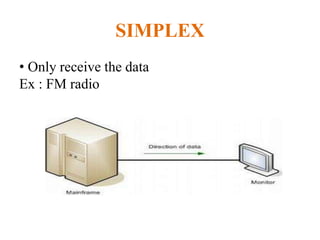
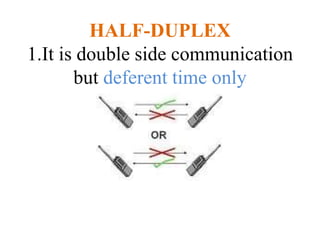
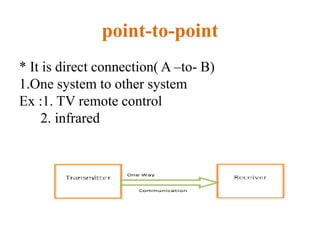
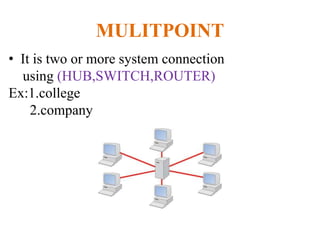
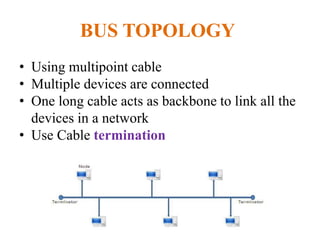
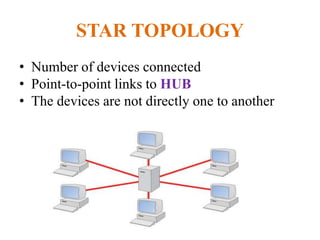
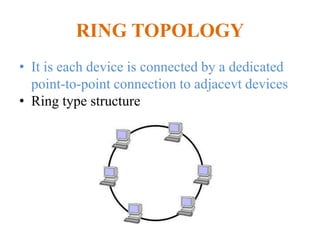
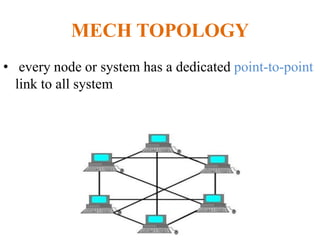
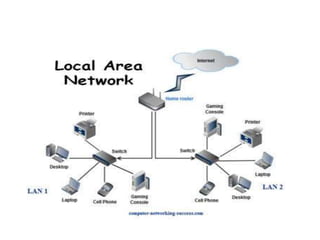
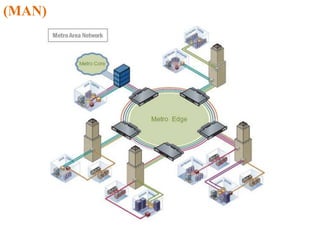
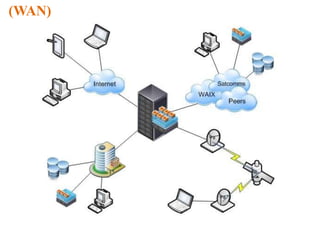
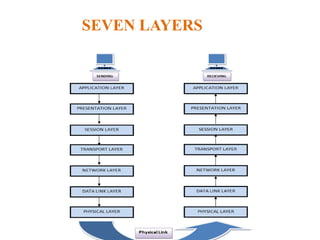
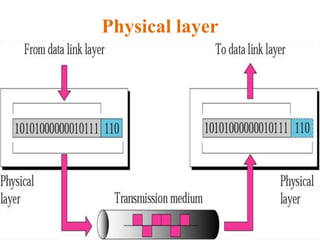
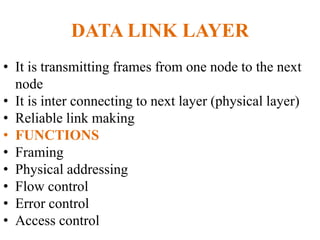
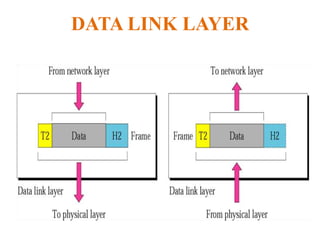
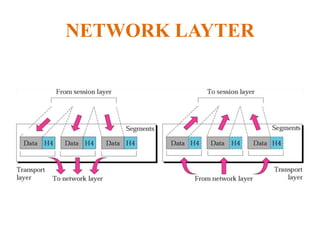
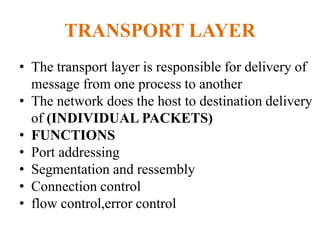
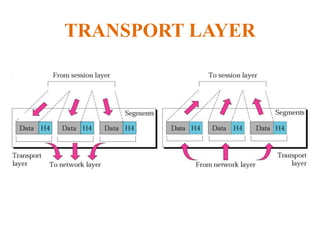
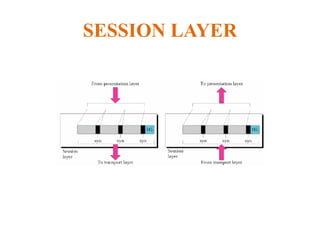
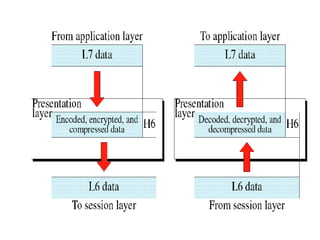
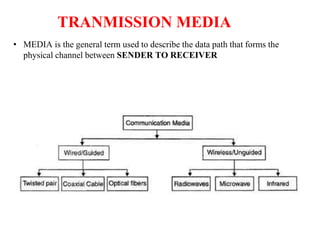
