Huffman's algorithm is a method for compressing text documents using a binary tree to assign variable-length codes to characters based on their frequency. Introduced by David Huffman in 1952, it is a lossless data compression technique utilized in various applications including JPEG image compression. The process involves counting character occurrences, creating a priority queue, and constructing a binary tree which encodes each character using unique binary paths.


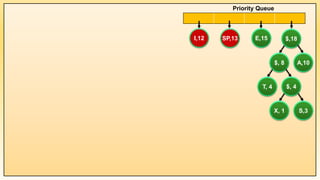
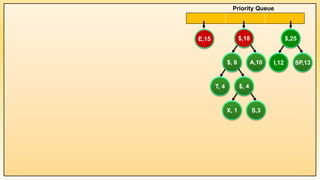
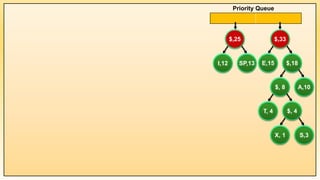
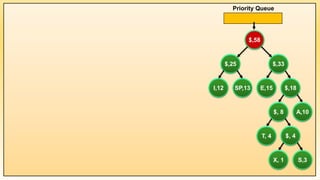


![void Generate_Huffman_Tree(char data[], size_t freq[], size_t size) {
New_Node* left;
New_Node* right;
Priority_Queue <New_Node*>PQ;
for(size_t i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
PQ.Push(new New_Node(data[i], freq[i]));
}
PQ.Show();
while(PQ.size() != 1) {
left = PQ.Top(); PQ.Pop();
right = PQ.Top(); PQ.Pop();
root = new New_Node('$', left->freq + right->freq);
root->left = left; root->right = right;
PQ.Push(root); PQ.Show();
}
Print_Code(PQ.Top(), "");
}
};
14
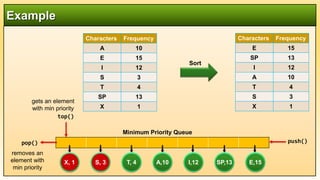
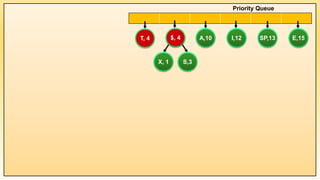
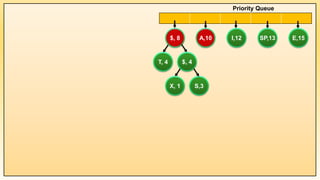
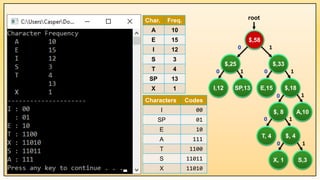
Example 1: Implementation of Huffman Coding Algorithm
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ds16huffmancoding-240518111039-a7c856d2/85/Data-Structures-and-Agorithm-DS-16-Huffman-Coding-pptx-14-320.jpg)
![int main() {
Huffman_Codes Huff;
char data [] = { 'A', 'E', 'I', 'S', 'T', ' ', 'X'};
size_t freq [] = { 10 , 15, 12, 3, 4, 13, 1};
size_t size = sizeof(data);
cout <<"Character Frequency" << endl;
for (size_t i=0 ; i<size ; i++)
cout <<" "<< data[i] << " " << freq[i] << endl;
cout <<"---------------------" << endl;
Huff.Generate_Huffman_Tree(data, freq, size);
system("PAUSE"); return 0;
}
15
Example 1: Implementation of Huffman Coding Algorithm
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ds16huffmancoding-240518111039-a7c856d2/85/Data-Structures-and-Agorithm-DS-16-Huffman-Coding-pptx-15-320.jpg)