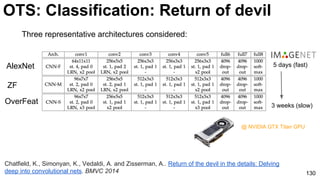
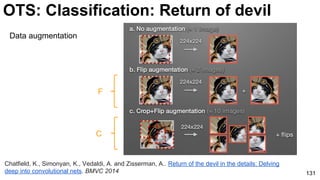
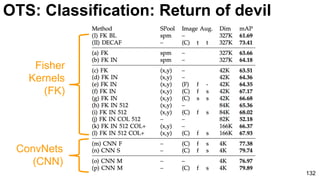
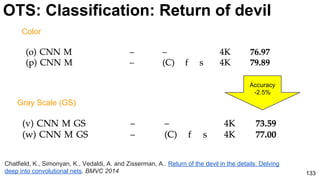
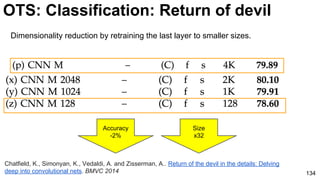
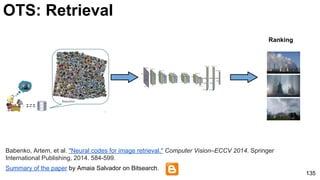
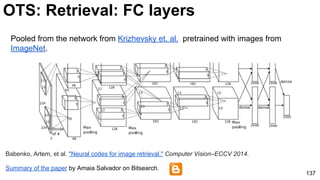
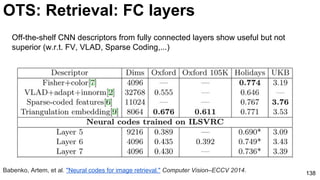
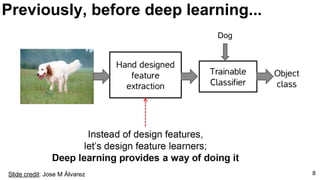
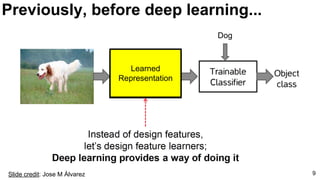
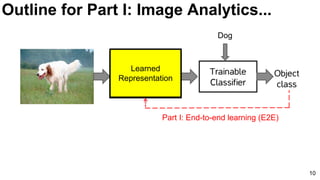
The document discusses deep learning techniques for computer vision and image analytics, focusing on the use of deep convolutional networks (CNNs) for image classification and retrieval tasks. It outlines the evolution of these methods, including the introduction of end-to-end learning and notable architectures like AlexNet and GoogLeNet. Additionally, the presentation covers key challenges and advancements in the field, including the importance of visualization and regularization techniques.





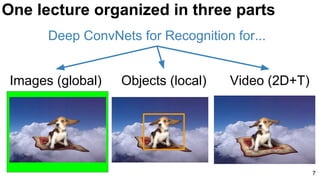


![E2E: Classification: Databases
18
Li Fei-Fei, “How we’re teaching computers to understand
pictures” TEDTalks 2014.
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H., Krause, J., Satheesh, S., Ma, S., ... & Fei-Fei, L. (2015). Imagenet large scale visual
recognition challenge. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.0575. [web]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-18-320.jpg)
![19
E2E: Classification: Databases
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H., Krause, J., Satheesh, S., Ma, S., ... & Fei-Fei, L. (2015). Imagenet large scale visual
recognition challenge. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.0575. [web]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-19-320.jpg)
![20
Zhou, Bolei, Agata Lapedriza, Jianxiong Xiao, Antonio Torralba, and Aude Oliva. "Learning deep features for scene recognition
using places database." In Advances in neural information processing systems, pp. 487-495. 2014. [web]
E2E: Classification: Databases
● 205 scene classes (categories).
● Images:
○ 2.5M train
○ 20.5k validation
○ 41k test](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-20-320.jpg)

