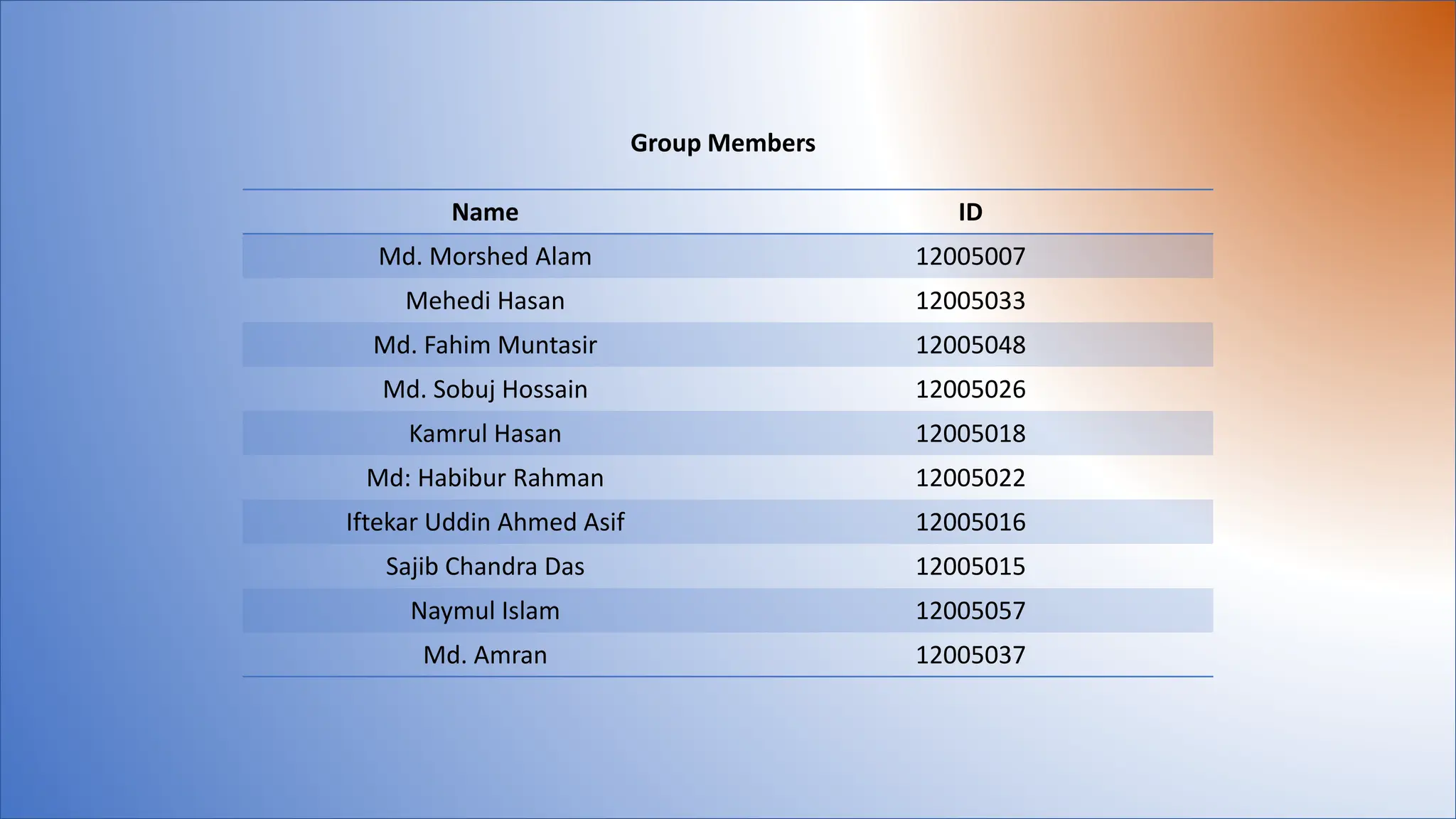
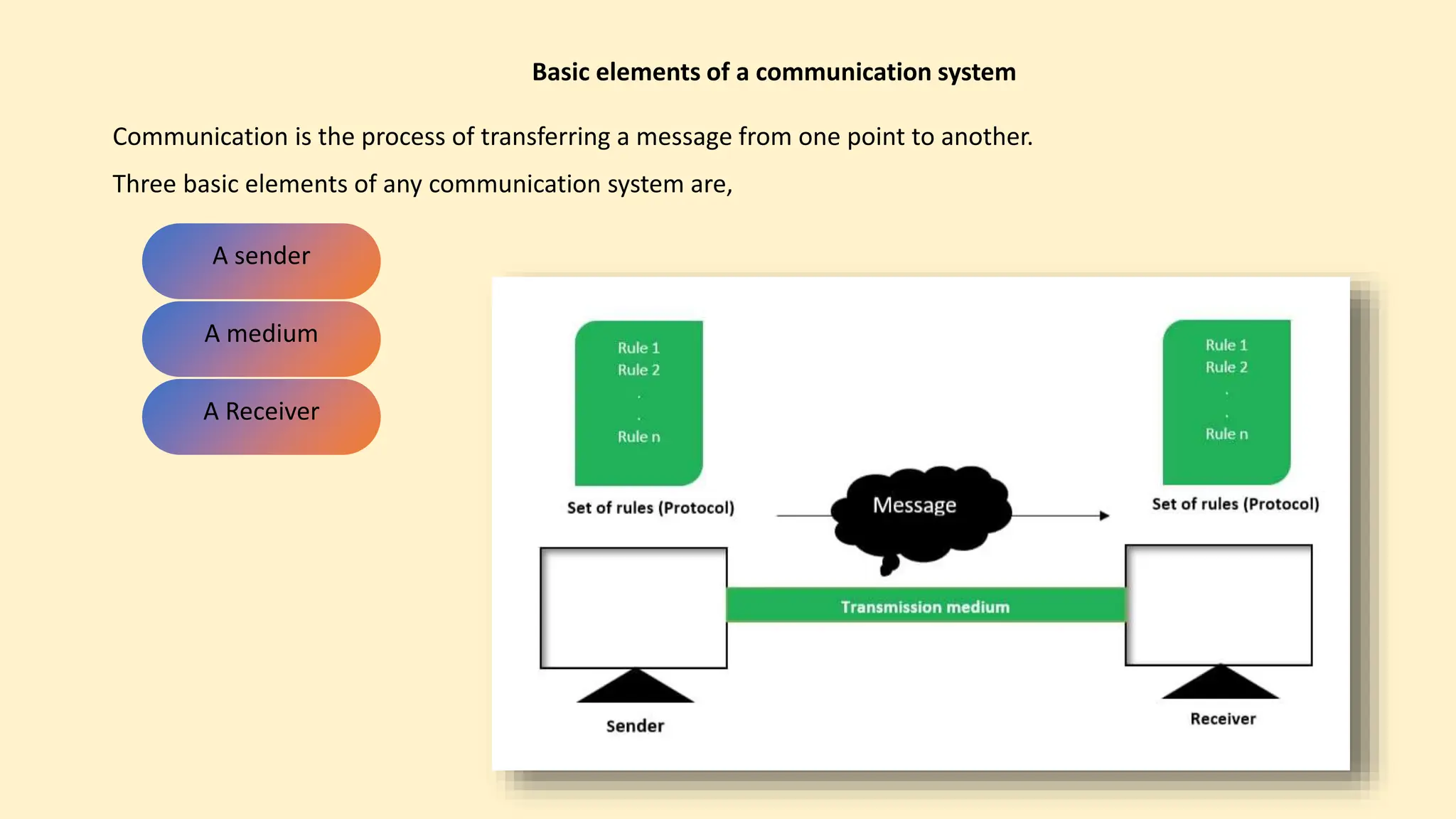
