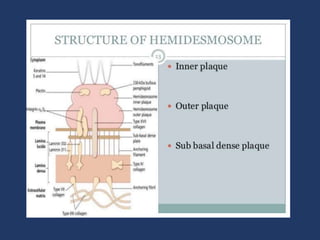
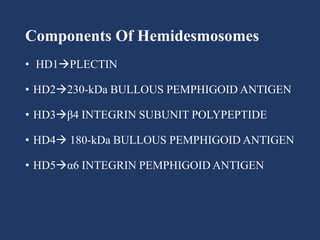
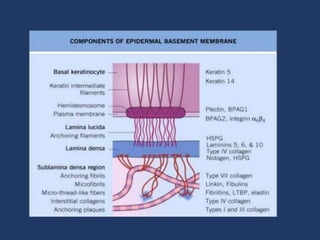
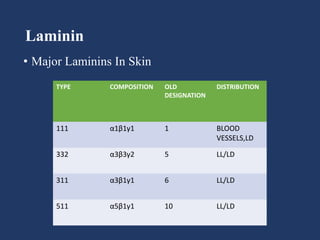
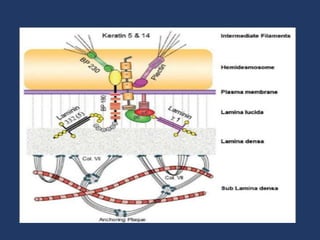
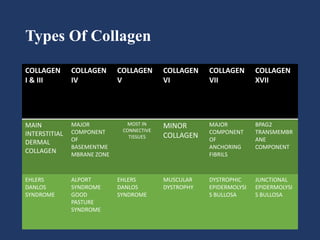
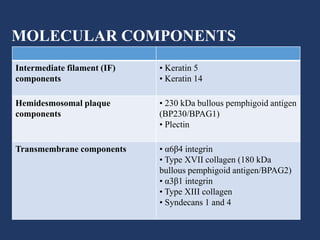
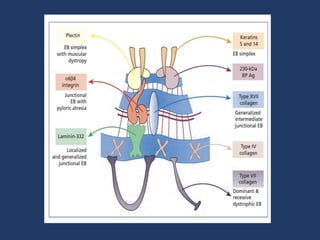
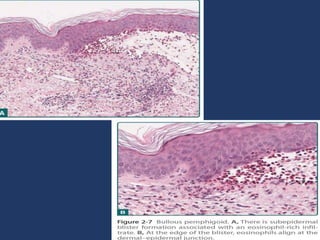
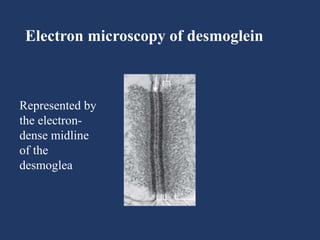
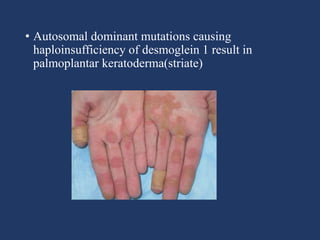
The document examines the dermoepidermal junction (DEJ), detailing its development, structure, and components, particularly the role of desmogleins in skin stability and adhesion. It describes the evolution of the DEJ from the embryonic stage to a complex adult structure, including key components such as type IV collagen and various laminins. Additionally, it explores the implications of desmogleins in skin diseases and genetic disorders affecting skin integrity.