![E2E: Classification: ImageNet ILSRVC
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H., Krause, J., Satheesh, S., Ma, S., ... & Fei-Fei, L. (2015). Imagenet large scale visual
recognition challenge. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.0575. [web]
● Predict 5 classes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-22-320.jpg)
![Slide credit:
Rob Fergus (NYU)
Image Classifcation 2012
-9.8%
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H., Krause, J., Satheesh, S., Ma, S., ... & Fei-Fei, L. (2014). Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1409.0575. [web] 23
E2E: Classification: ILSRVC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-23-320.jpg)
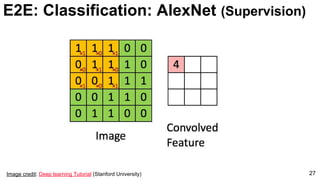
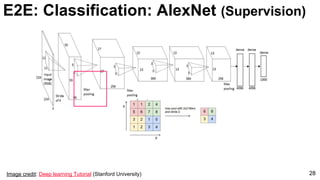
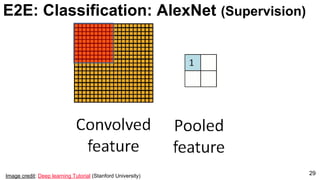
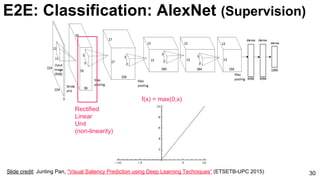
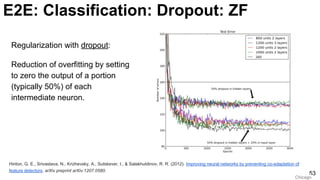
![ImageNet Classification 2013
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H., Krause, J., Satheesh, S., Ma, S., ... & Fei-Fei, L. (2015). Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1409.0575. [web]
Slide credit:
Rob Fergus (NYU)
32
E2E: Classification: ImageNet ILSRVC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-32-320.jpg)

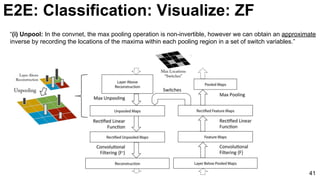
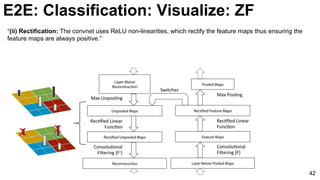
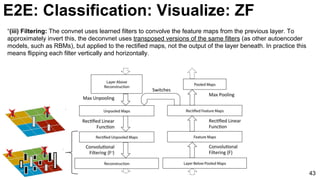
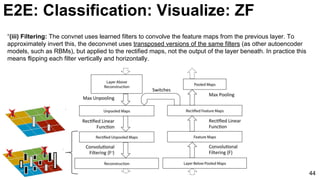




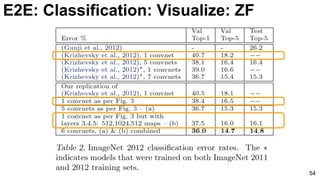
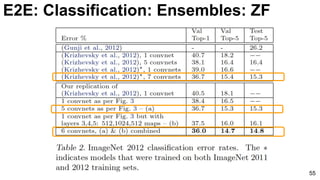
![ImageNet Classification 2013
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H., Krause, J., Satheesh, S., Ma, S., ... & Fei-Fei, L. (2015). Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1409.0575. [web]
-5%
Slide credit:
Rob Fergus (NYU)
56
E2E: Classification: ImageNet ILSRVC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-56-320.jpg)
![ImageNet Classification 2013
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H., Krause, J., Satheesh, S., Ma, S., ... & Fei-Fei, L. (2015). Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1409.0575. [web]
-5%
Slide credit:
Rob Fergus (NYU)
57
E2E: Classification: ImageNet ILSRVC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-57-320.jpg)

