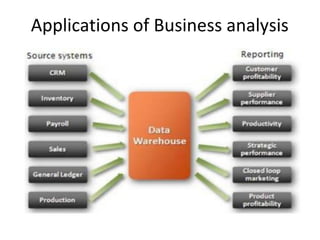
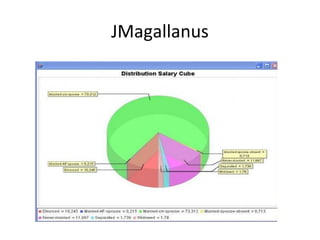
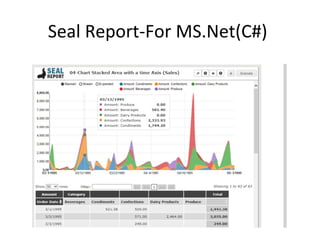
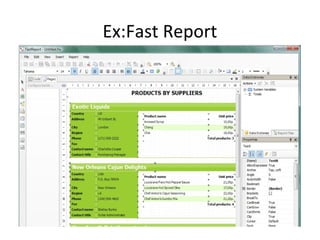
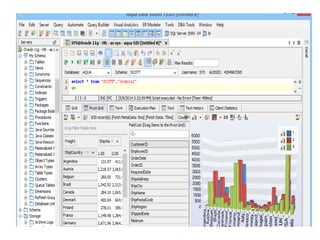
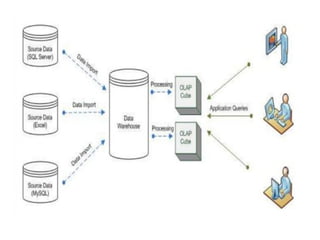
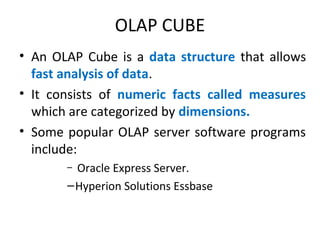
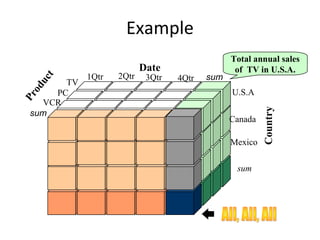
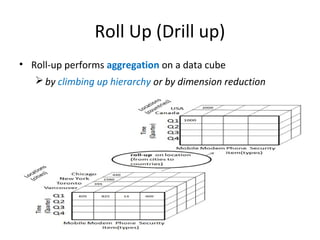
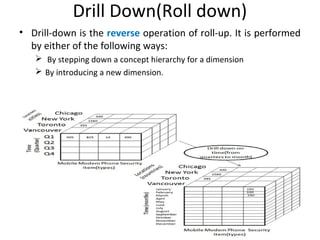
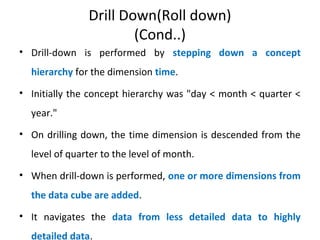
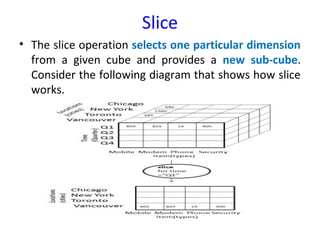
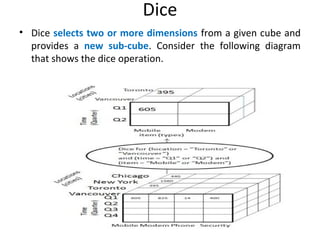
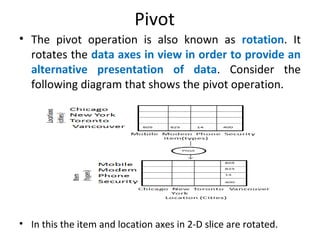
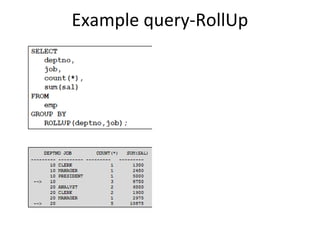
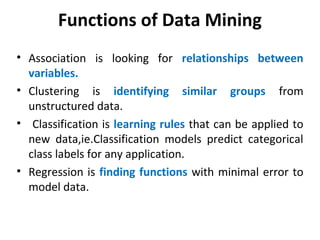
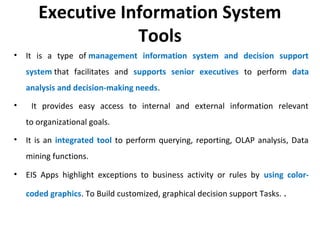
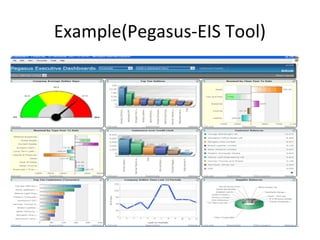
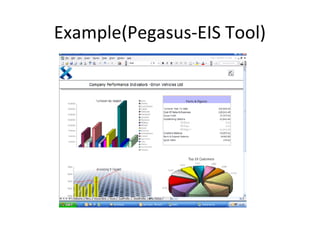
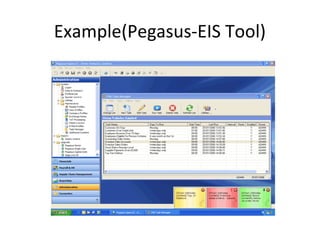
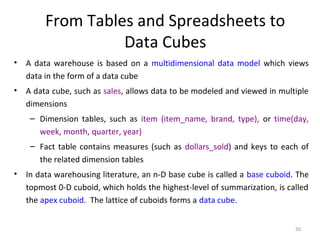
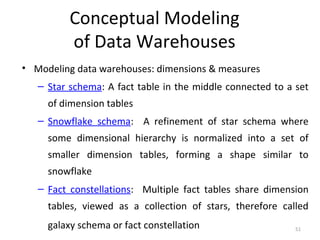
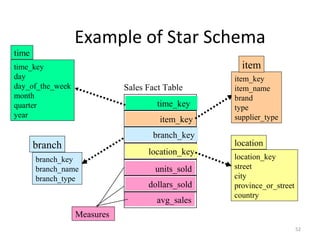
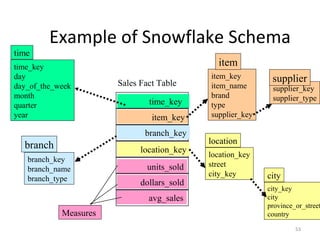
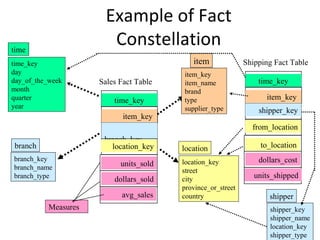
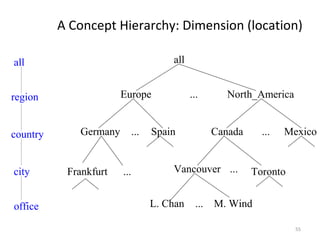
