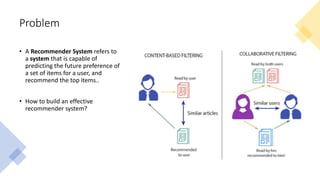
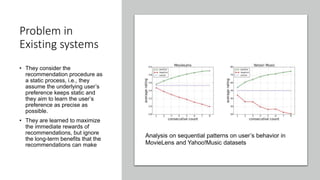
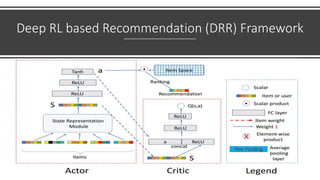
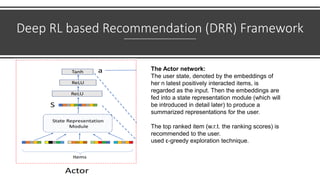
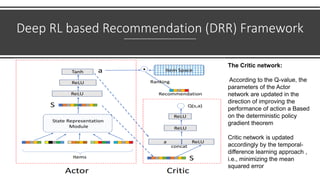
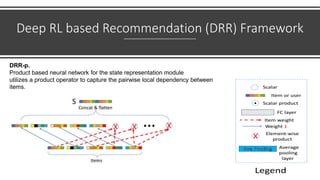
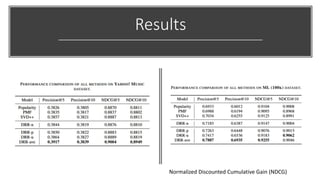
The document presents a deep reinforcement learning (DRL) framework for recommendation systems, addressing the limitations of existing methods that treat recommendations as static. The proposed DRL framework uses an actor-critic structure to optimize recommendations by considering both immediate and long-term rewards, incorporating user-item interactions and sequential decision-making processes. Experiments show that this approach outperforms traditional recommendation methods across various datasets.