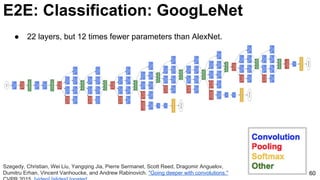

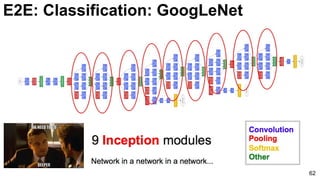
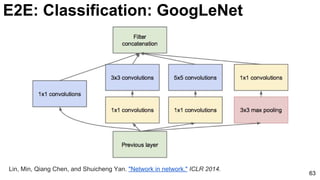
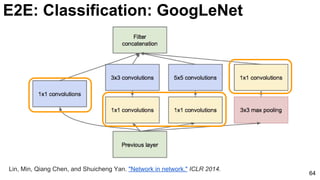
![E2E: Classification: GoogLeNet (NiN)
65
3x3 and 5x5 convolutions deal with
different scales.
Lin, Min, Qiang Chen, and Shuicheng Yan. "Network in network." ICLR 2014. [Slides]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-65-320.jpg)
![66
1x1 convolutions does dimensionality reduction (c3<c2) and
accounts for rectified linear units (ReLU).
Lin, Min, Qiang Chen, and Shuicheng Yan. "Network in network." ICLR 2014. [Slides]
E2E: Classification: GoogLeNet (NiN)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-66-320.jpg)
![67
In NiN, the Cascaded 1x1 Convolutions compute reductions after the
convolutions.
Lin, Min, Qiang Chen, and Shuicheng Yan. "Network in network." ICLR 2014. [Slides]
E2E: Classification: GoogLeNet (NiN)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-67-320.jpg)
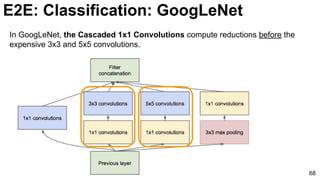
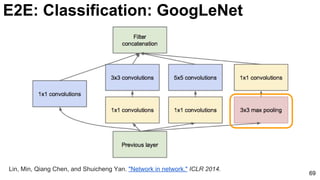
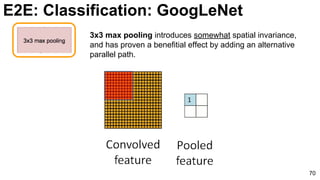
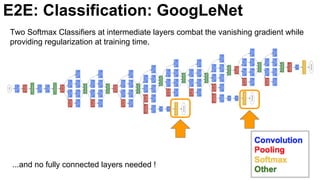
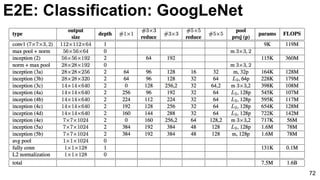
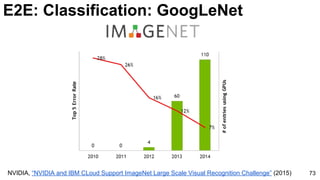
![E2E: Classification: GoogLeNet
74
Szegedy, Christian, Wei Liu, Yangqing Jia, Pierre Sermanet, Scott Reed, Dragomir Anguelov, Dumitru Erhan, Vincent
Vanhoucke, and Andrew Rabinovich. "Going deeper with convolutions." CVPR 2015. [video] [slides] [poster]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-74-320.jpg)
![E2E: Classification: VGG
75
Simonyan, Karen, and Andrew Zisserman. "Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition."
International Conference on Learning Representations (2015). [video] [slides] [project]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-75-320.jpg)
![E2E: Classification: VGG
76
Simonyan, Karen, and Andrew Zisserman. "Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition."
International Conference on Learning Representations (2015). [video] [slides] [project]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-76-320.jpg)
![E2E: Classification: VGG: 3x3 Stacks
77
Simonyan, Karen, and Andrew Zisserman. "Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image
recognition." International Conference on Learning Representations (2015). [video] [slides] [project]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-77-320.jpg)
![E2E: Classification: VGG
78
Simonyan, Karen, and Andrew Zisserman. "Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image
recognition." International Conference on Learning Representations (2015). [video] [slides] [project]
● No poolings between some convolutional layers.
● Convolution strides of 1 (no skipping).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-78-320.jpg)
![E2E: Classification: ResNet
80
He, Kaiming, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, and Jian Sun. "Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition." arXiv preprint arXiv:1512.03385
(2015). [slides]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-80-320.jpg)
![E2E: Classification: ResNet
81
● Deeper networks (34 is deeper than 18) are more difficult to train.
