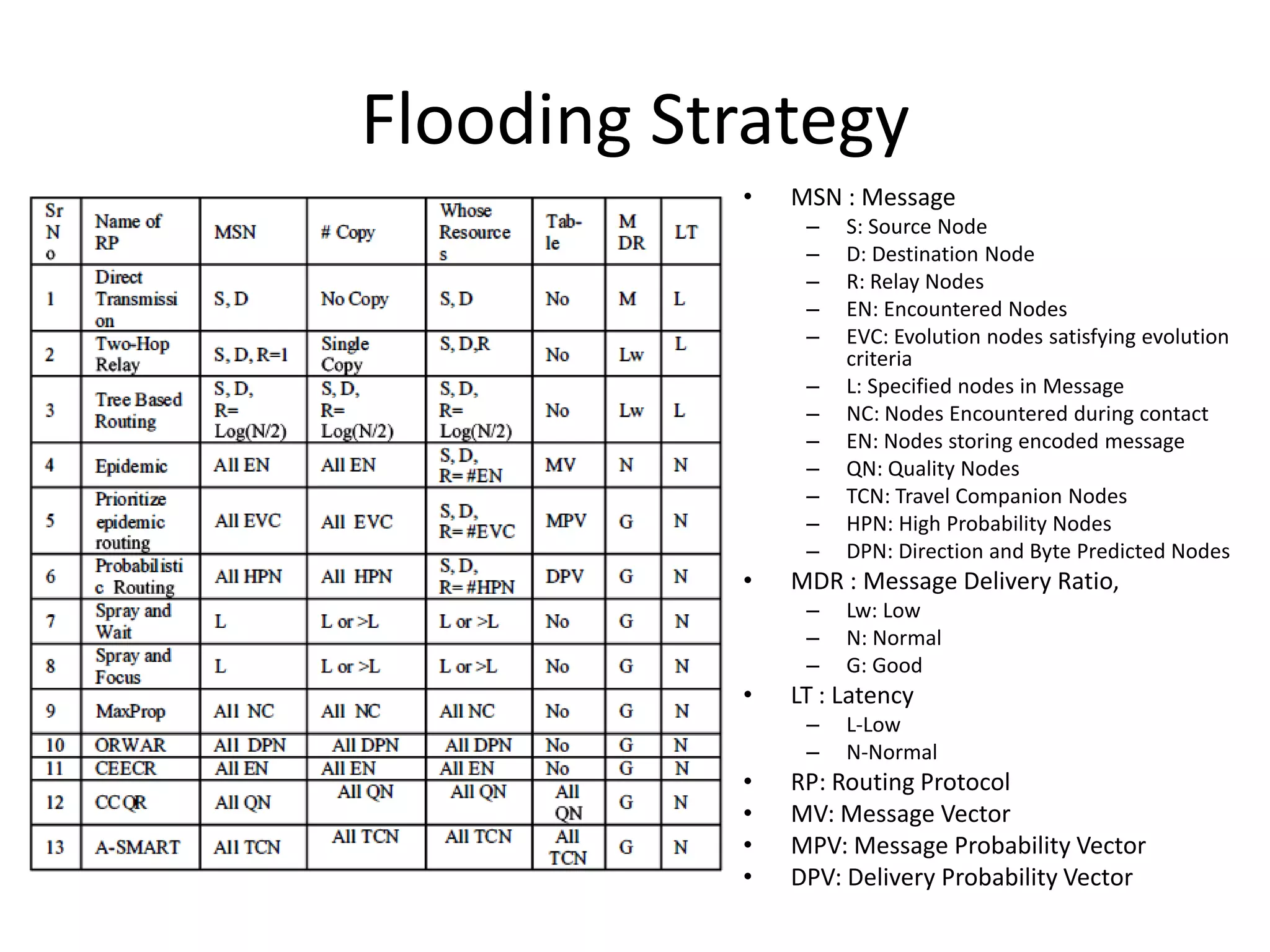
Routing protocols for delay tolerant networks can be categorized as either flooding or forwarding strategies. Flooding strategies replicate messages to multiple nodes to increase delivery probability but use more resources, while forwarding strategies select a single path using network knowledge to minimize resource usage but have lower delivery probability. The survey compares these routing protocol categories and their advantages for different applications in delay tolerant networks, which must deal with intermittent connectivity and large delays.