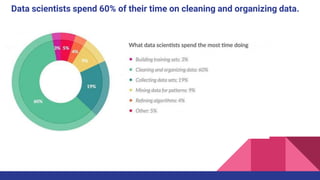
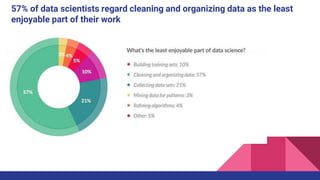
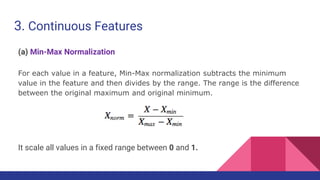
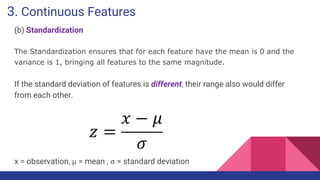
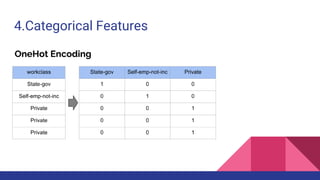
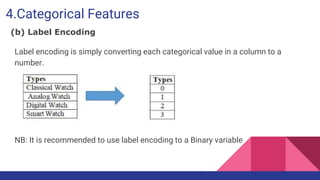
This document provides an overview of feature engineering and selection in machine learning, emphasizing the importance of preparing data and handling missing values. It discusses techniques for managing continuous and categorical features, as well as different strategies for feature selection to improve model accuracy. The document highlights that effective feature engineering and selection can significantly impact the success of machine learning models.