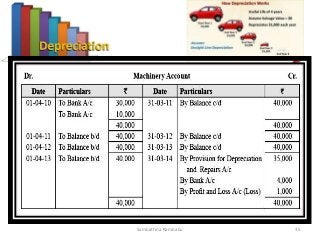
The document provides a comprehensive overview of depreciation accounting, detailing definitions, types of depreciation (Straight Line Method and Written Down Value Method), calculation formulas, and recording methods. It includes practical examples and journal entries for various scenarios, such as acquisition, depreciation provision, and sale of assets, emphasizing the importance of proper accounting entries. Additionally, it covers changes in depreciation methods and provides multiple illustrative cases for better understanding.