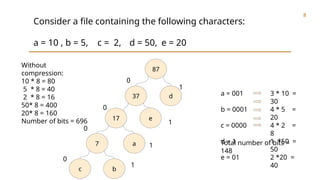
The document outlines a project on text file compression using the Huffman coding algorithm, which reduces redundancy in text files for efficient storage and transmission. It details the implementation process, including character frequency analysis, tree construction, and code generation, and highlights the data structures utilized. The project aims to demonstrate a lossless compression technique that effectively encodes characters based on their frequency, achieving significant reductions in overall file size.