He, Kaiming, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, and Jian Sun. "Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition." arXiv preprint arXiv:1512.03385
(2015). [slides]
Thin curves: training error
Bold curves: validation error](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-81-320.jpg)
![E2E: Classification: ResNet
82
● Residual learning: reformulate the layers as learning residual functions with
reference to the layer inputs, instead of learning unreferenced functions
He, Kaiming, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, and Jian Sun. "Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition." arXiv preprint arXiv:1512.03385
(2015). [slides]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-82-320.jpg)
![E2E: Classification: ResNet
83
He, Kaiming, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, and Jian Sun. "Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition." arXiv preprint arXiv:1512.03385
(2015). [slides]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-83-320.jpg)
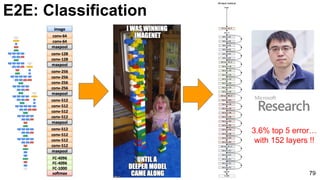
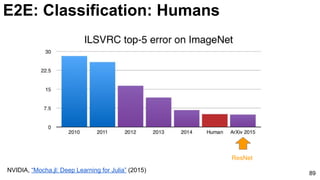
![84
E2E: Classification: Humans
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H., Krause, J., Satheesh, S., Ma, S., ... & Fei-Fei, L. (2015). Imagenet large scale visual
recognition challenge. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.0575. [web]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-84-320.jpg)
![85
E2E: Classification: Humans
“Is this a Border terrier” ?
Crowdsourcing
Yes
No
● Binary ground truth annotation from the crowd.
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H., Krause, J., Satheesh, S., Ma, S., ... & Fei-Fei, L. (2015). Imagenet large scale visual
recognition challenge. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.0575. [web]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-85-320.jpg)
![86
● Annotation Problems:
Carlier, Axel, Amaia Salvador, Ferran Cabezas, Xavier Giro-i-Nieto, Vincent Charvillat, and Oge Marques. "Assessment of
crowdsourcing and gamification loss in user-assisted object segmentation." Multimedia Tools and Applications (2015): 1-28.
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H., Krause, J., Satheesh, S., Ma, S., ... & Fei-Fei, L. (2015). Imagenet large scale visual
recognition challenge. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.0575. [web]
Crowdsource loss (0.3%) More than 5 objects classes
E2E: Classification: Humans](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-86-320.jpg)
![87
Andrej Karpathy, “What I learned from competing against a computer on ImageNet” (2014)
● Test data collection from one human. [interface]
E2E: Classification: Humans](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-87-320.jpg)
![88
Andrej Karpathy, “What I learned from competing against a computer on ImageNet” (2014)
● Test data collection from one human. [interface]
“Aww, a cute dog! Would you like to spend 5 minutes scrolling through 120
breeds of dog to guess what species it is ?”
E2E: Classification: Humans](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-88-320.jpg)








