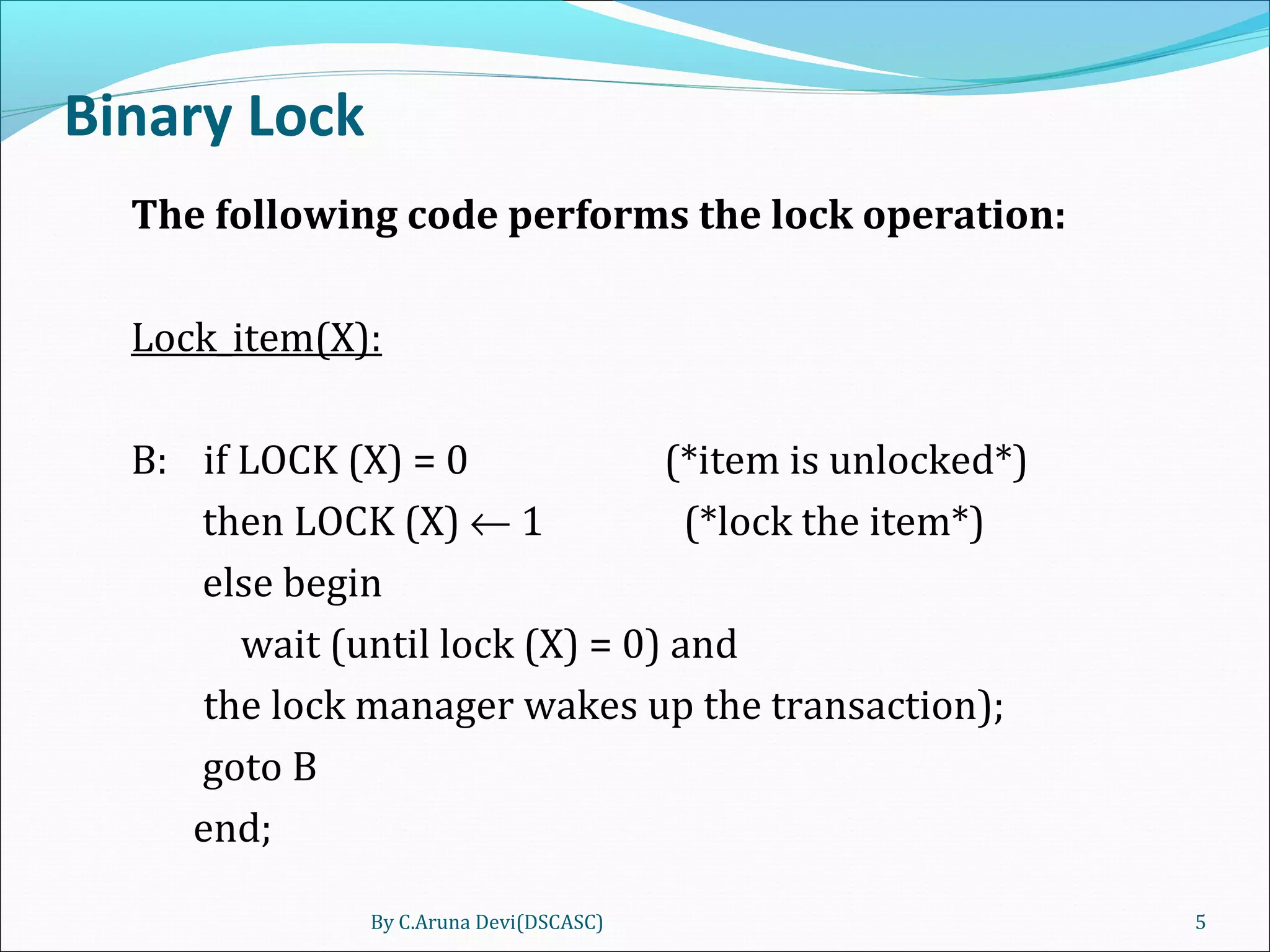
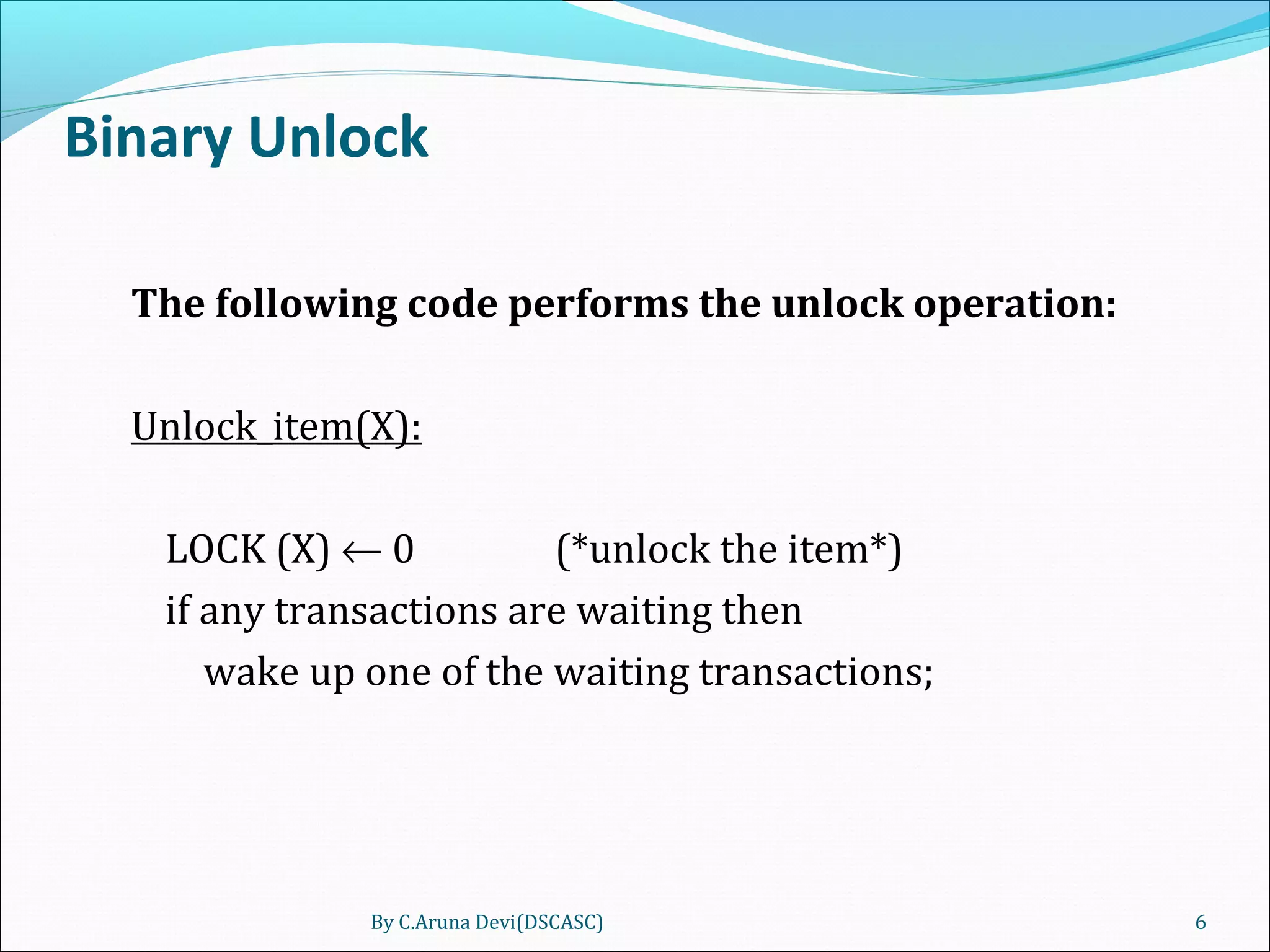
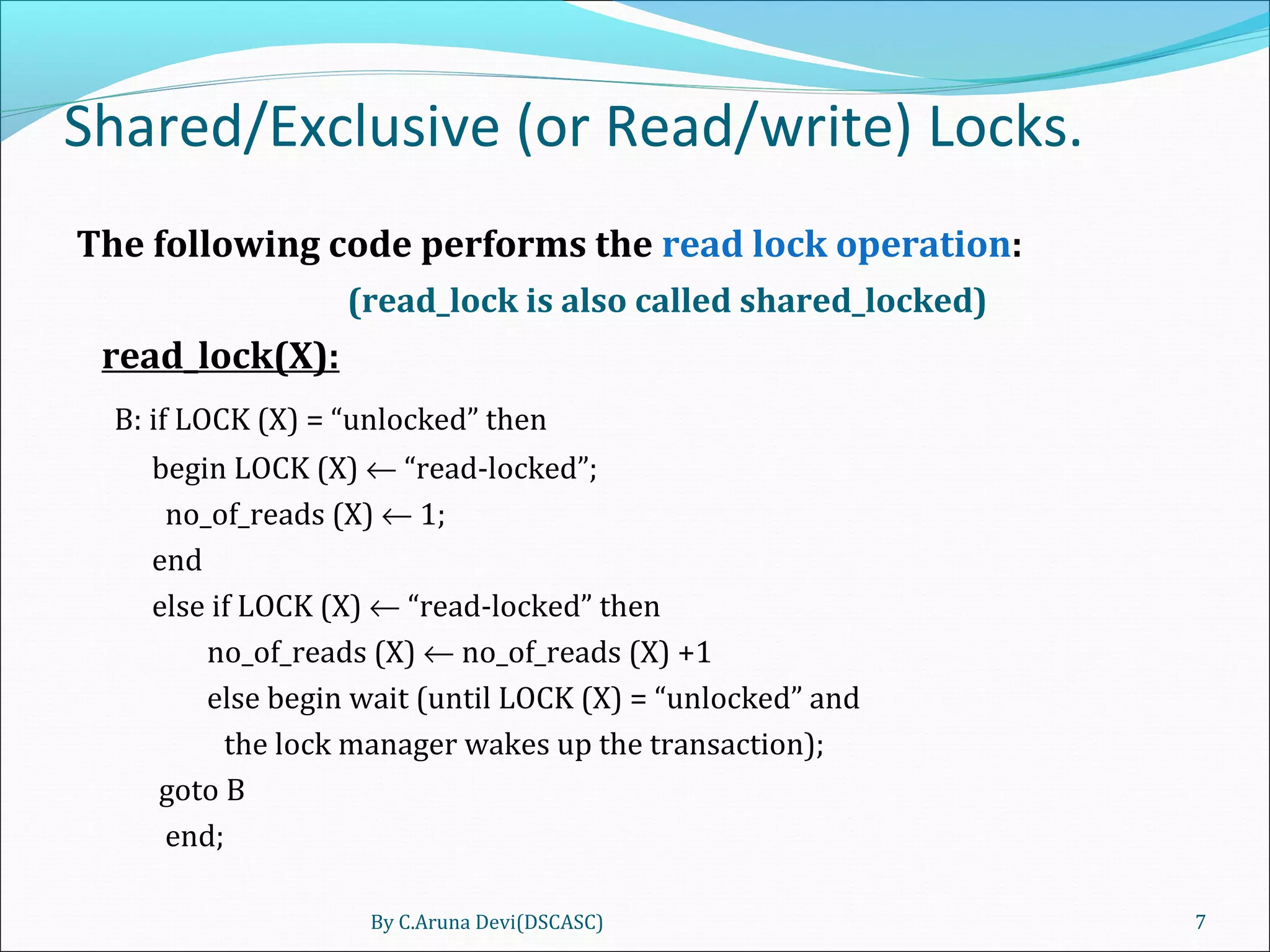
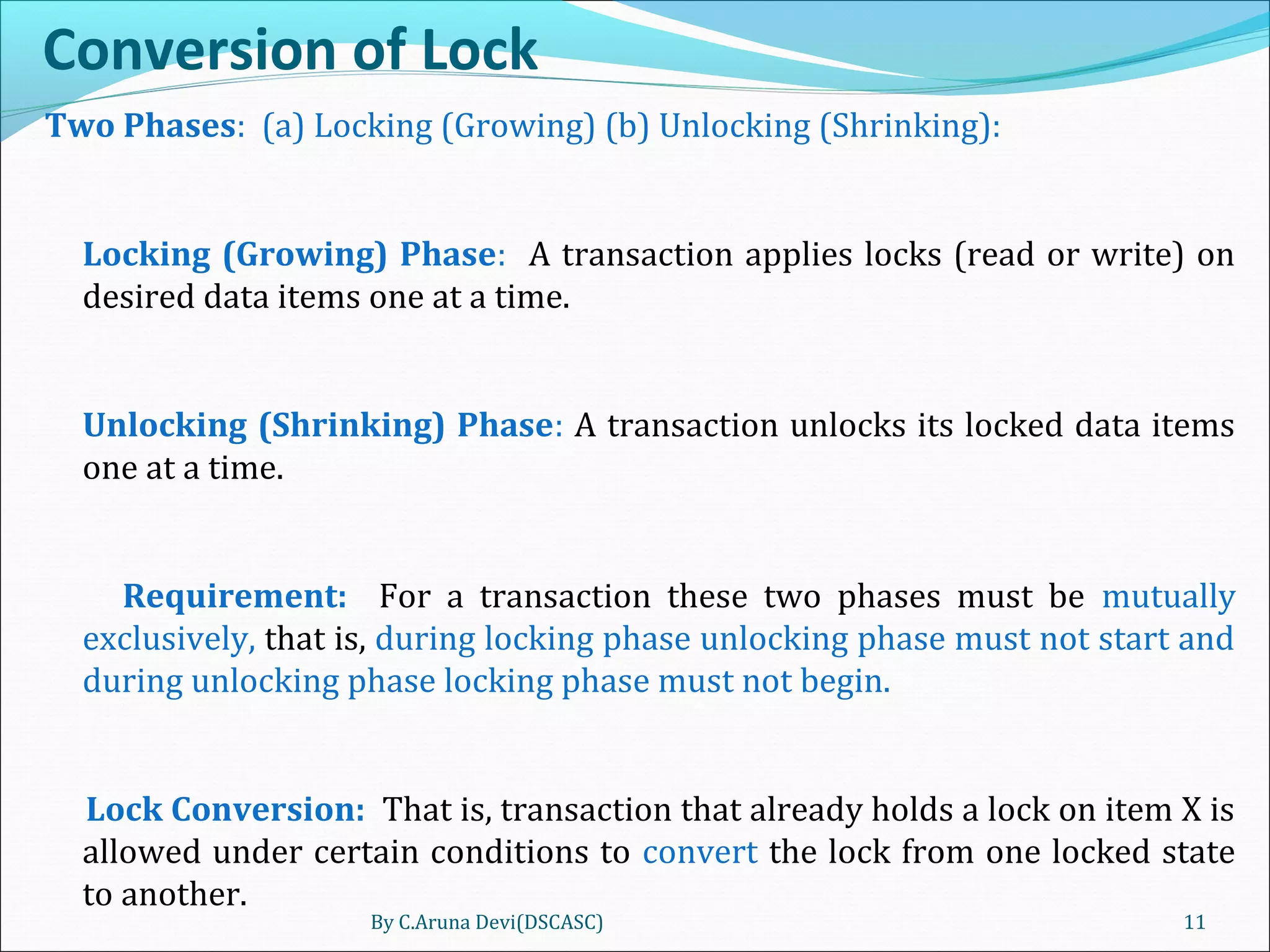
