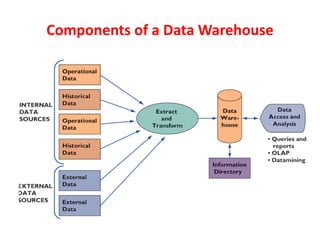
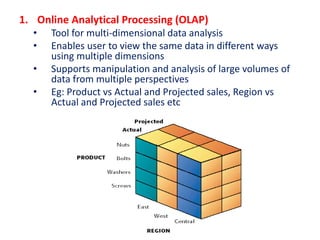
The document discusses the foundations of business intelligence, focusing on data warehouses and data mining. It explains data warehouses as centralized databases for decision makers, while data marts are smaller, focused subsets for specific subjects. Additionally, it details tools for analyzing data, such as OLAP, data mining, and text/web mining, to uncover patterns, relationships, and insights for informed decision making.