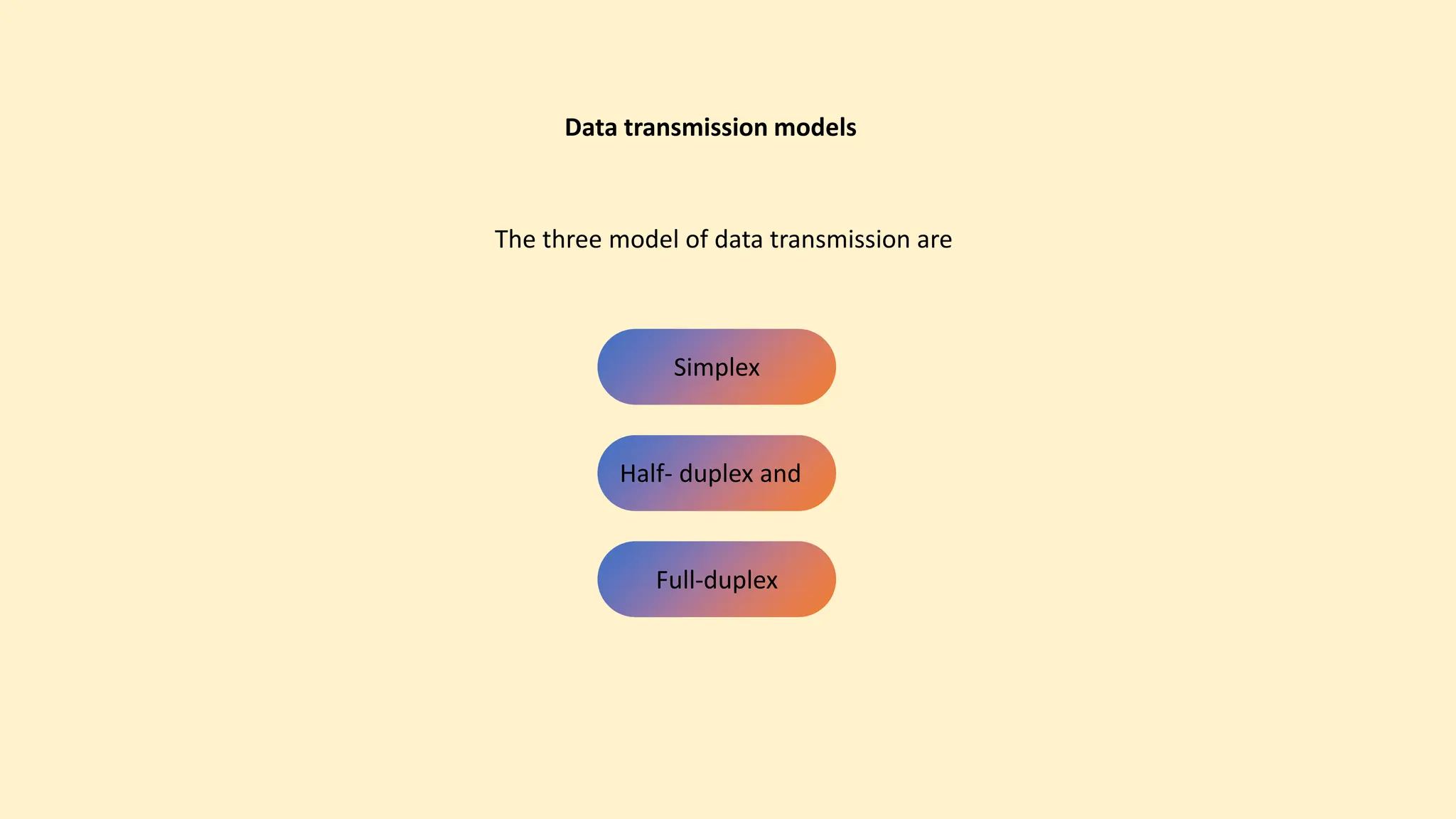
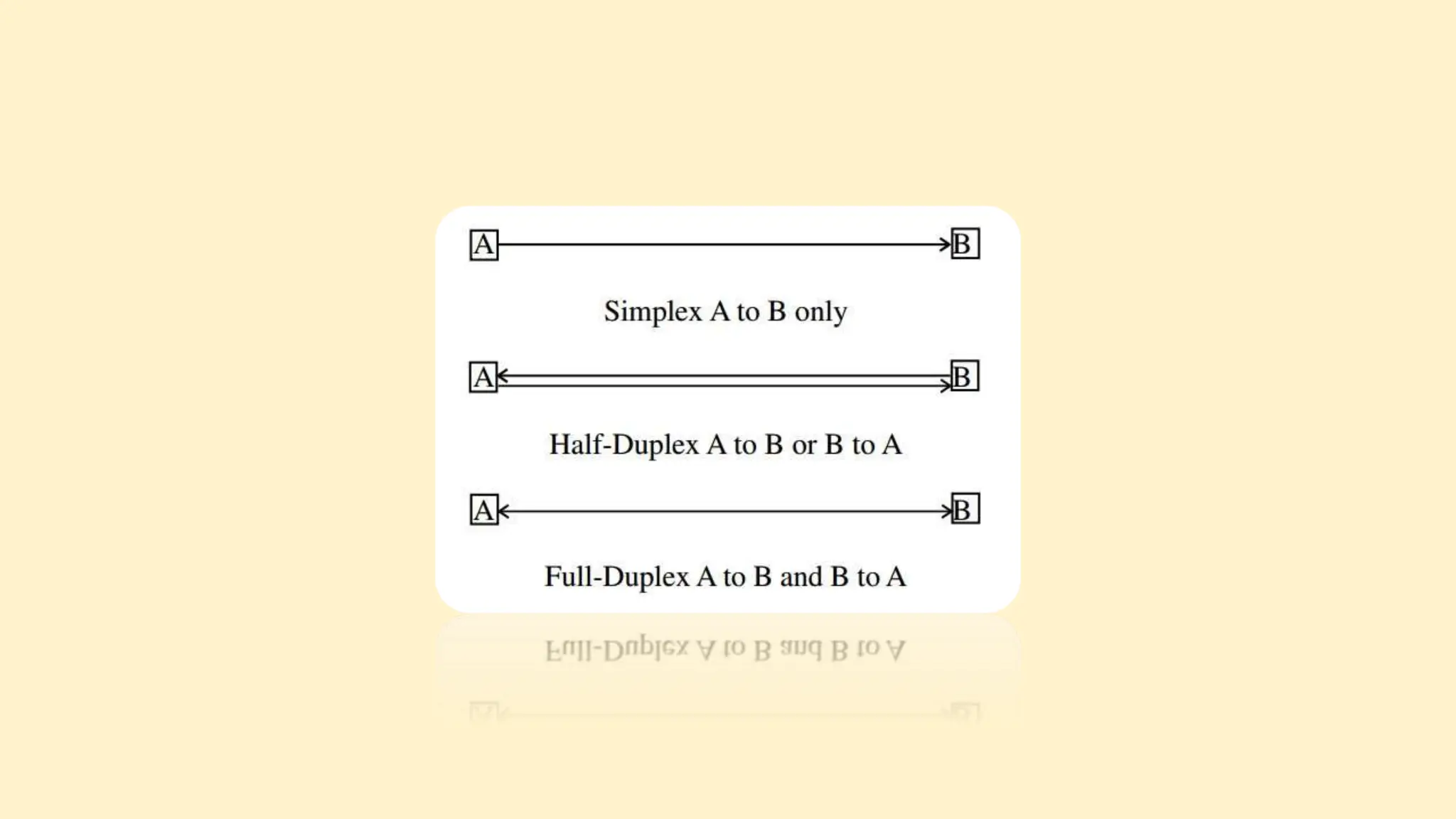
