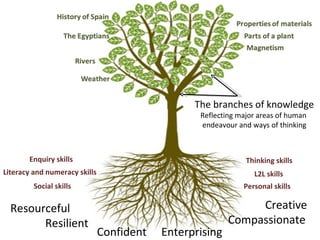
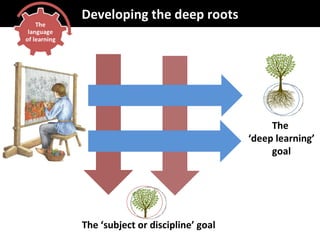
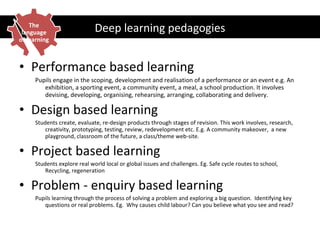
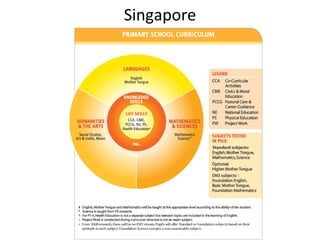
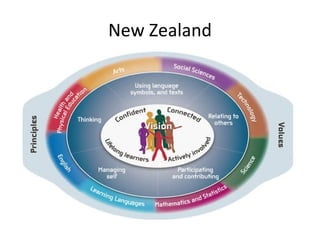
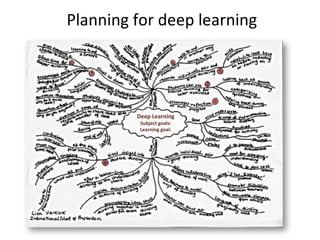
This document discusses developing a learning-focused curriculum and school environment. It emphasizes cultivating deep learning goals and skills like collaboration, problem-solving, creativity and resilience in students. It advocates giving schools freedom over their curriculum design while maintaining a national minimum standard. Various learning approaches are mentioned, like performance, project and problem-based learning. Developing student autonomy and celebrating successes are priorities. The highest performing education systems internationally are looked to for curriculum guidance.