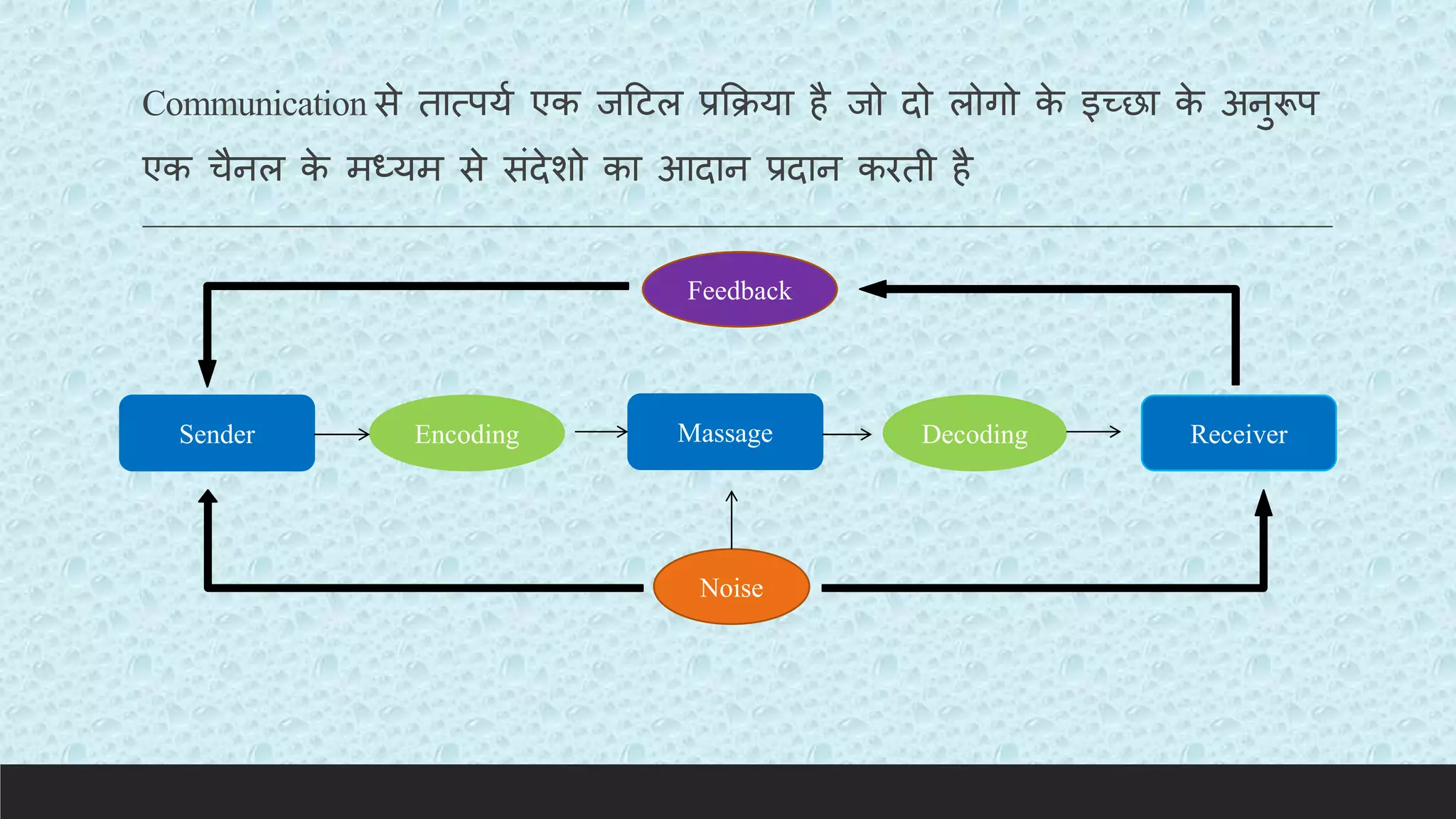
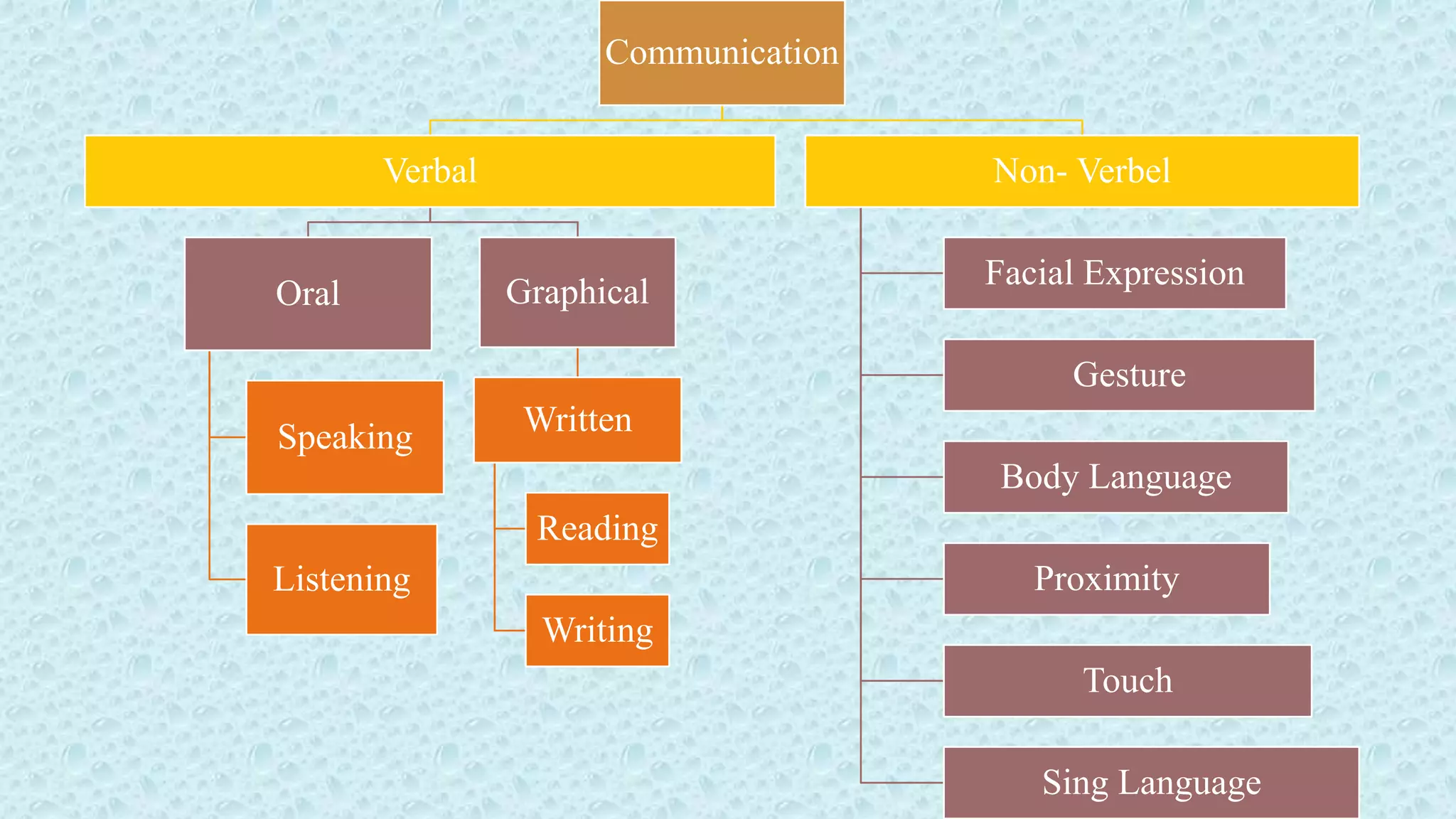
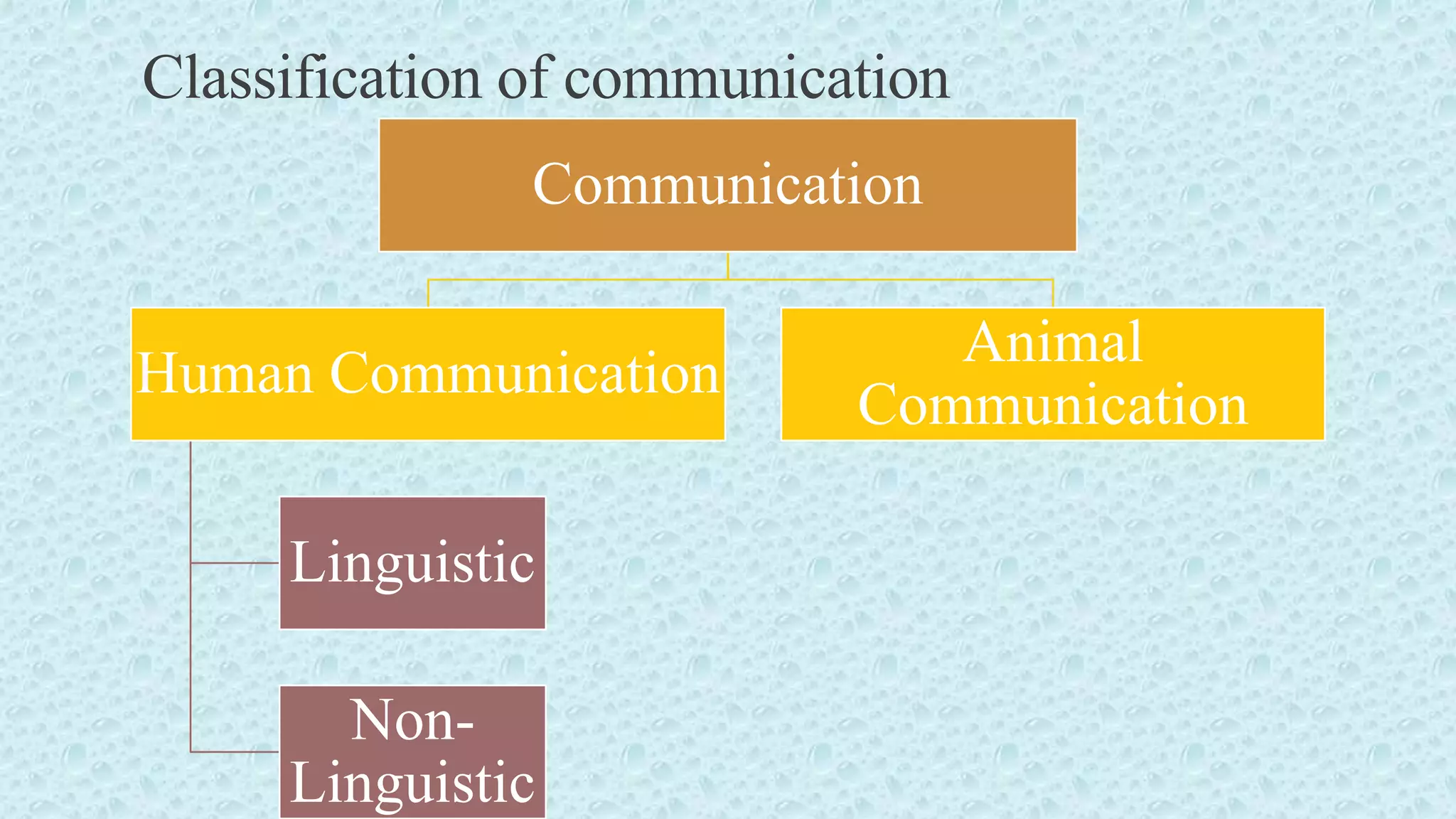
Definition,Meaning, and Scope of communication.
Human and Animal Communication
Human Communicaton (Lingustic and Non-Lingustic)
Definition, Meaning, and Scope of Language
Structure, Characteristics, and Funcation of Language
Innateness of Languge
(Hind and English)