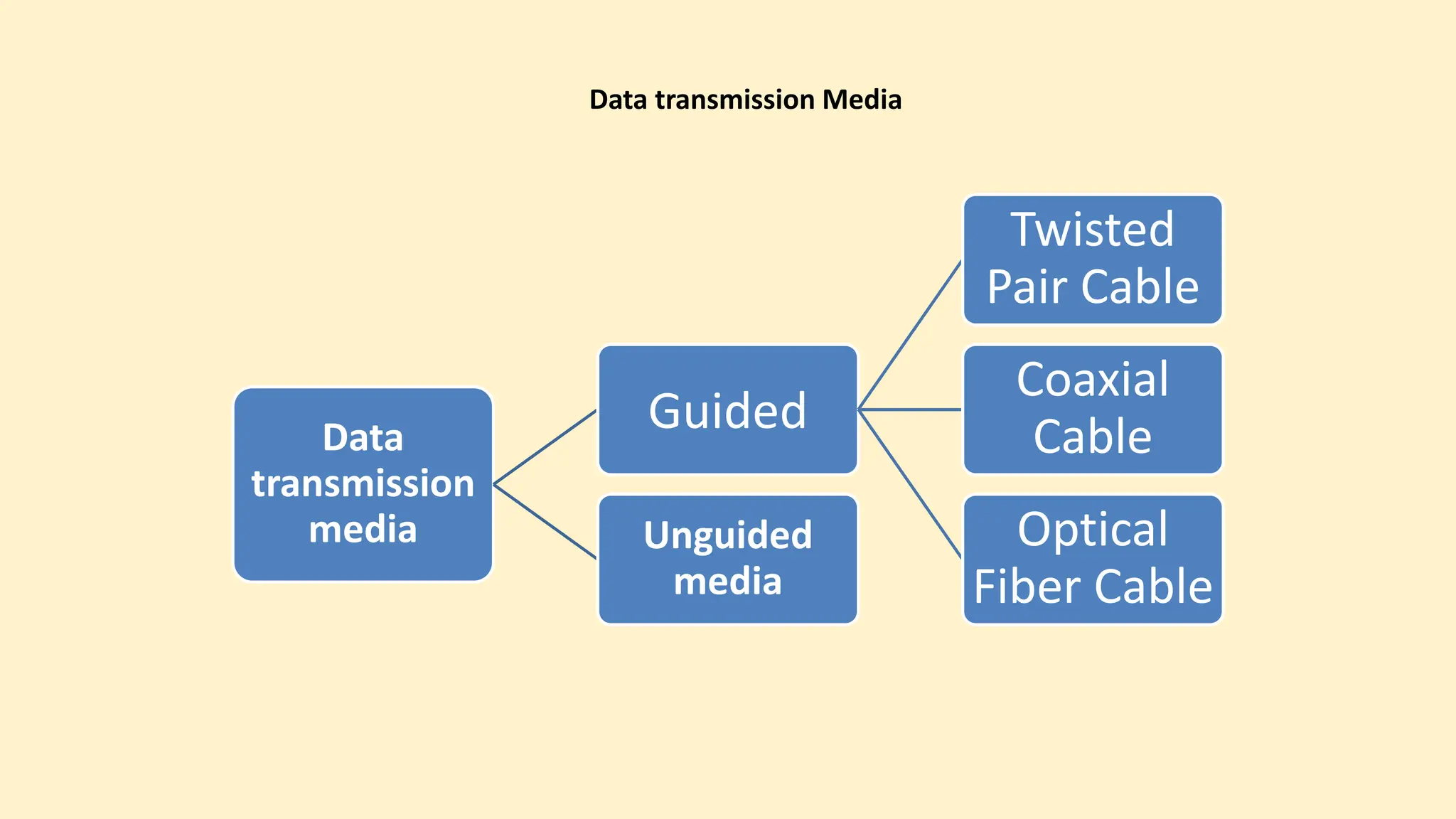
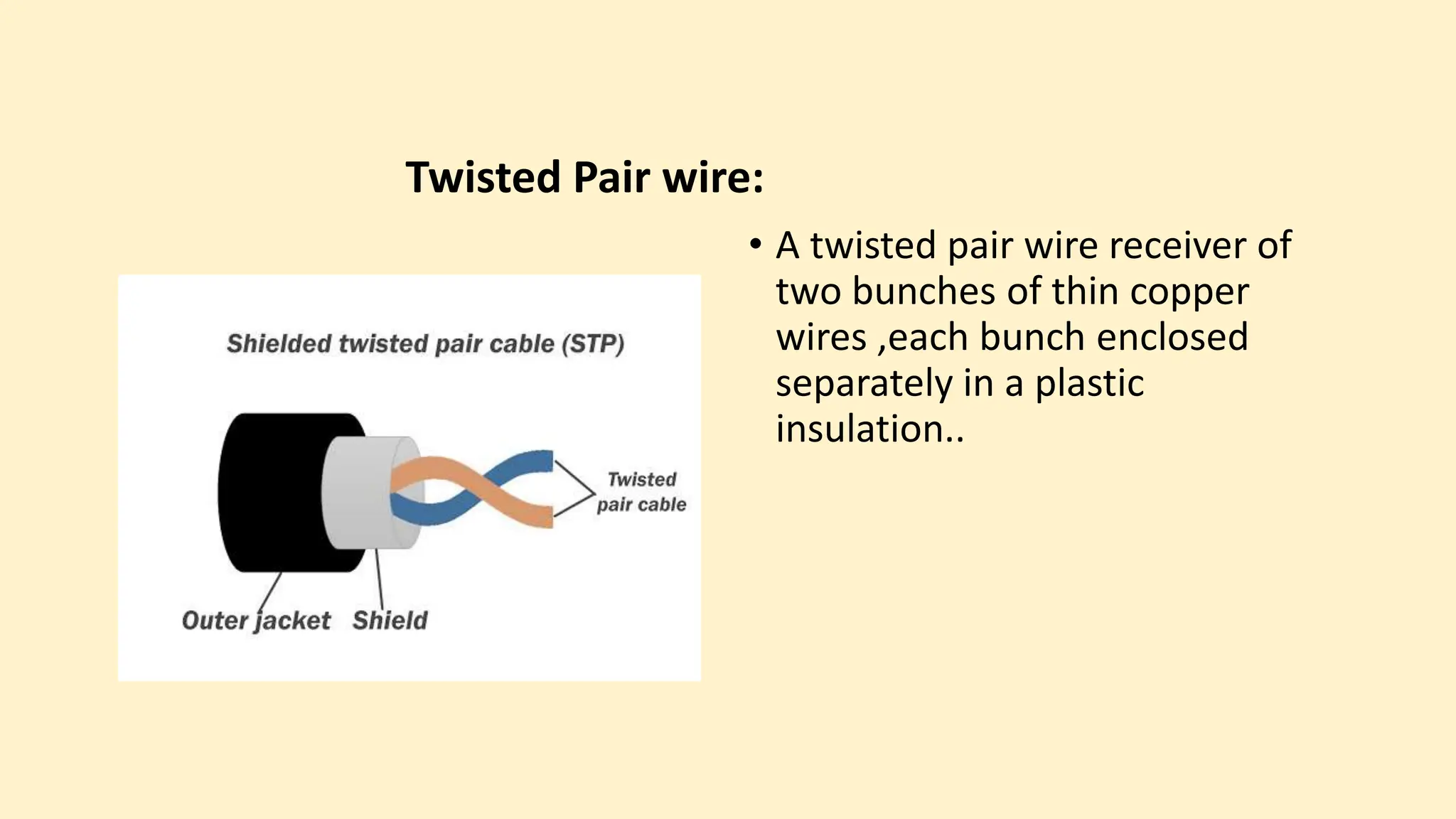
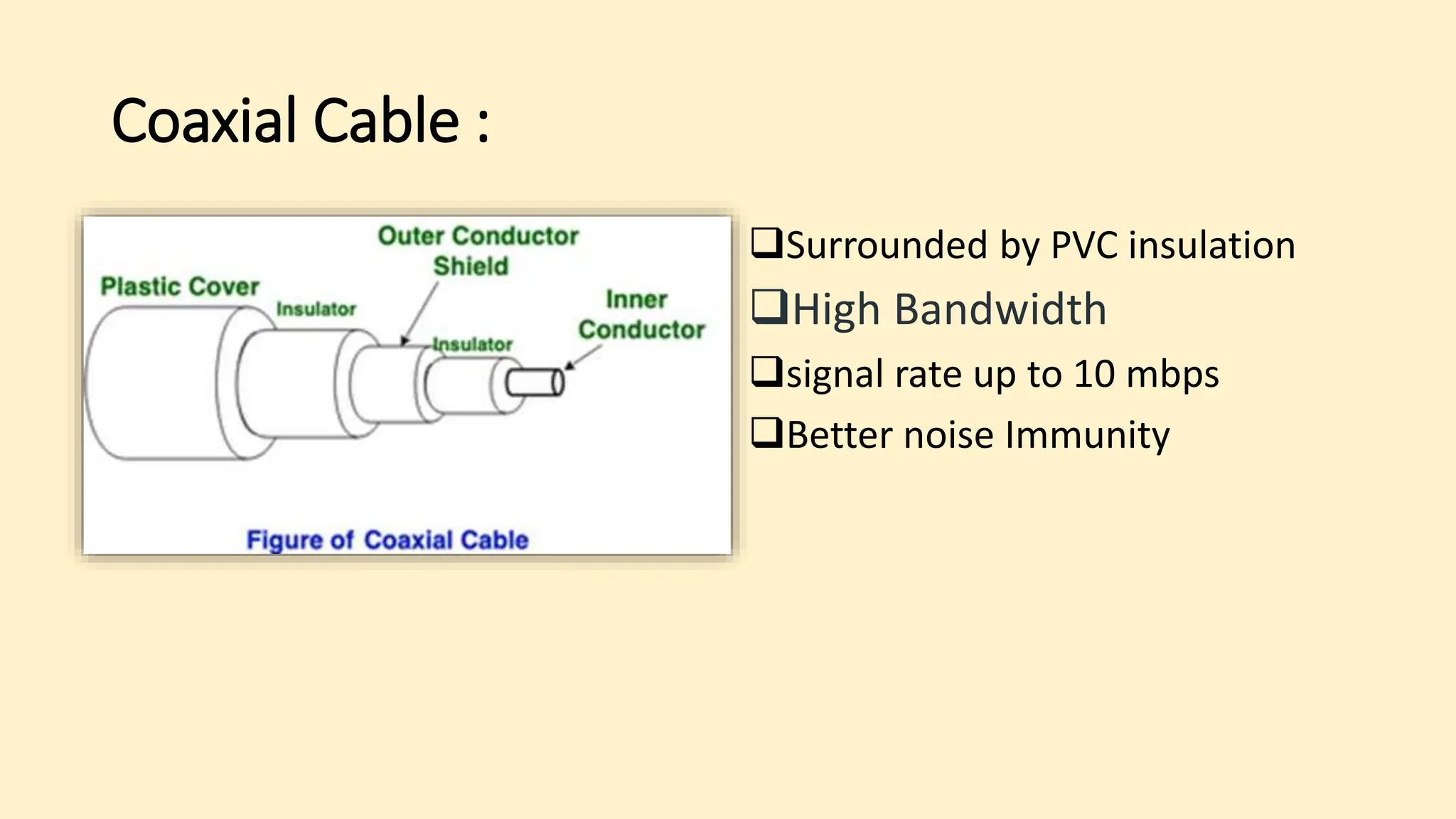
