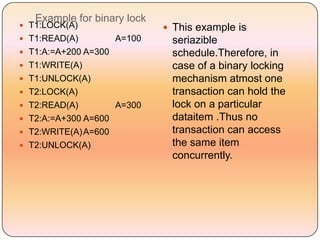
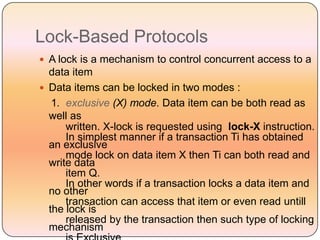
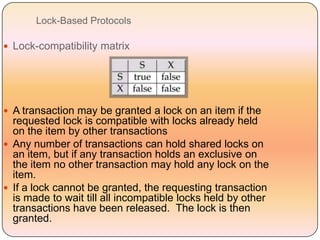
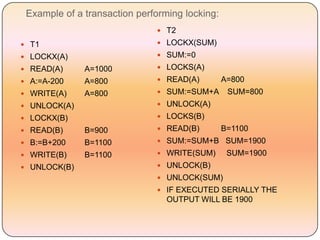
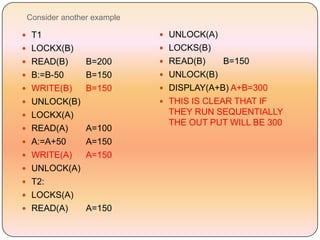
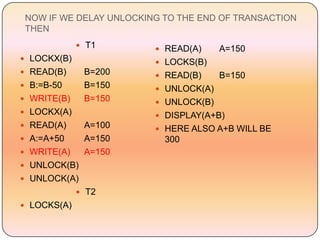
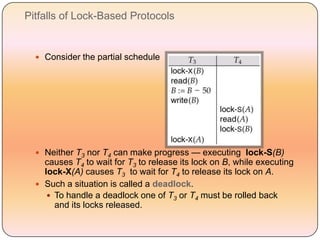
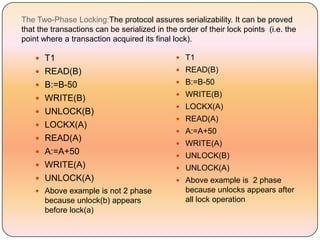
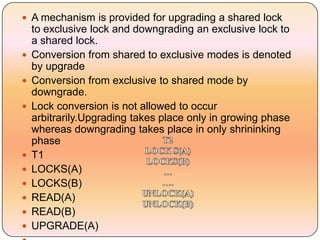
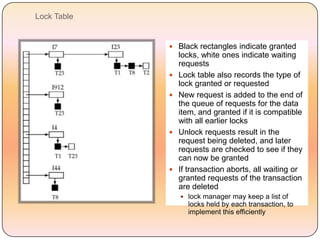
Concurrency control techniques like locking are used to ensure transactions execute consistently in a concurrent database. There are different types of locks like shared and exclusive locks. The two-phase locking protocol requires transactions to acquire all locks in a growing phase before releasing any locks in a shrinking phase, ensuring serializability. However, deadlocks are still possible. Strict two-phase locking requires transactions to hold exclusive locks until commit to prevent cascading rollbacks. Conversion between shared and exclusive locks allows more flexibility while maintaining serializability.