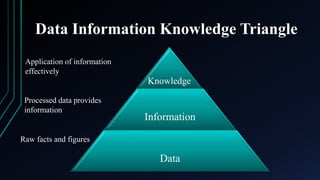
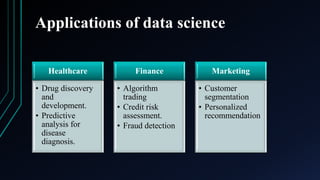
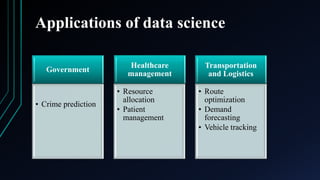
Data science is an interdisciplinary field that applies scientific methods and algorithms to extract knowledge from both structured and unstructured data. It transforms raw data into meaningful information, which can then be used to generate insights and guide decision-making across various sectors, including healthcare, finance, and education. The document outlines the data-information-knowledge triangle and highlights applications of data science in different domains.