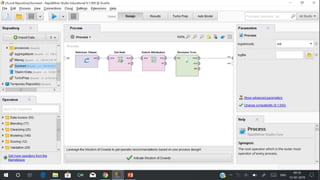
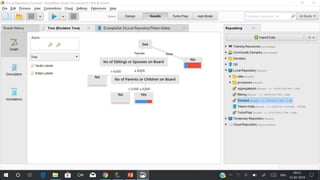
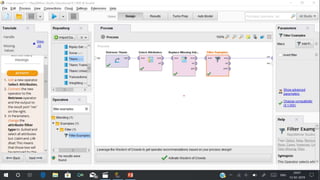
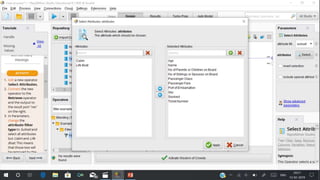
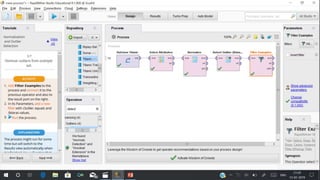
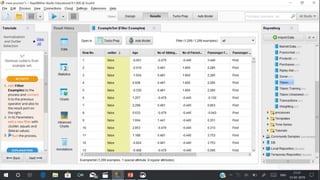
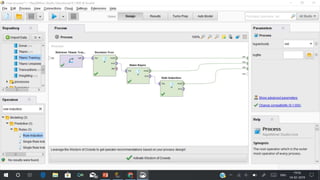
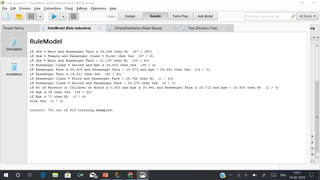
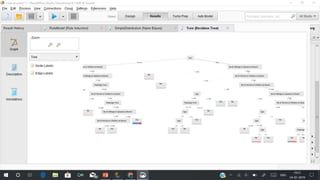
RapidMiner is an open-source platform for data mining, launched in 2006, that offers tools for data preparation, machine learning, and predictive analytics. The software supports various applications and has received high satisfaction ratings, with over 250,000 users including major companies like eBay and Intel. It provides functionalities for data cleansing, predictive modeling, and cross-validation to improve data analysis outcomes.