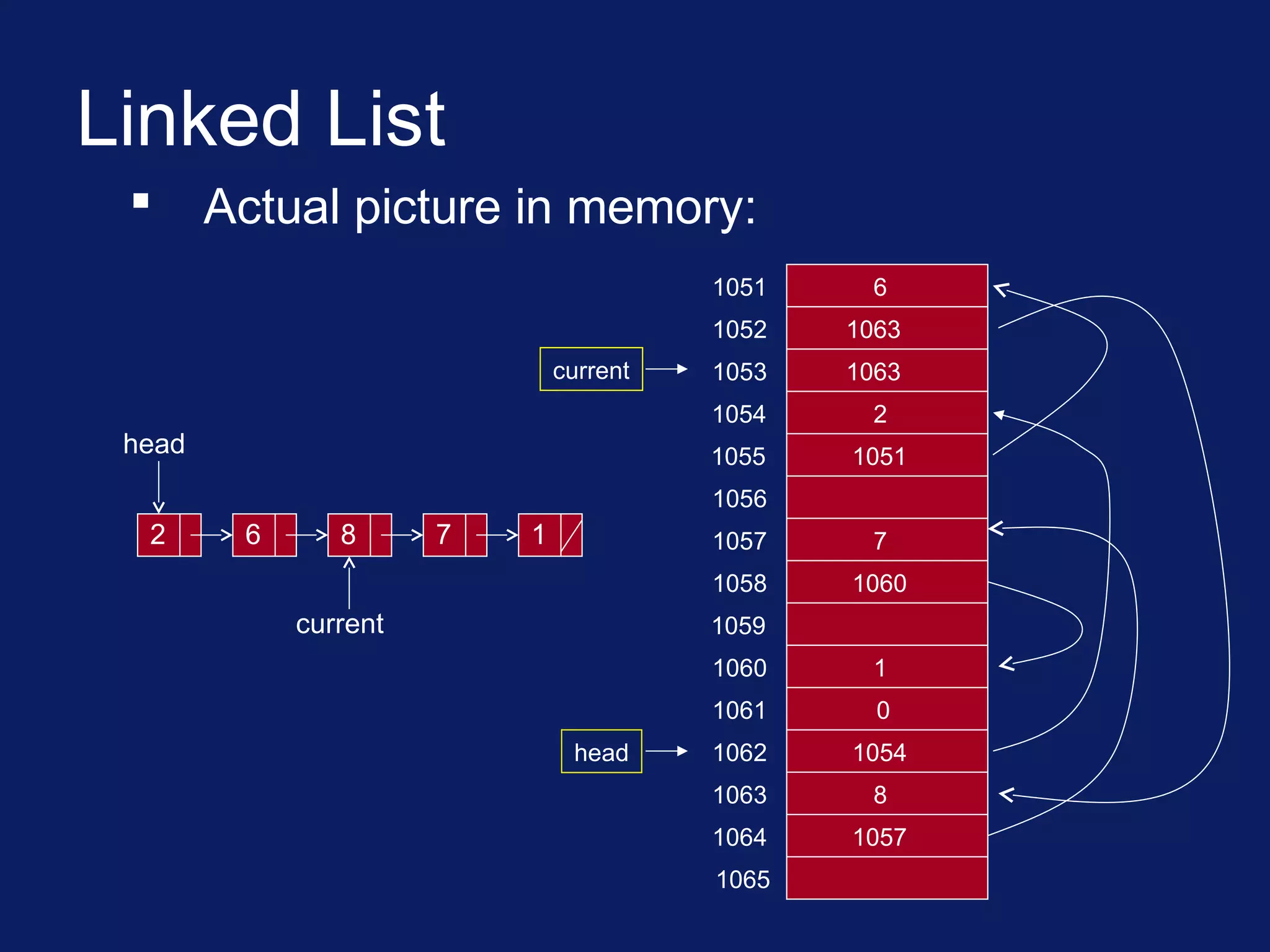
This lecture covers the implementation of lists in data structures, focusing on array-based and linked list implementations. It discusses operations like adding, removing, and finding elements, along with the complexity of these operations. The linked list is highlighted as a structure that requires a head pointer and allows non-contiguous memory allocation for storing list elements.









![Implementing Lists
find(X): traverse the array until X is located.
int find(int X)
{
int j;
for(j=1; j < size+1; j++ )
if( A[j] == X ) break;
if( j < size+1 ) { // found X
current = j; // current points to where X found
return 1; // 1 for true
}
return 0; // 0 (false) indicates not found
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cs301-lec02-150119235419-conversion-gate01/75/Data-Structure-lec-2-10-2048.jpg)
![Implementing Lists
Other operations:
get() return A[current];
update(X) A[current] = X;
length() return size;
back() current--;
start() current = 1;
end() current = size;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cs301-lec02-150119235419-conversion-gate01/75/Data-Structure-lec-2-11-2048.jpg)