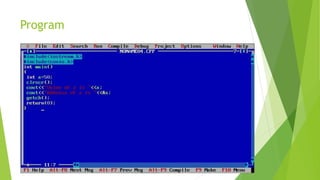
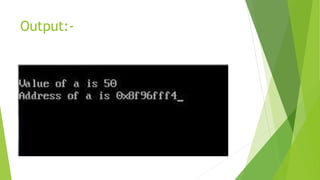
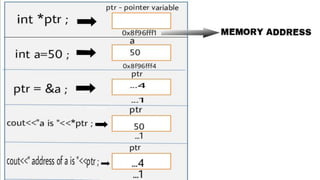
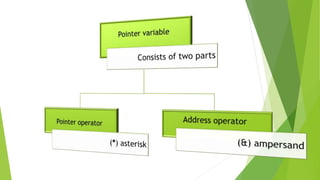
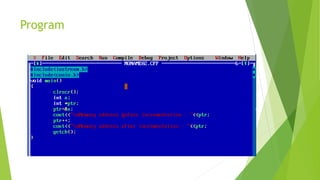
This document discusses pointers in C++. It defines pointers as variables that store memory addresses of other variables. It covers declaring and initializing pointers, using the address and dereference operators, pointer arithmetic, references, and passing pointers as function arguments. The document includes examples of pointer code and output to demonstrate these concepts.