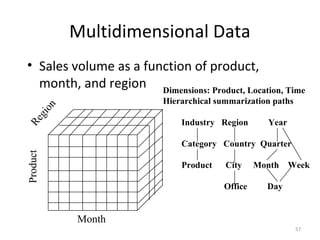
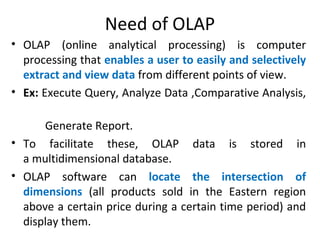
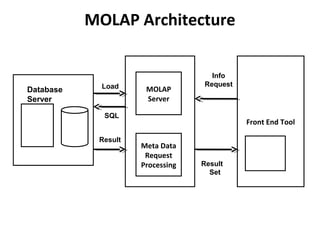
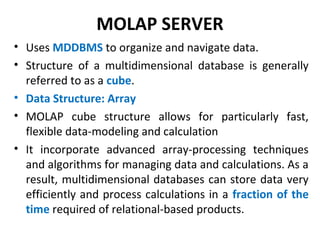
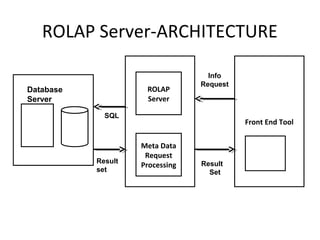
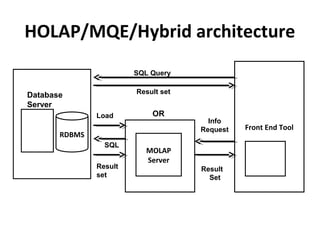
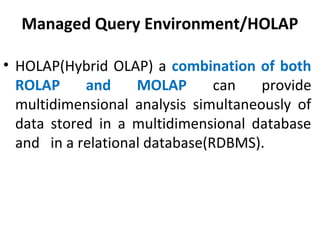
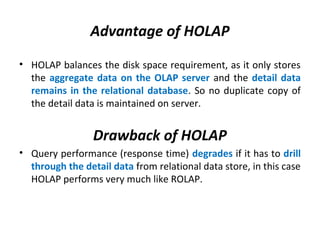
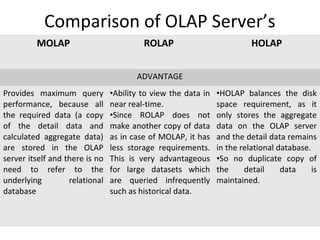
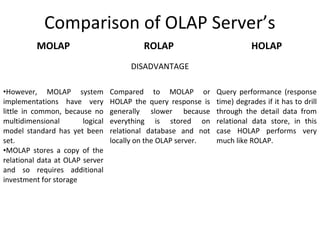
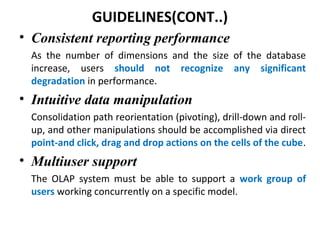
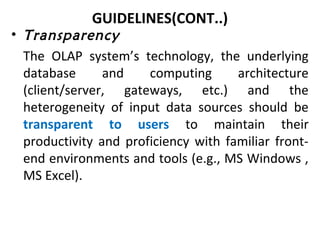
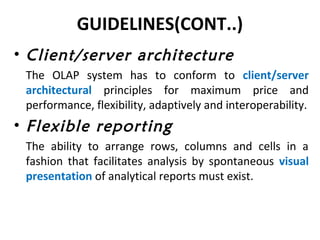
The document discusses various business analysis tools and techniques. It begins by defining business analysis and the responsibilities of business analysts. It then covers topics like reporting tools, query tools, OLAP, data mining, and executive information systems. Under OLAP, it discusses multidimensional data modeling concepts like star schemas, snowflake schemas, and fact constellations. It also covers OLAP operations and different types of OLAP servers including MOLAP, ROLAP, and HOLAP servers.