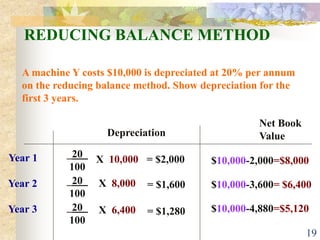
This document discusses various methods of depreciation for fixed assets. It defines depreciation as the allocation of the cost of a fixed asset over its useful life. Common causes of depreciation include physical deterioration, obsolescence, depletion, and passage of time. Popular depreciation methods include straight-line, reducing balance, revaluation, units-of-output, double-declining balance, and sum-of-the-years'-digits. Each method calculates depreciation expense differently, with advantages and disadvantages to consider.