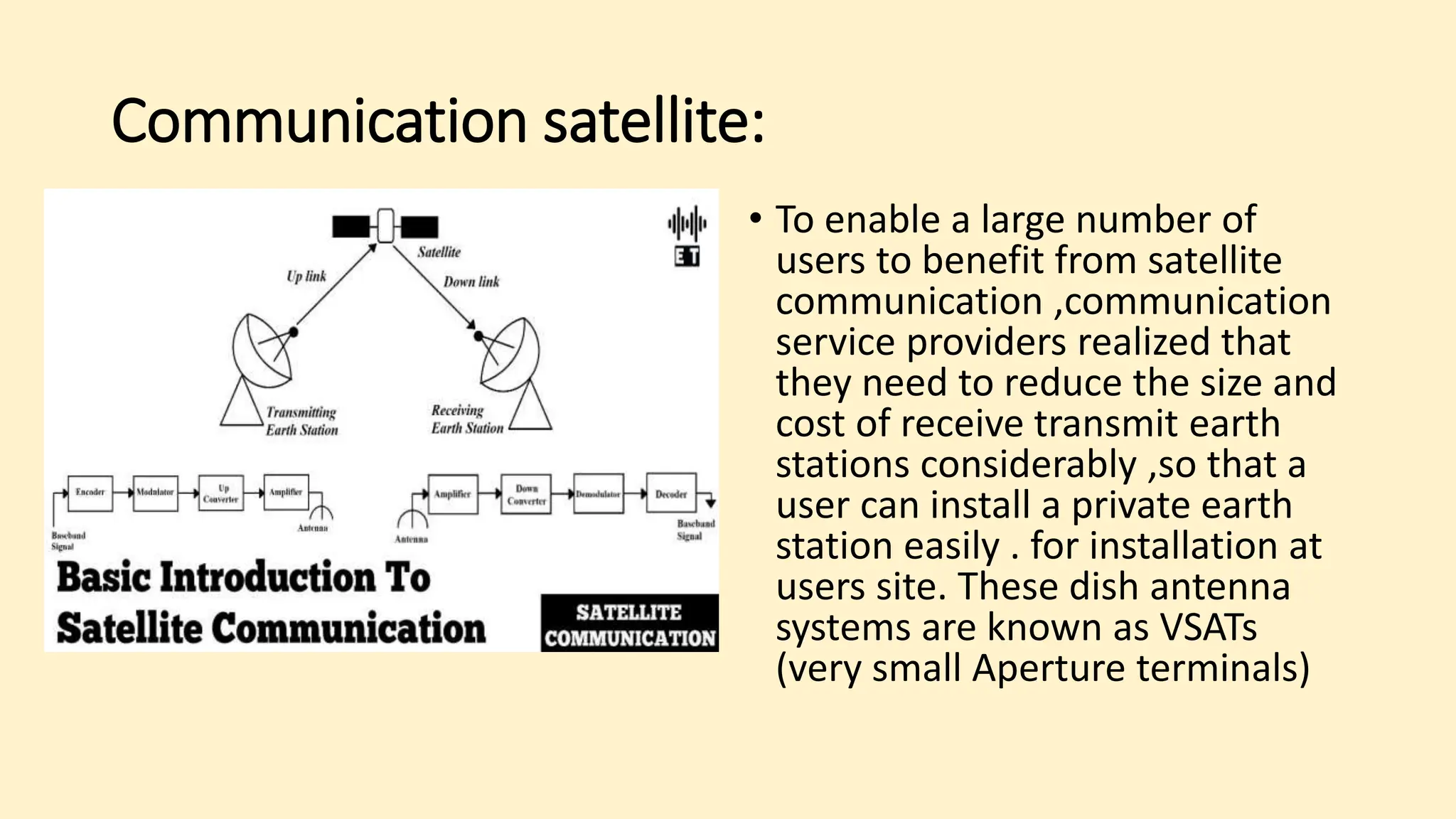
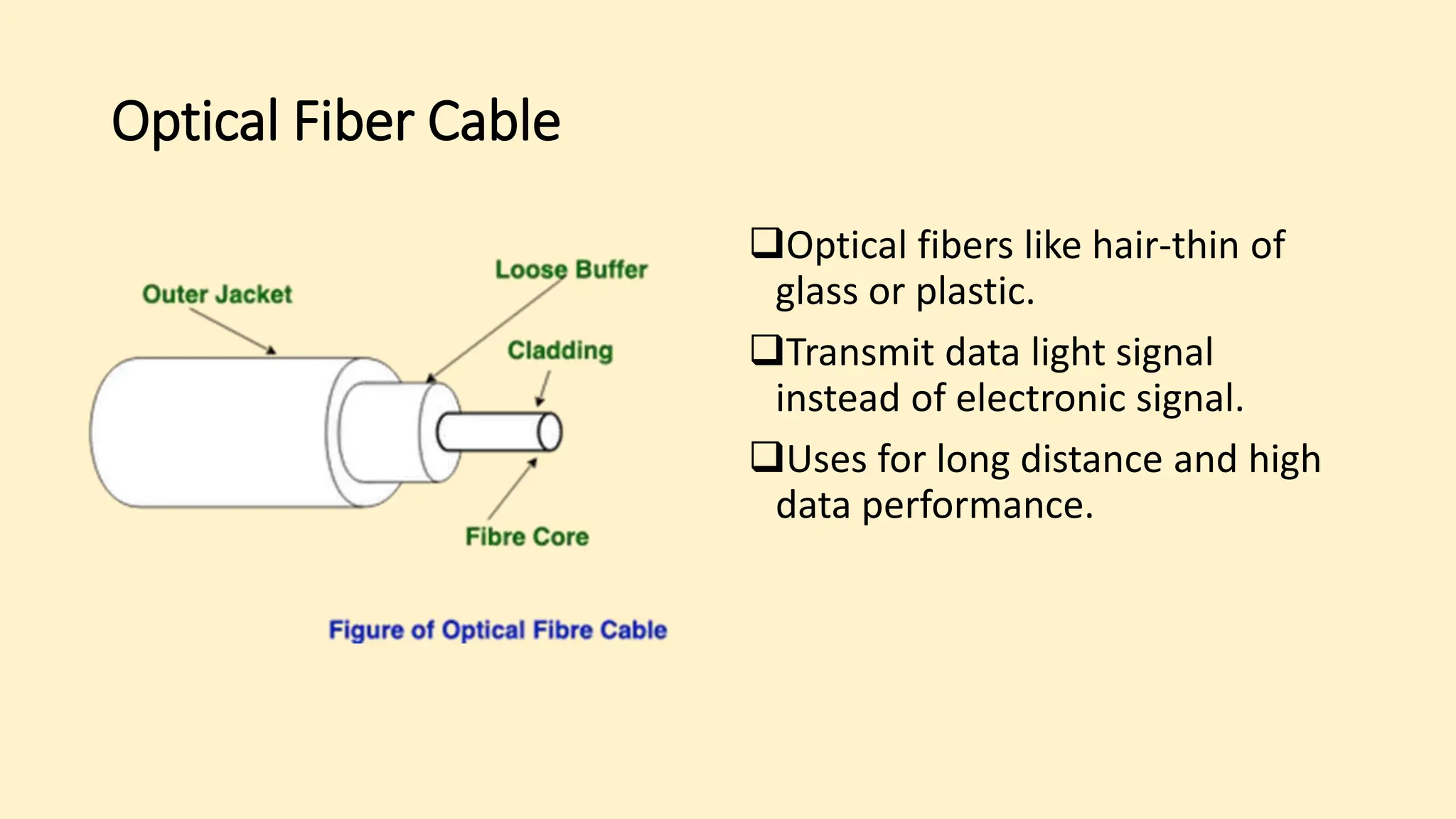
