This document provides an overview of research characteristics, purposes, types and approaches. It discusses the following:
- Characteristics of good research include accuracy, objectiveness, timeliness, relevance and clarity. Research should also be systematic.
- The purposes of research include learning independently and scientifically, gaining in-depth knowledge, improving skills, and familiarizing oneself with research tools and techniques.
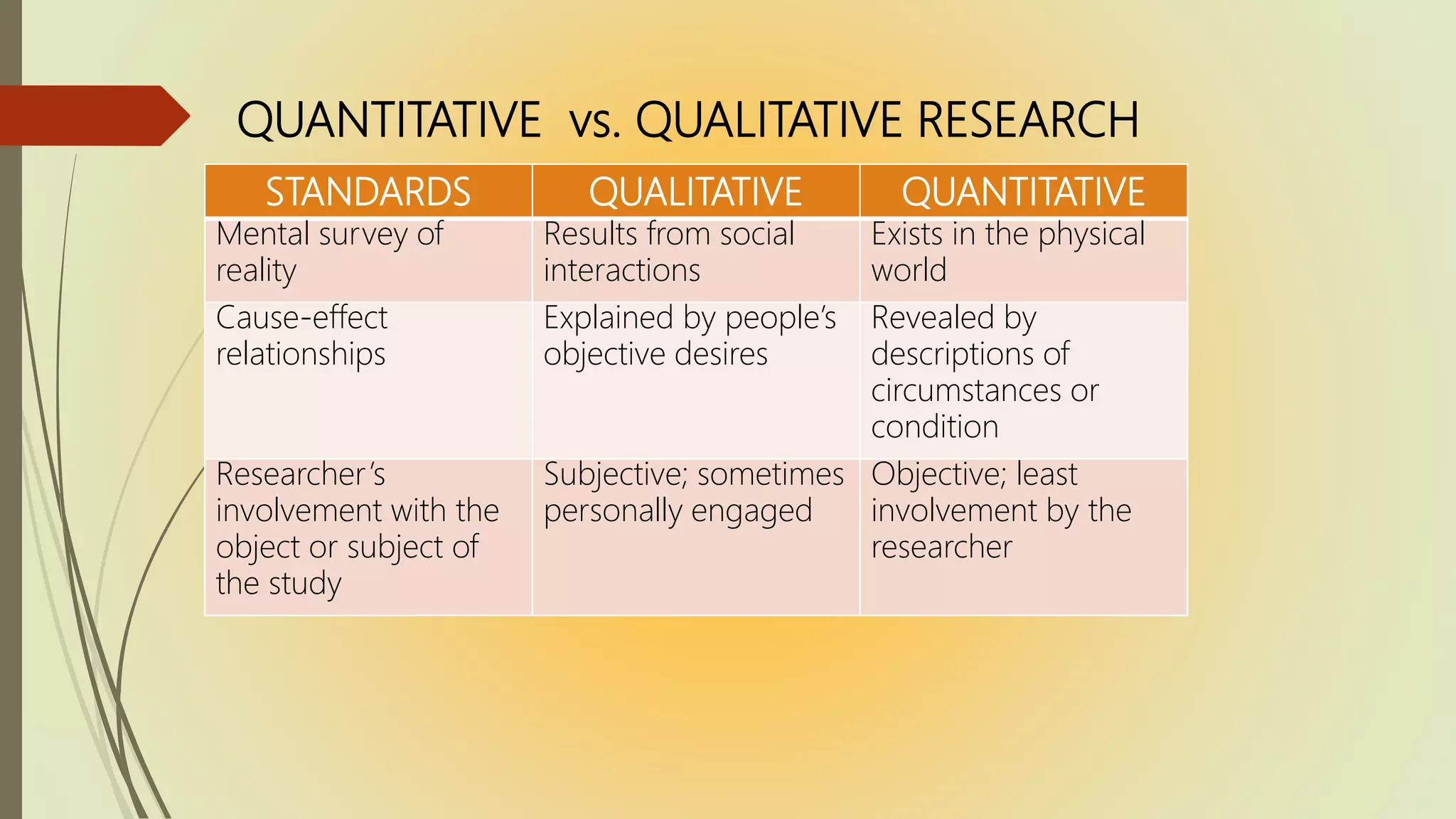
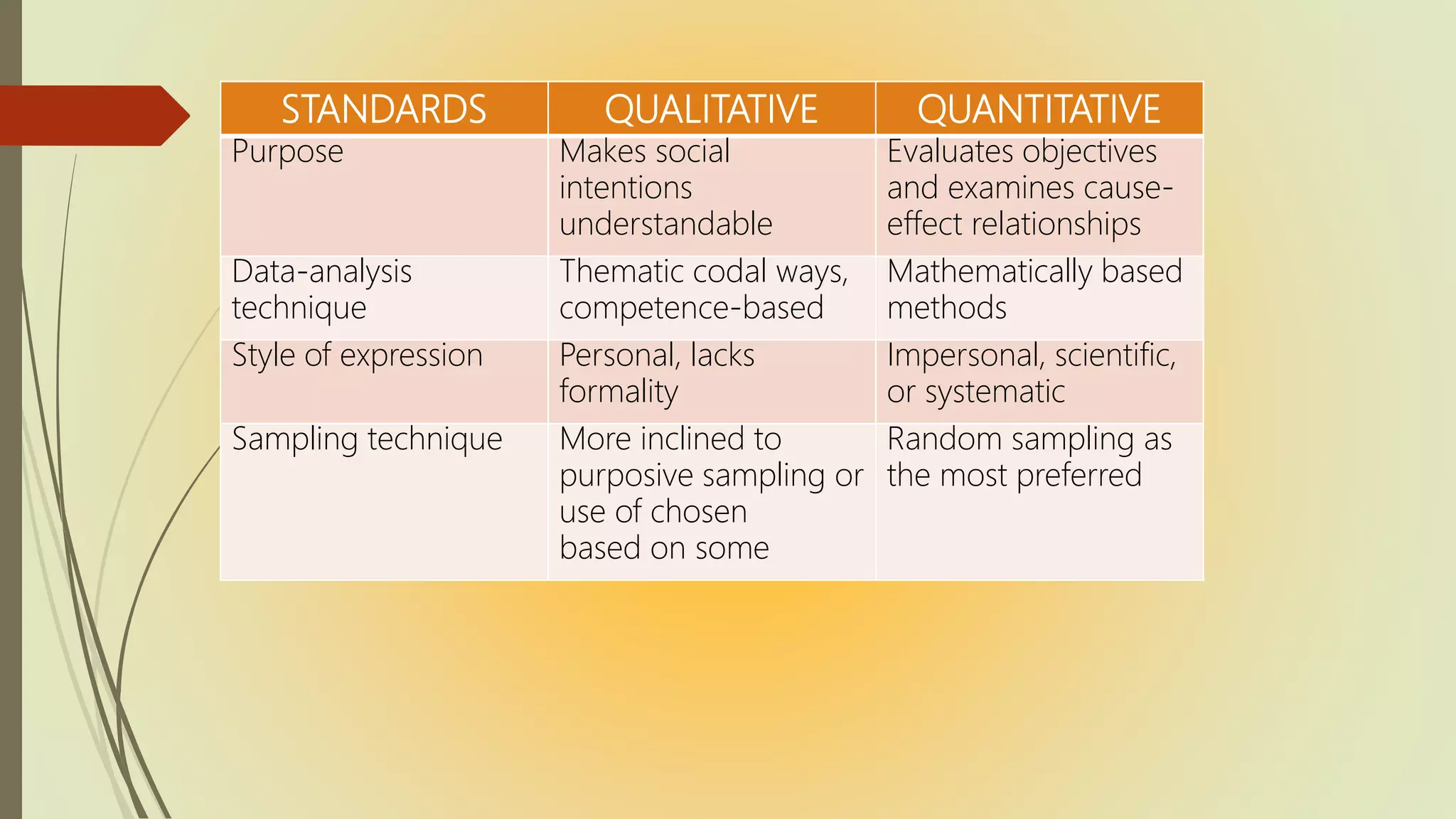
- Research can be classified based on application (pure vs applied), purpose (descriptive, correlational, explanatory, exploratory, action), data type (qualitative vs quantitative), and approaches (scientific, naturalistic, triangulation).
- Qualitative research uses words rather than numbers while quantitative research uses measurement and statistics