![100
TRAIN VALIDATION TEST
10,000 5,000 5,000
6,000 926 2,000
CAT2000 [Borji’15] 2,000 - 2,000
MIT300 [Judd’12] 300 - -Large
Scale
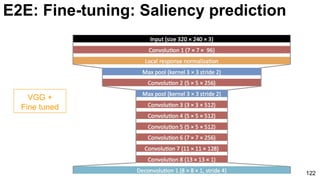
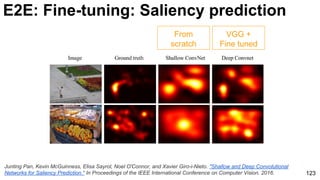
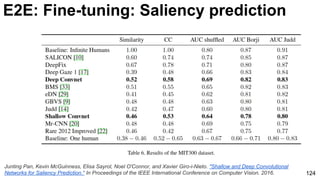
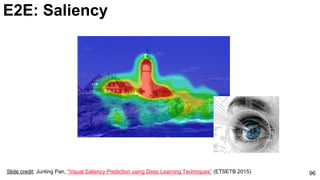
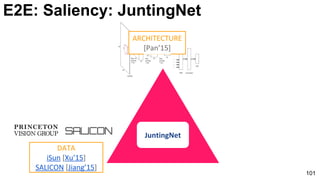
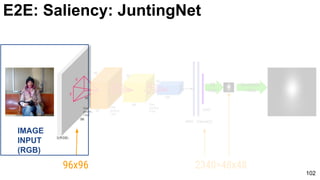
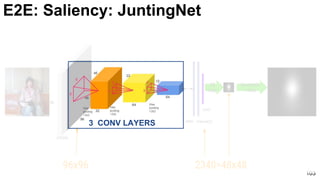
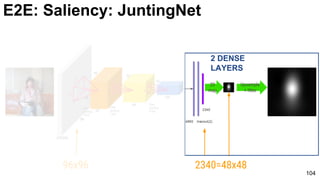
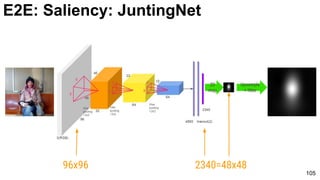
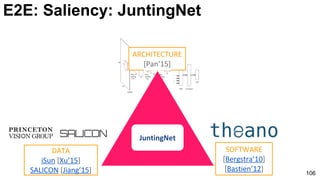
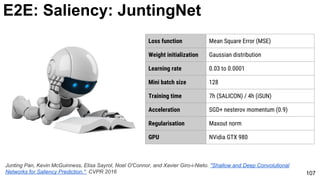
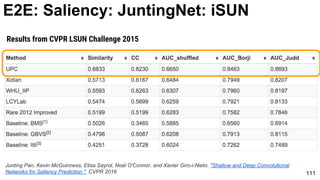
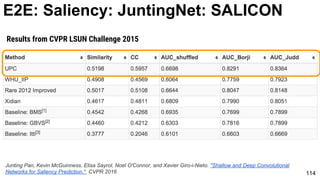
E2E: Saliency: JuntingNet
Junting Pan, Kevin McGuinness, Elisa Sayrol, Noel O'Connor, and Xavier Giro-i-Nieto. "Shallow and Deep Convolutional
Networks for Saliency Prediction." CVPR 2016](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-100-320.jpg)







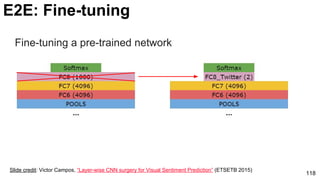


![121
E2E: Fine-tuning: Cultural events
ChaLearn Workshop
A. Salvador, Zeppelzauer, M., Manchon-Vizuete, D., Calafell-Orós, A., and Giró-i-Nieto, X., “Cultural
Event Recognition with Visual ConvNets and Temporal Models”, in CVPR ChaLearn Looking at People
Workshop 2015, 2015. [slides]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01lasallemmmdlcv-imageanalytics-160505220919/85/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-4-Image-Analytics-laSalle-2016-121-320.jpg)