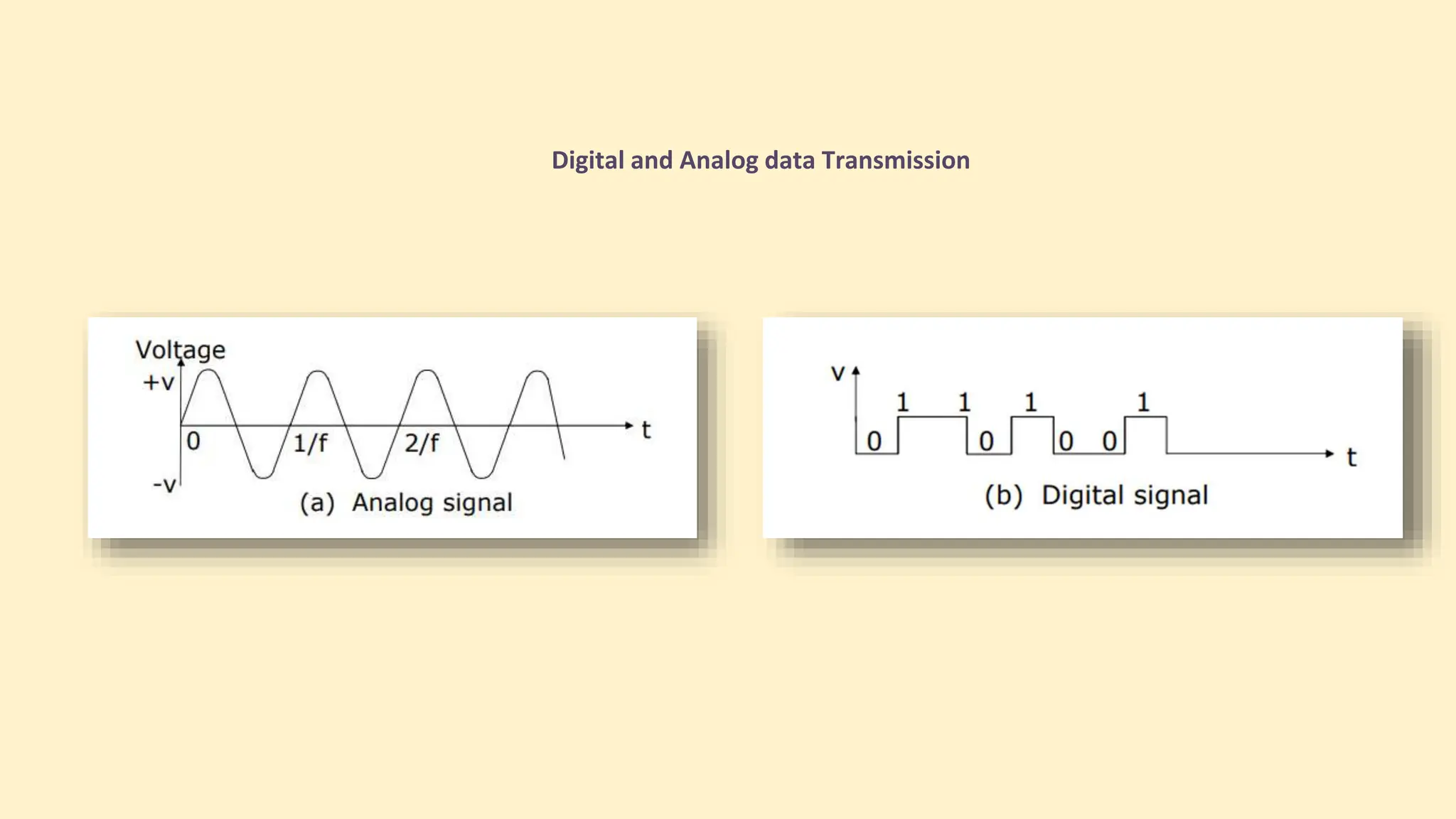
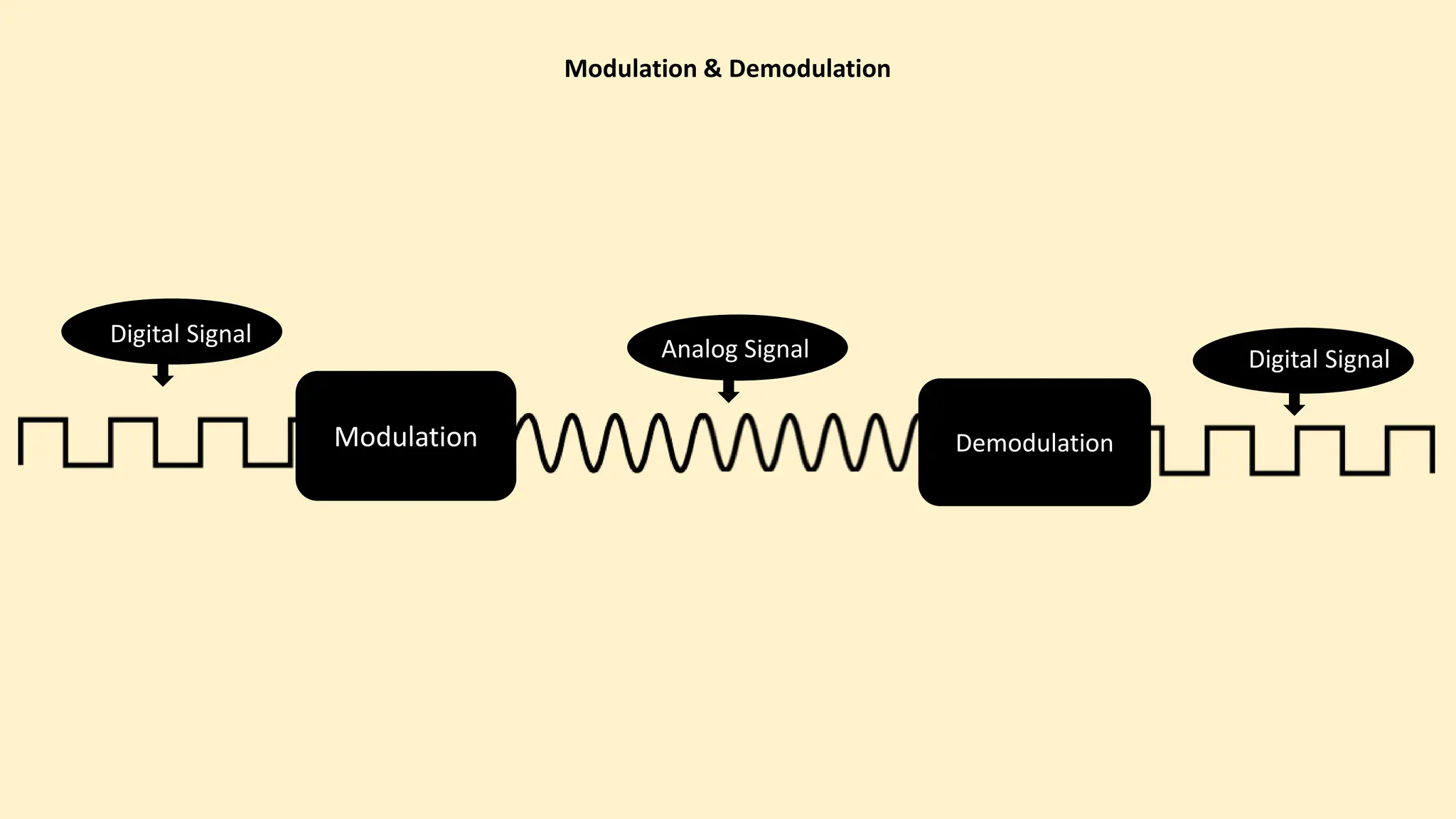
