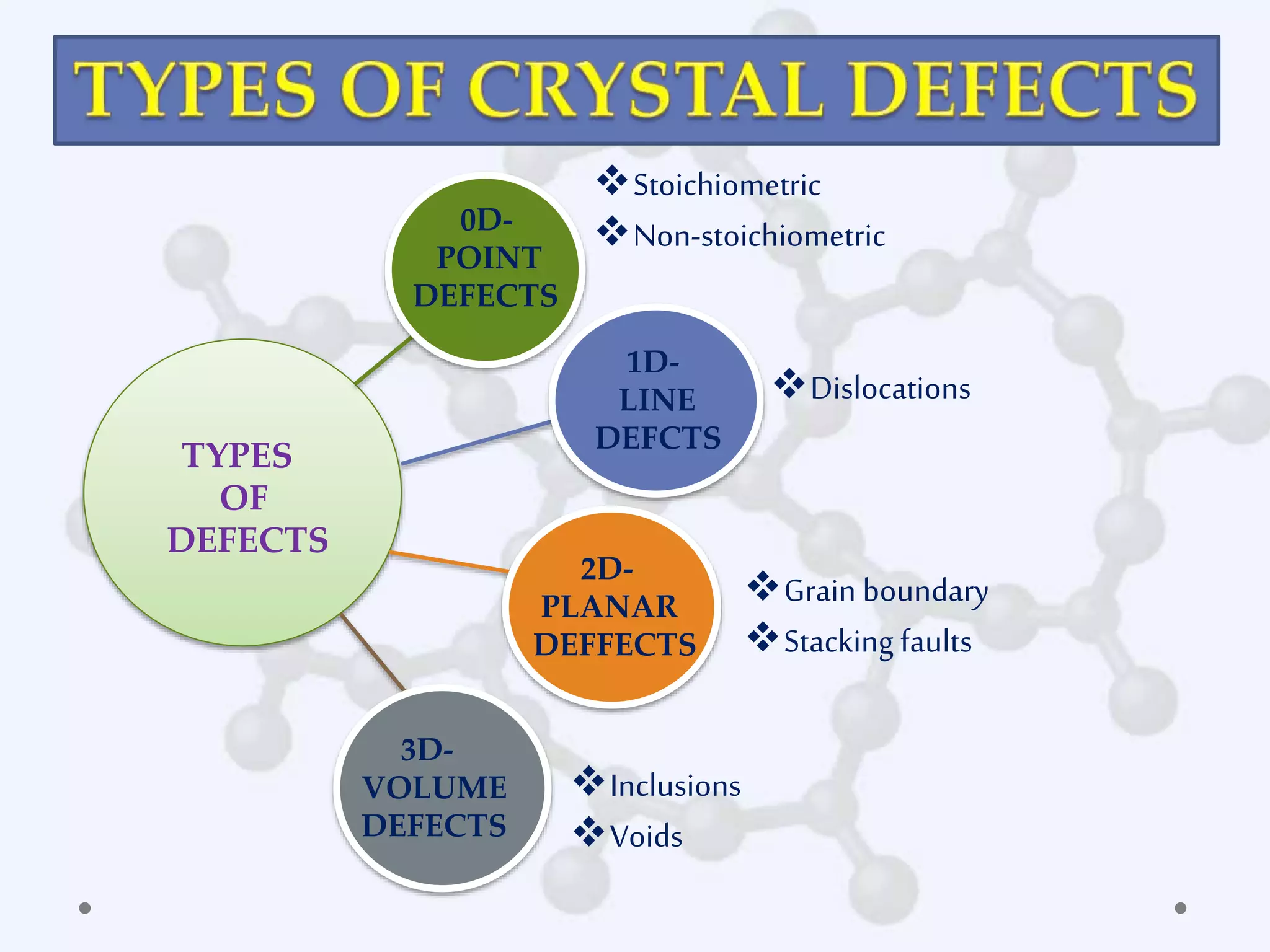
This document discusses point defects in crystals. It defines point defects as deviations from the ideal crystal structure arising from missing or displaced atoms. It describes several types of point defects including vacancies, interstitials, Frenkel defects, Schottky defects, and non-stoichiometric defects involving excess or deficient metal atoms. The concentration of vacancy defects increases exponentially with temperature. Point defects can impact material properties and are useful in applications such as semiconductors and gemstones.