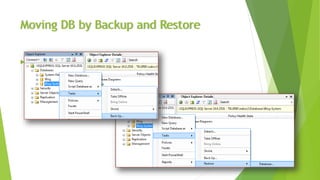
SQL Server is a relational database management system developed by Microsoft that uses Structured Query Language (SQL) to store, manipulate and retrieve data. It includes several services like the SQL Server Database Engine for managing databases, SQL Server Agent for scheduling tasks, and MSdb for alerts and jobs. There are also system databases like Master, Model and MSdb that maintain metadata and temporary databases like Tempdb. User databases contain application schemas and data. The .mdf file stores core data and the .ldf file tracks transactions. Databases can be moved between servers using backup/restore, detach/attach of database files, or exporting to a SQL script and importing. SQL Server LocalDB is a lightweight version of SQL Express that auto


















![SSMS Setting Server Account
You can use SSMS to create database user / give permissions to Windows users
Follow these steps:
1. Right click on the [Security / Login] folder in Object Explorer and choose "New
Login…"
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-230928111825-4a980937/85/2-Introduction-to-MSSQL-Server-pptx-20-320.jpg)
![SSMS Setting Server Account (2)
2. In the next dialog click the [Search] button
Select one of the Windows accounts in a typical Windows
fashion
Leave the authentication method set to Windows
authentication
Click [OK]
Thus you create an SQL Server User account
Account permissions could be assigned later
Windows administrators already have access
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-230928111825-4a980937/85/2-Introduction-to-MSSQL-Server-pptx-21-320.jpg)
![SSMS Setting Database Account
1. Right click on the "Security" under some of the databases and choose "New"
"User"
2. Enter username and select one of the Server accounts to use
3. Assign the roles for this user
4. Click [OK] to confirm
By selecting the [Name-of-Database] "Properties" "Permissions" you can also
set specific permissions for the accounts
24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-230928111825-4a980937/85/2-Introduction-to-MSSQL-Server-pptx-22-320.jpg)

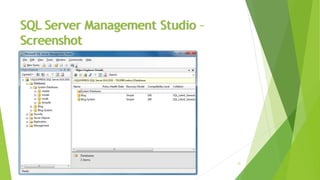
![Using SQL Server Management Studio
SSMS can be used to visually edit the structure or data in a database
It can execute T-SQL queries
Select the database you want to work with in the Object Explorer
Click the [New Query] button
Write the query in the window to the right of Object Explorer
Click the [Execute] button
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-230928111825-4a980937/85/2-Introduction-to-MSSQL-Server-pptx-24-320.jpg)