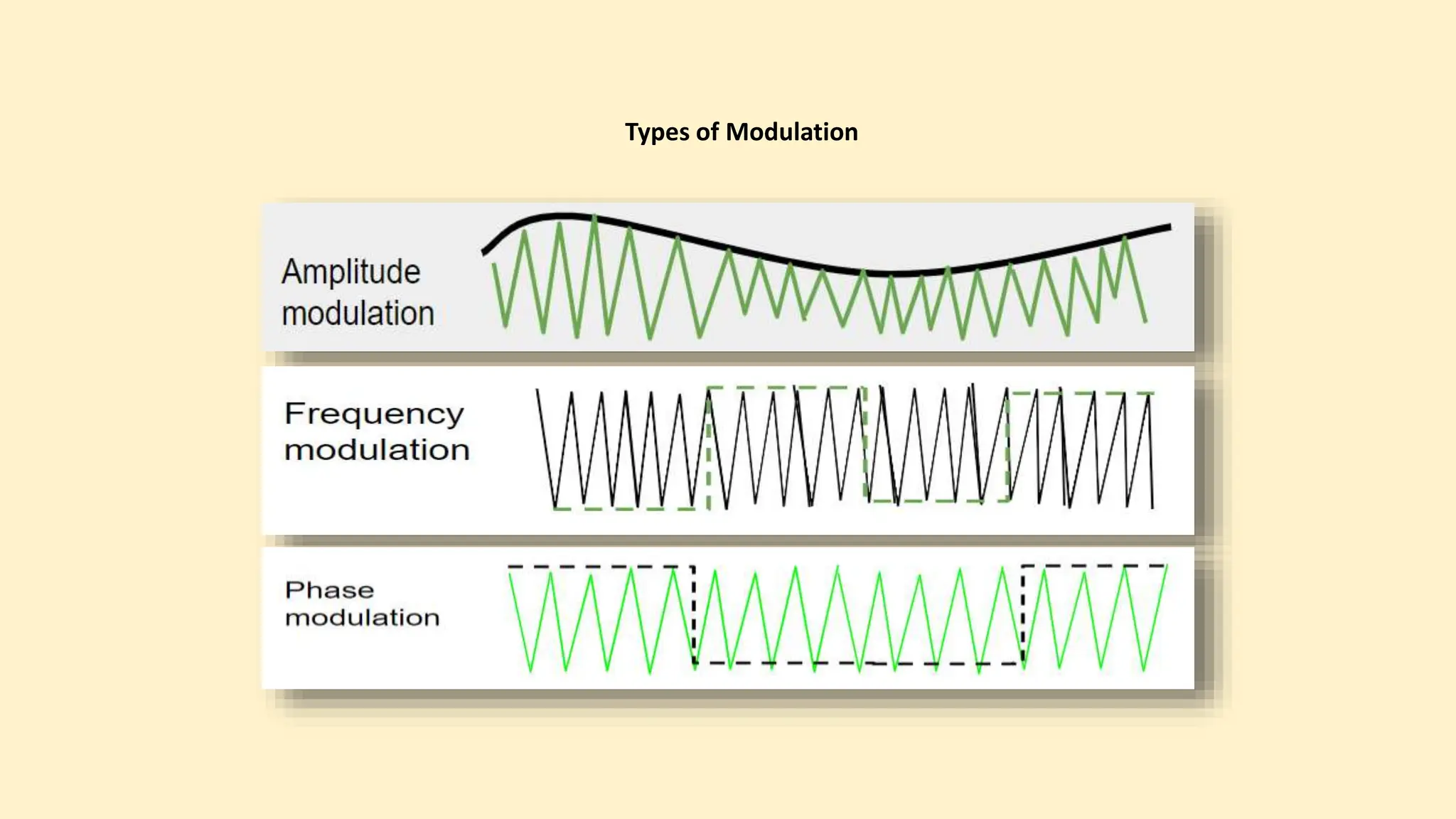
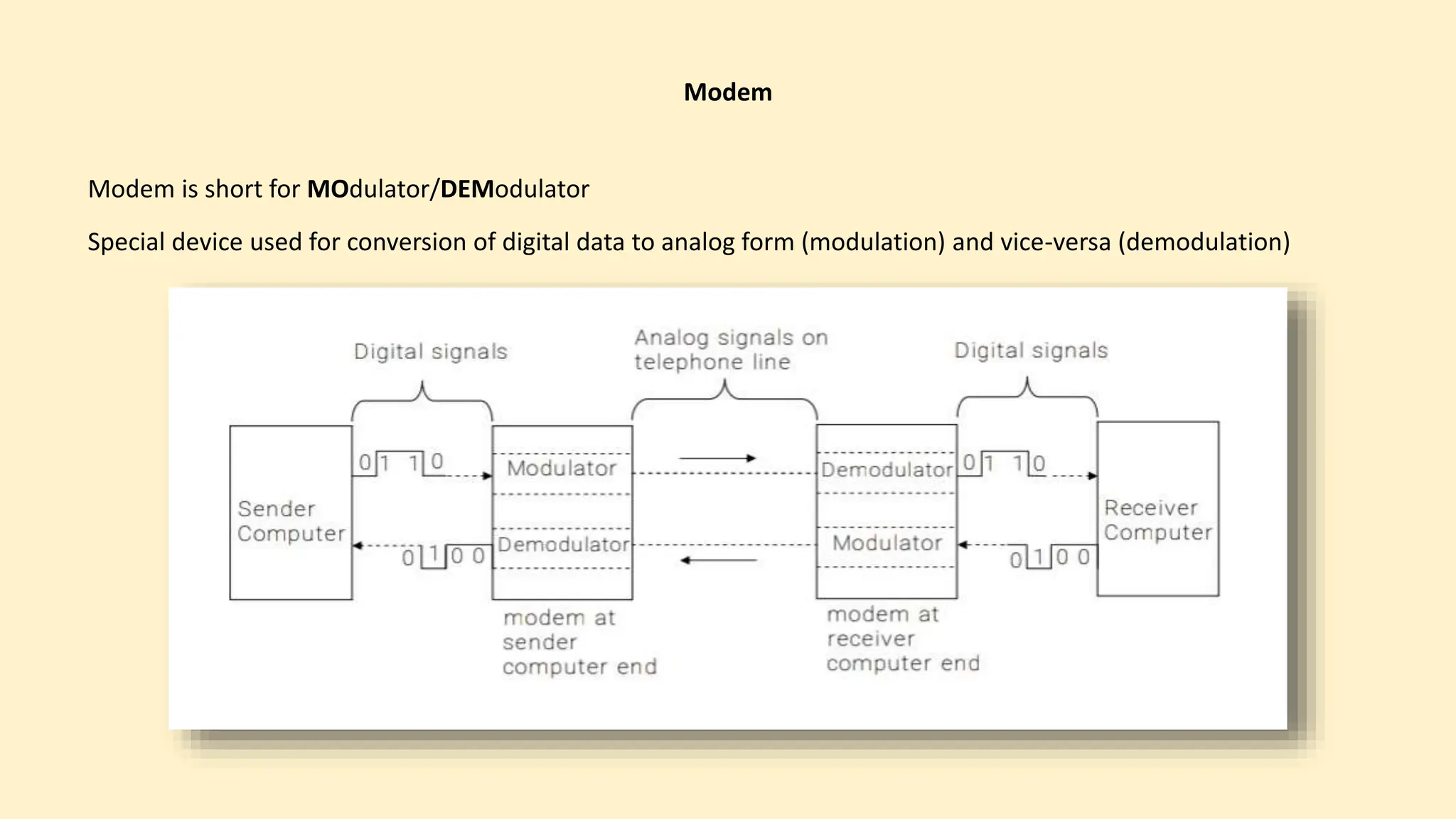
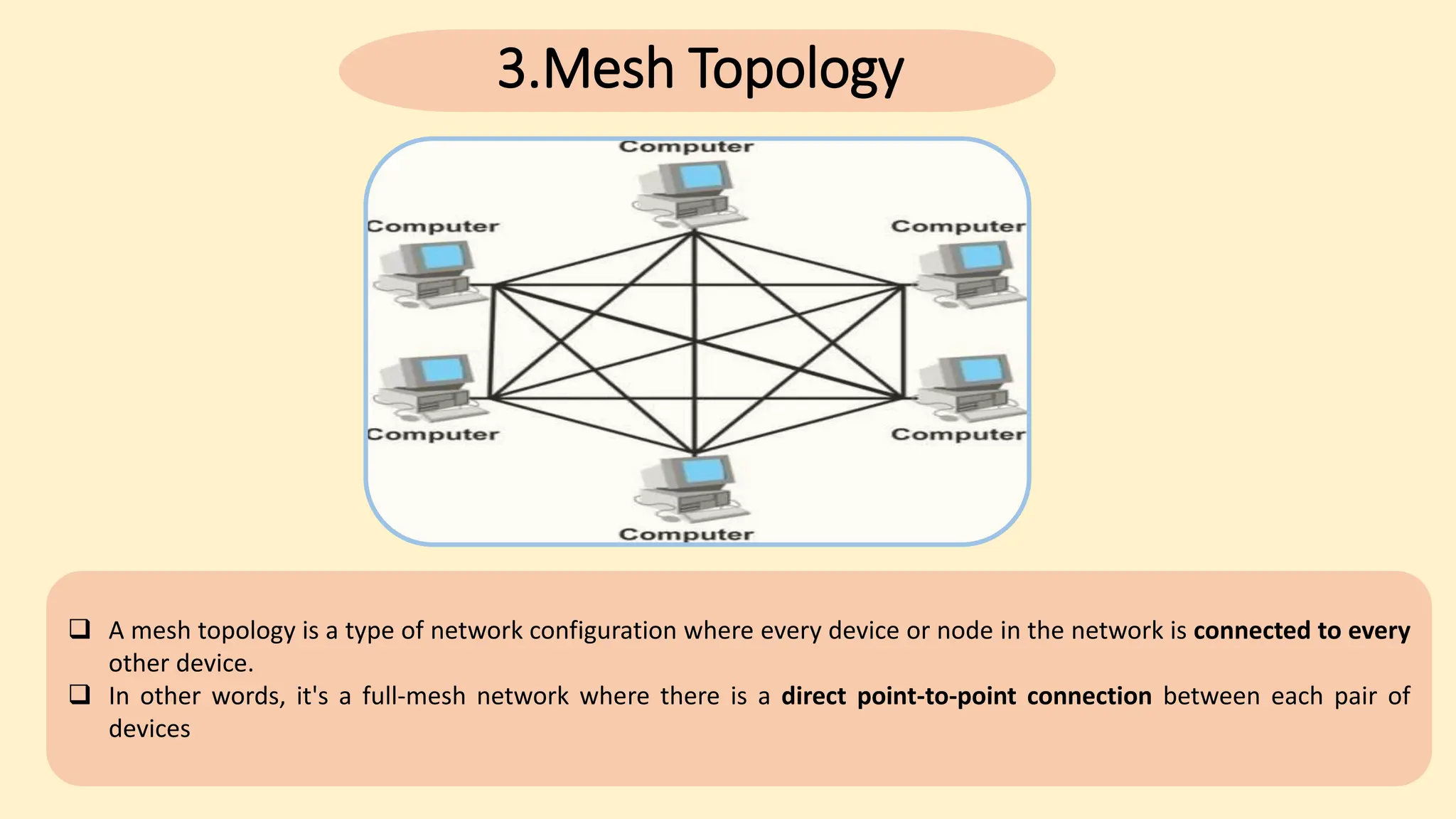