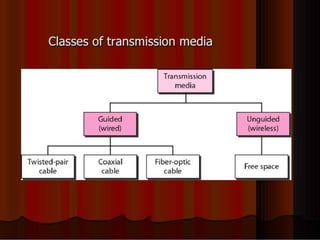
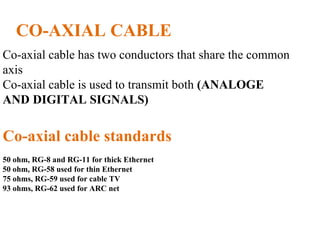
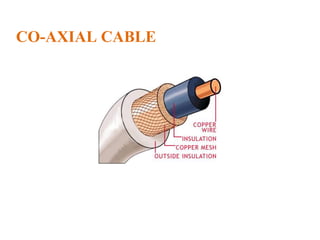
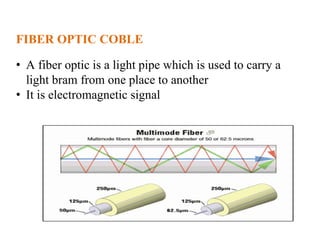
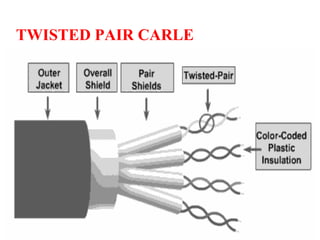
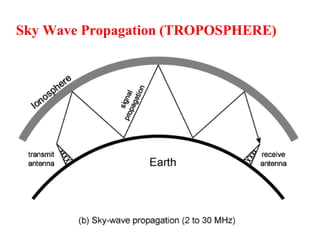
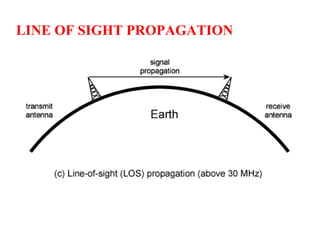
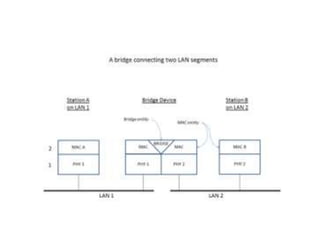
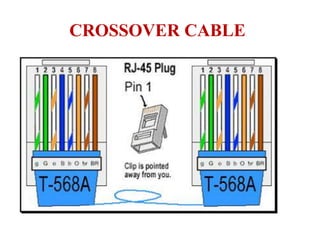
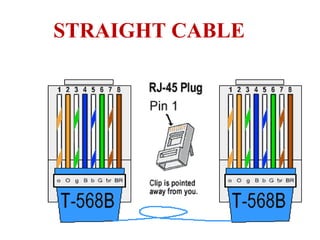
The document outlines key components of computer networks including messages, senders, receivers, mediums, and protocols. It details various topology types (bus, star, ring, mesh), connection types (point-to-point, multipoint), and categories of networks (LAN, MAN, WAN), as well as the ISO/OSI model layers and transmission media like coaxial and fiber optic cables. Additionally, it covers network devices such as bridges and firewalls, explaining their functions and advantages.