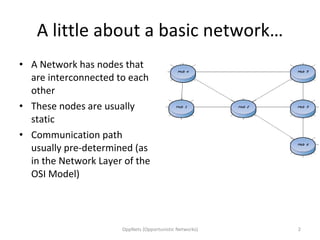
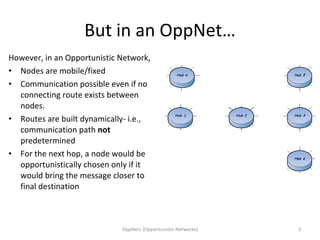
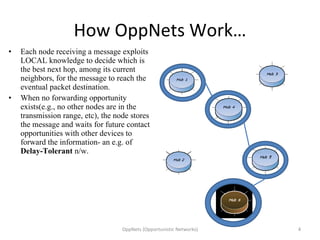
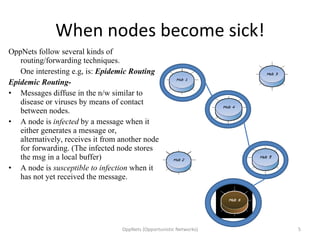
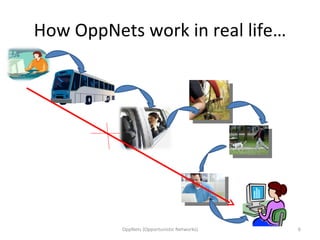
Opportunistic networks (OppNets) allow communication between nodes that are mobile or fixed even when there is no predetermined path connecting them. Nodes in an OppNet opportunistically choose the next hop to bring a message closer to its destination based on local knowledge of current neighbors. Messages are stored and forwarded whenever contact opportunities arise between devices in a delay-tolerant manner. Epidemic routing resembles the spread of disease as messages diffuse through the network by infecting nodes that receive them.
Two examples of OppNet projects are ZebraNet, which tracks wildlife in Kenya using cost-effective non-intrusive monitoring, and DakNet, providing internet access to rural villages in India using kiosks