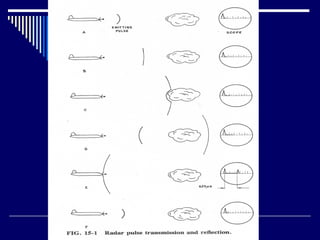
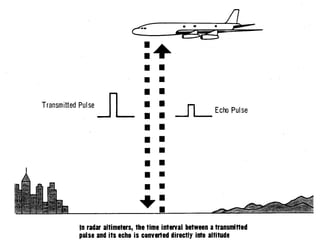
This document discusses several types of radar systems used in aviation. It describes how ATC radar works using UHF to monitor aircraft positions and allow air traffic controllers to direct pilots. It also explains weather radar systems that allow pilots to detect storms and avoid hazardous conditions. Different radar frequencies like C-band and X-band are discussed as well as other systems like radar altimeters, GPWS, and Stormscope that provide additional safety functions.