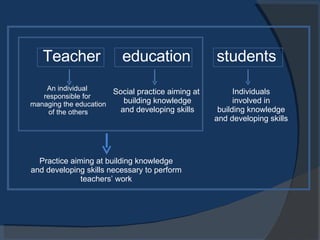
The document discusses developing a deep approach to learning for teacher education students. It emphasizes building knowledge of the world through socio-cultural and physical realities. Students should develop skills like flexibility, social skills, communication, and managing student activities. A deep approach involves vigorously interacting with content, relating ideas to prior knowledge and everyday experiences, and examining logic. Visual images can help communicate concepts. Teacher students need motivation, cognitive competence, and ICT/media skills to build knowledge and develop skills needed for their profession.