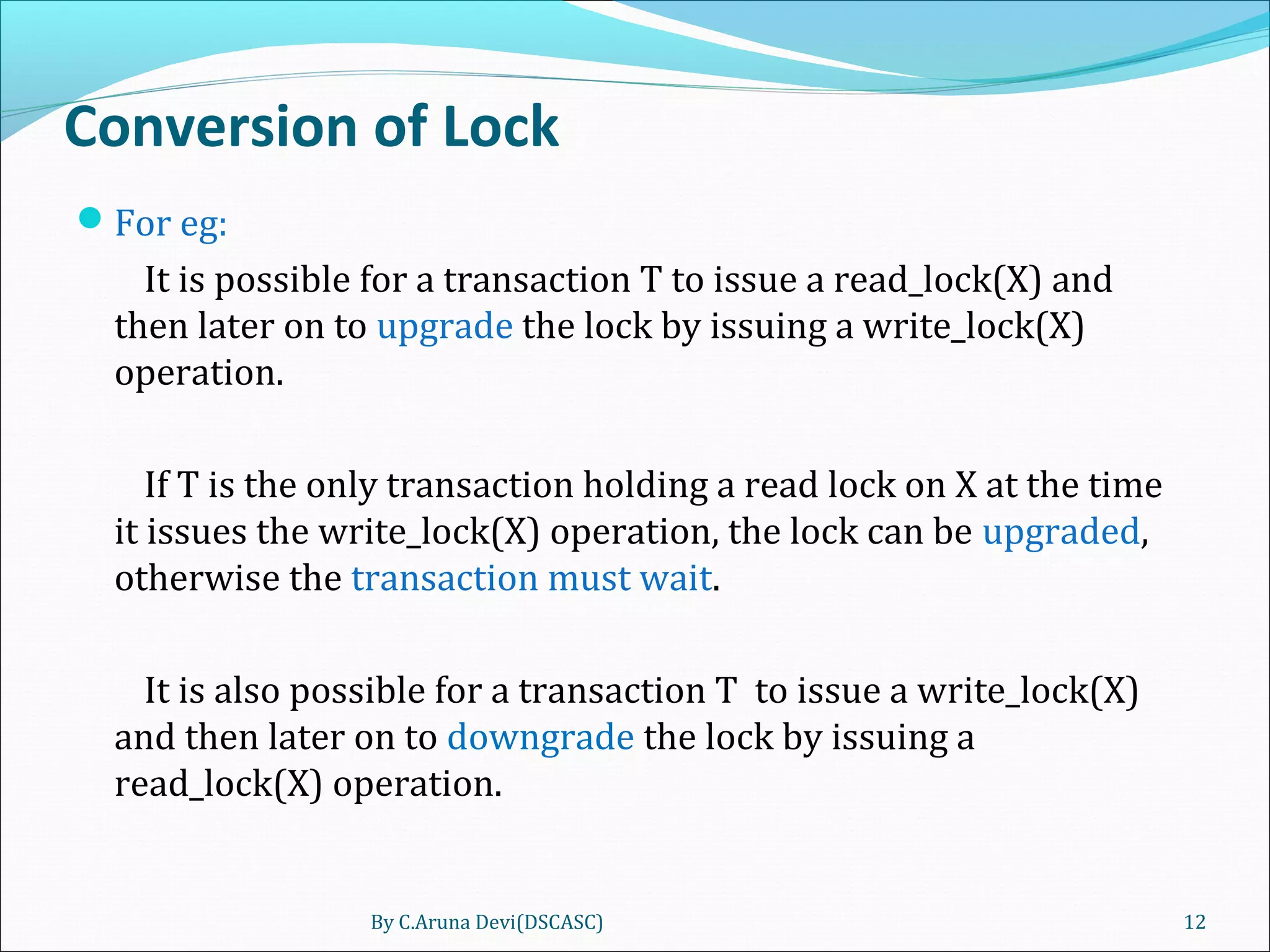
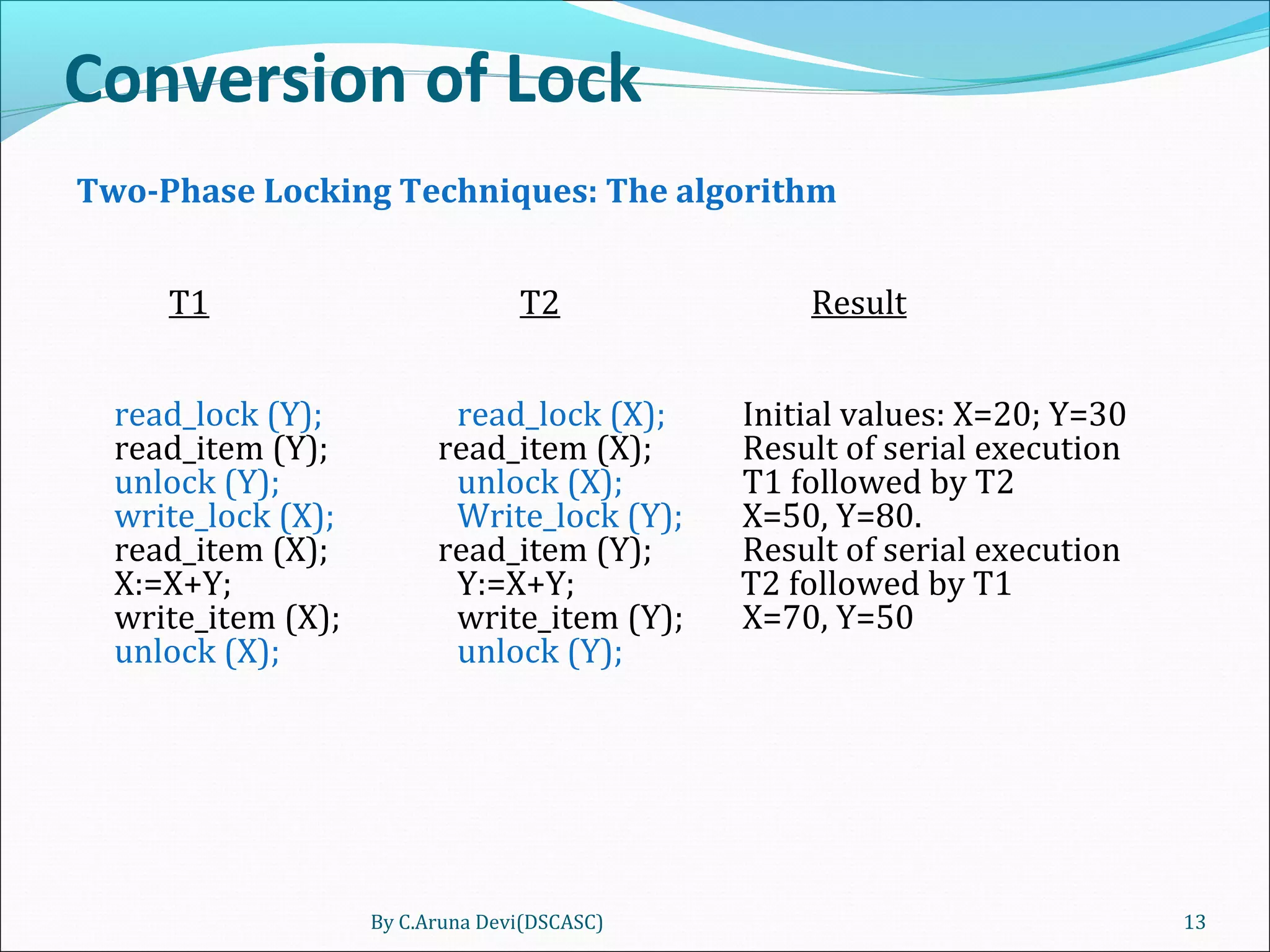
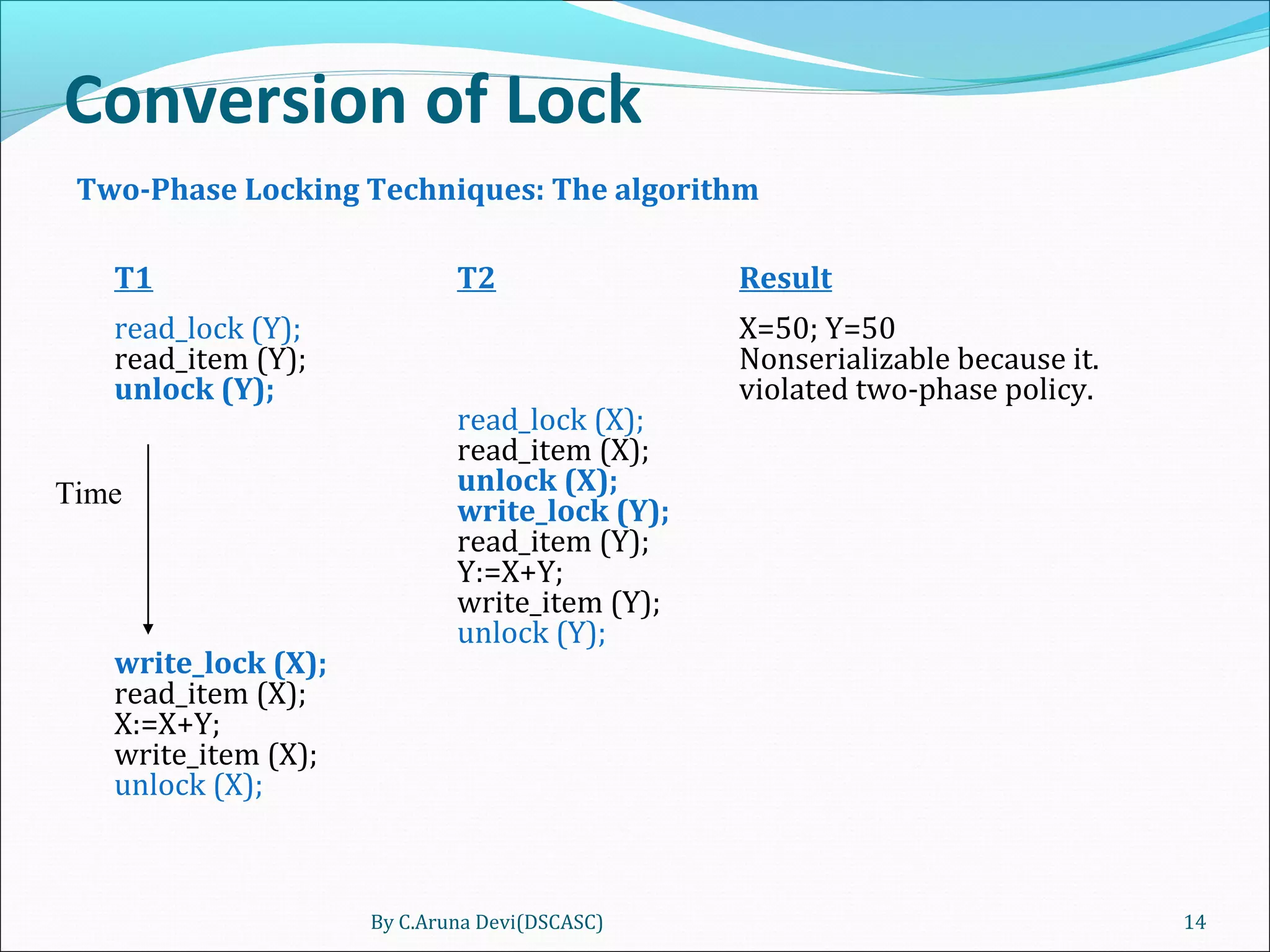
The document discusses different techniques for concurrency control in database management systems including locking techniques. It describes binary locks that can be in a locked or unlocked state, shared/exclusive locks that allow for read or write access, and conversion of locks where a transaction's lock on an item can be upgraded or downgraded. The two-phase locking technique requires that a transaction's growing and shrinking locking phases do not overlap to ensure serializability.
![Concurrency Control
Techniques
Chapter 10
UNIT V
By C.Aruna Devi(DSCASC) 1
Data Base Management System
[DBMS]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dbms-iimca-ch10-concurrency-control-2013-150630114326-lva1-app6891/75/Dbms-ii-mca-ch10-concurrency-control-2013-1-2048.jpg)