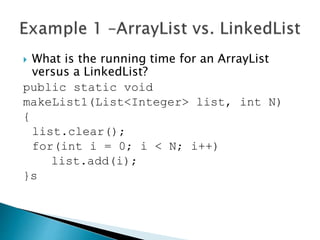
The document discusses different data structures for implementing lists, including arrays, linked lists, and doubly linked lists. It compares their performance for common list operations like insertion, deletion, accessing elements, and iterating. ArrayLists use arrays which provide constant time access but linear time insertion/deletion. LinkedLists have constant time insertion/deletion but linear access. Doubly linked lists also provide constant time insertion/deletion at the head and tail.




![ Use an array to store the elements of the list
◦ printList is O(n)
◦ findkth,get and set are constant time
◦ Insert and delete?
Also, arrays have a fixed capacity, but can fix
with implementation.
int arr[] = new int arr[10];
int newArr[] = new int[arr.length *2];
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
newArr[i] = arr[i];
arr = newArr;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/listinterface-160828194313/85/List-interface-5-320.jpg)