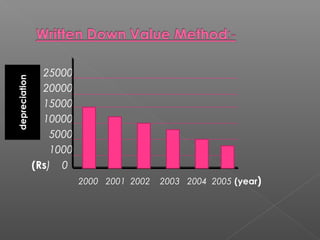
This document discusses depreciation of fixed assets. It defines depreciation as a permanent decline in the value of fixed assets over time due to factors like wear and tear, age, and obsolescence. It explains that depreciation is calculated to allocate the cost of a fixed asset over its useful life. The key methods of depreciation discussed are the straight-line method, where depreciation is equal each period, and the reducing balance method, where depreciation decreases each period as the asset's value declines.