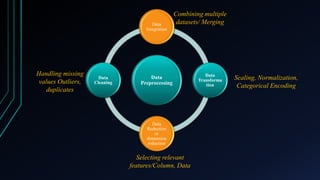
The document discusses key data preprocessing techniques in data science, focusing on feature selection and merging. Feature selection is the process of identifying the most relevant features for model building, while merging involves combining datasets based on common attributes. Various methods for feature selection and different types of joins for merging data are also described.