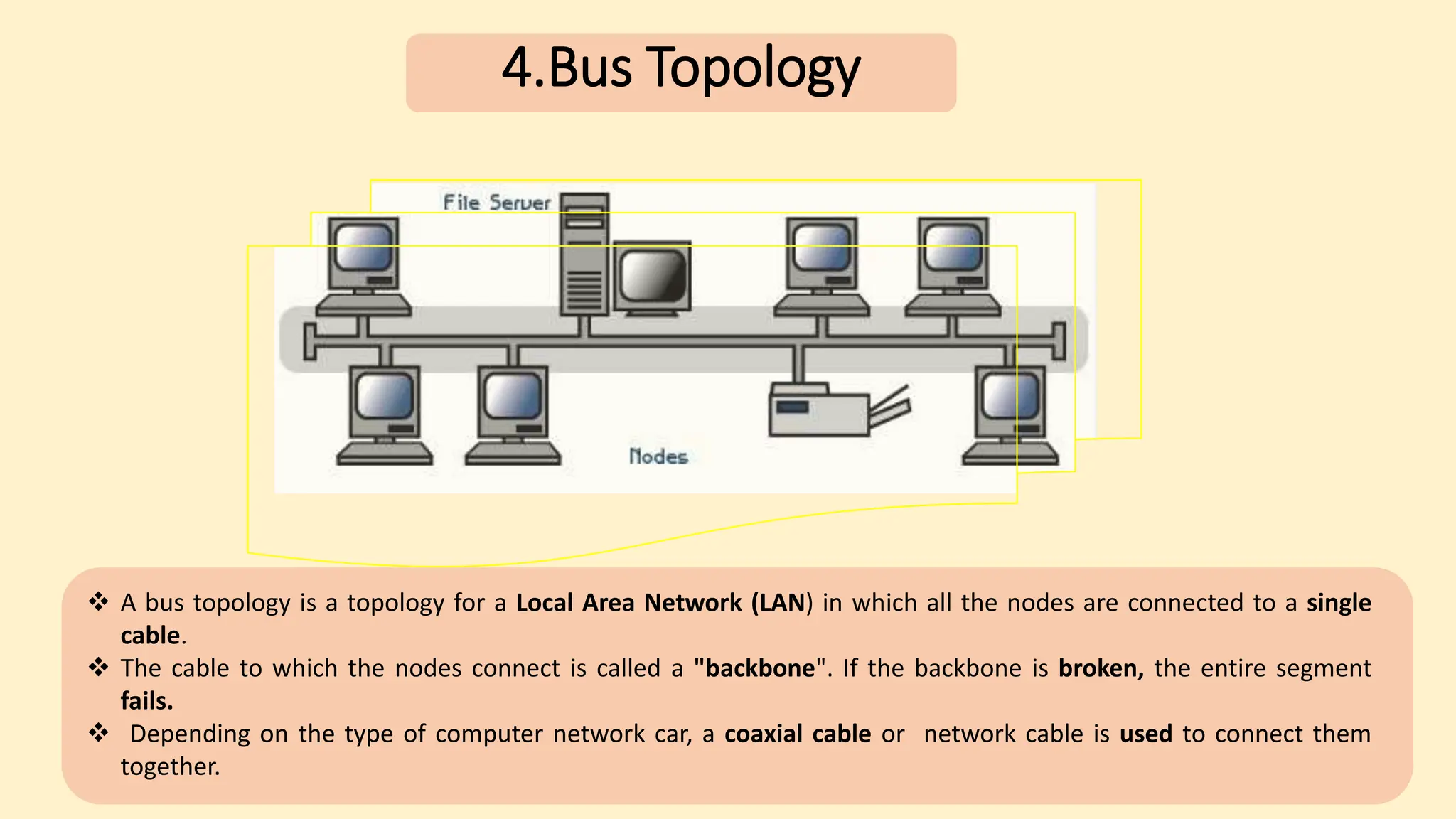
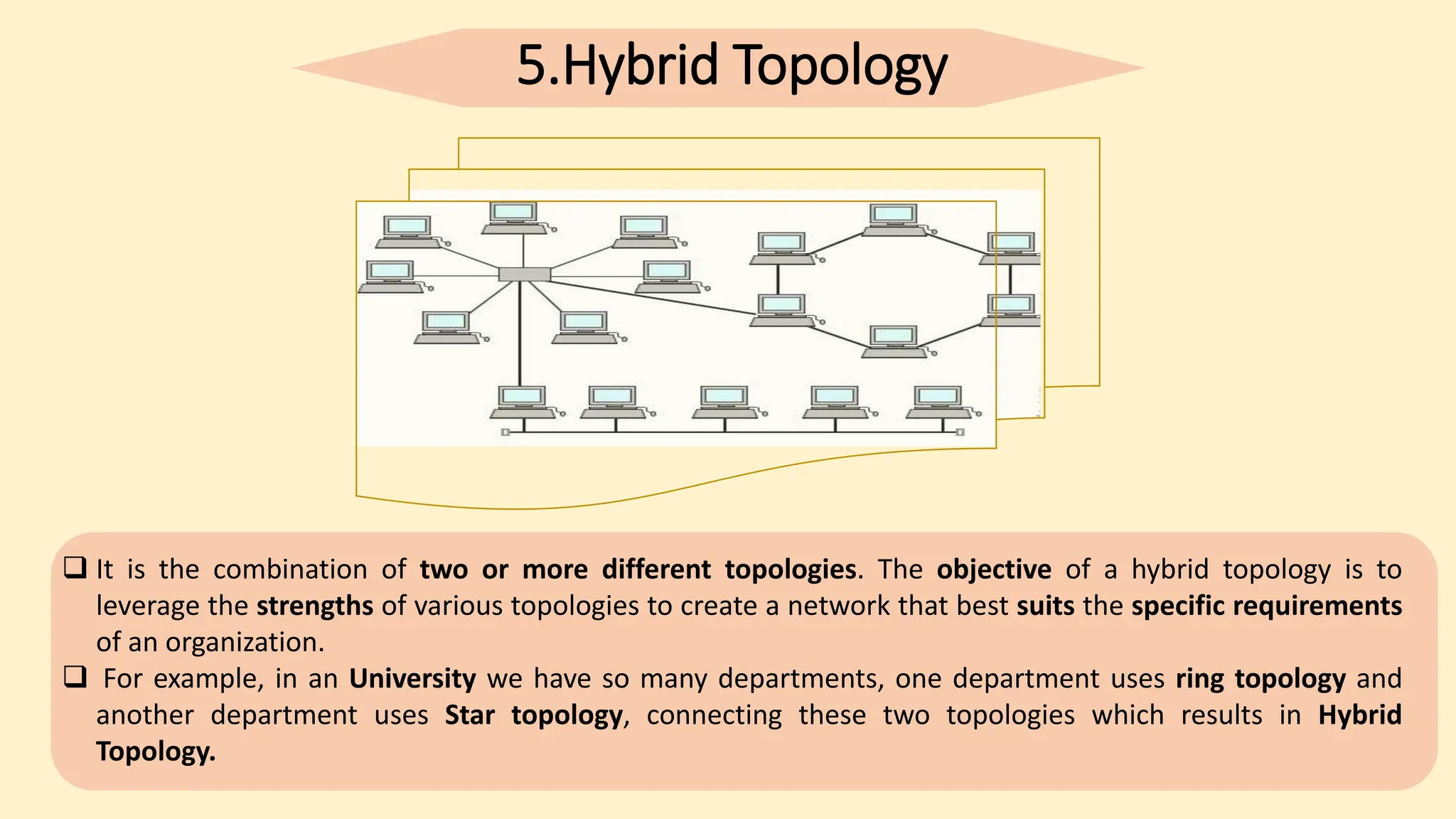
