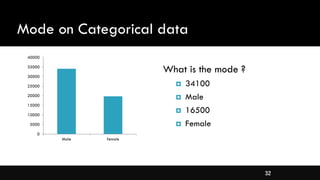
- Measures of central tendency like mean, median, and mode
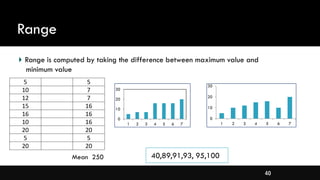
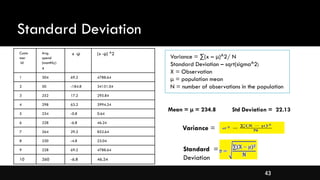
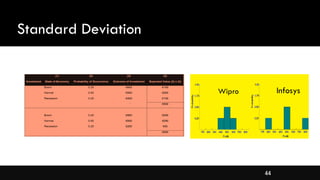
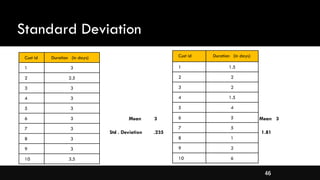
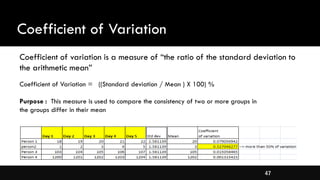
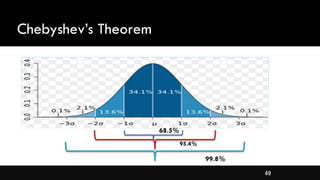
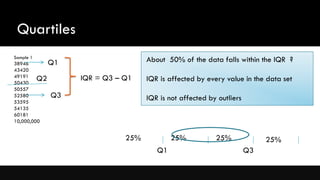
- Measures of spread like range, standard deviation, and interquartile range
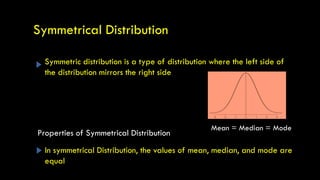
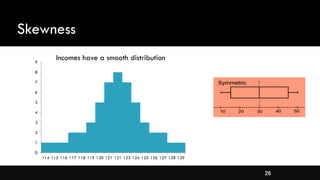
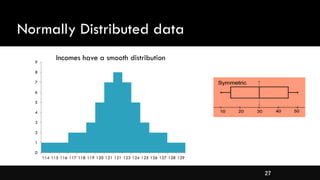
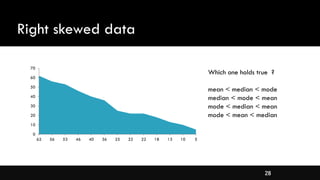
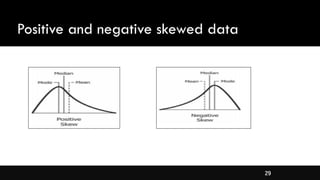
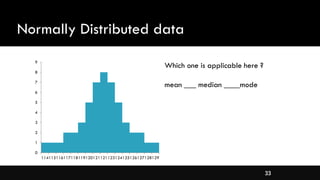
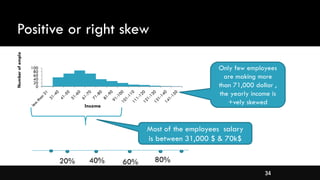
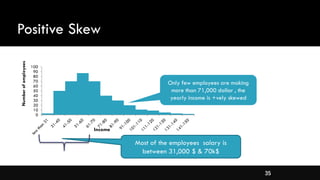
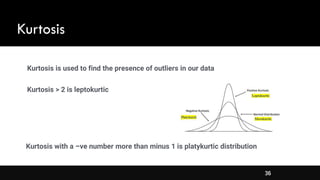
- Different types of distributions like symmetrical, skewed, and their properties
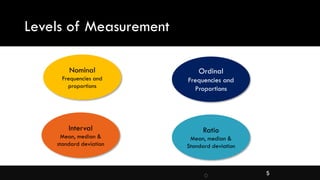
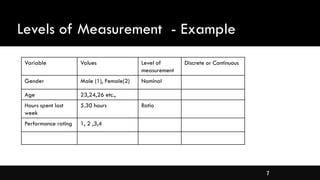
- Levels of measurement for variables and appropriate statistics for each level
The document serves as an introduction to descriptive statistics, the goals of which are to summarize key characteristics of data through numerical and visual methods.