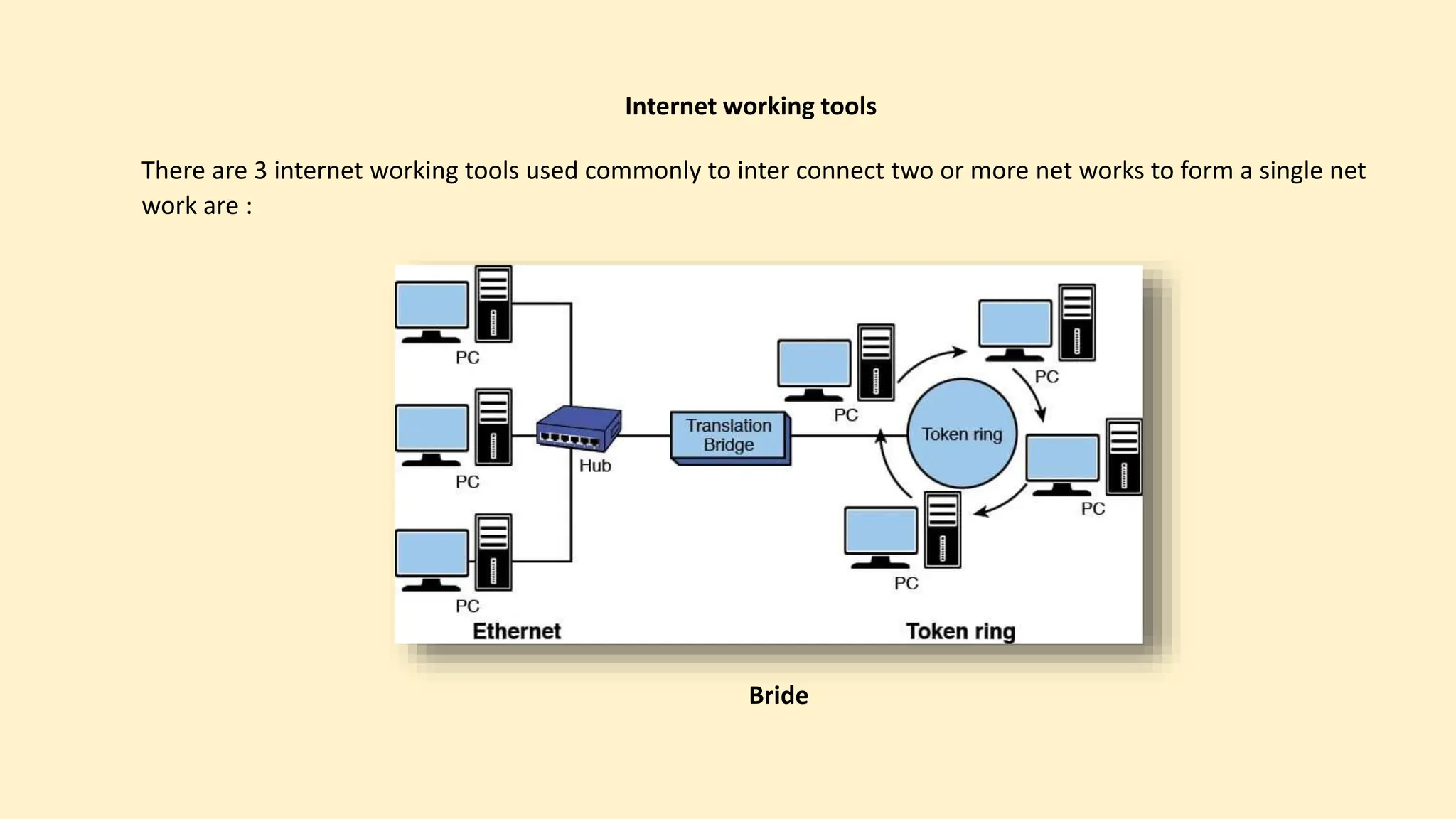
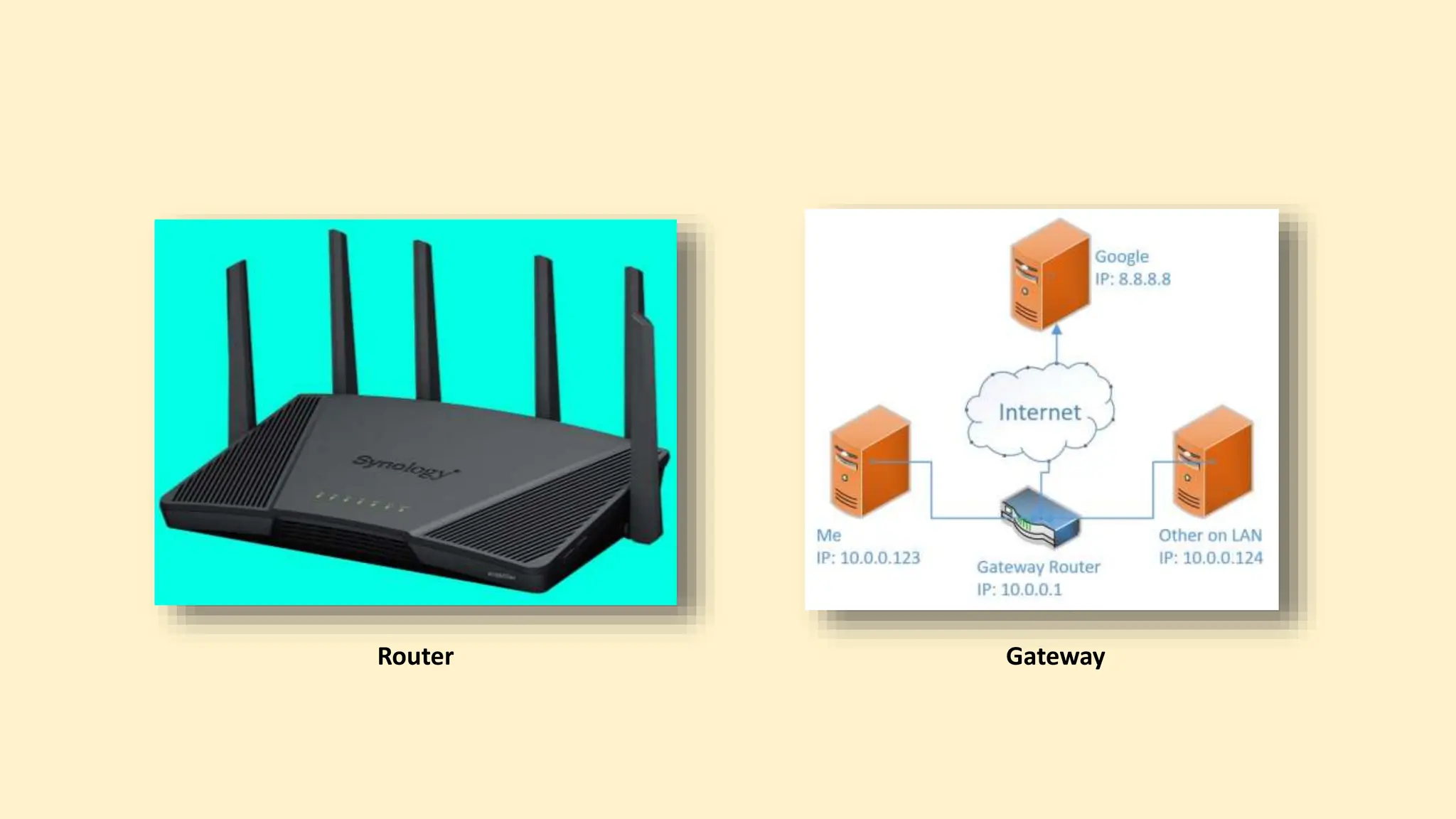
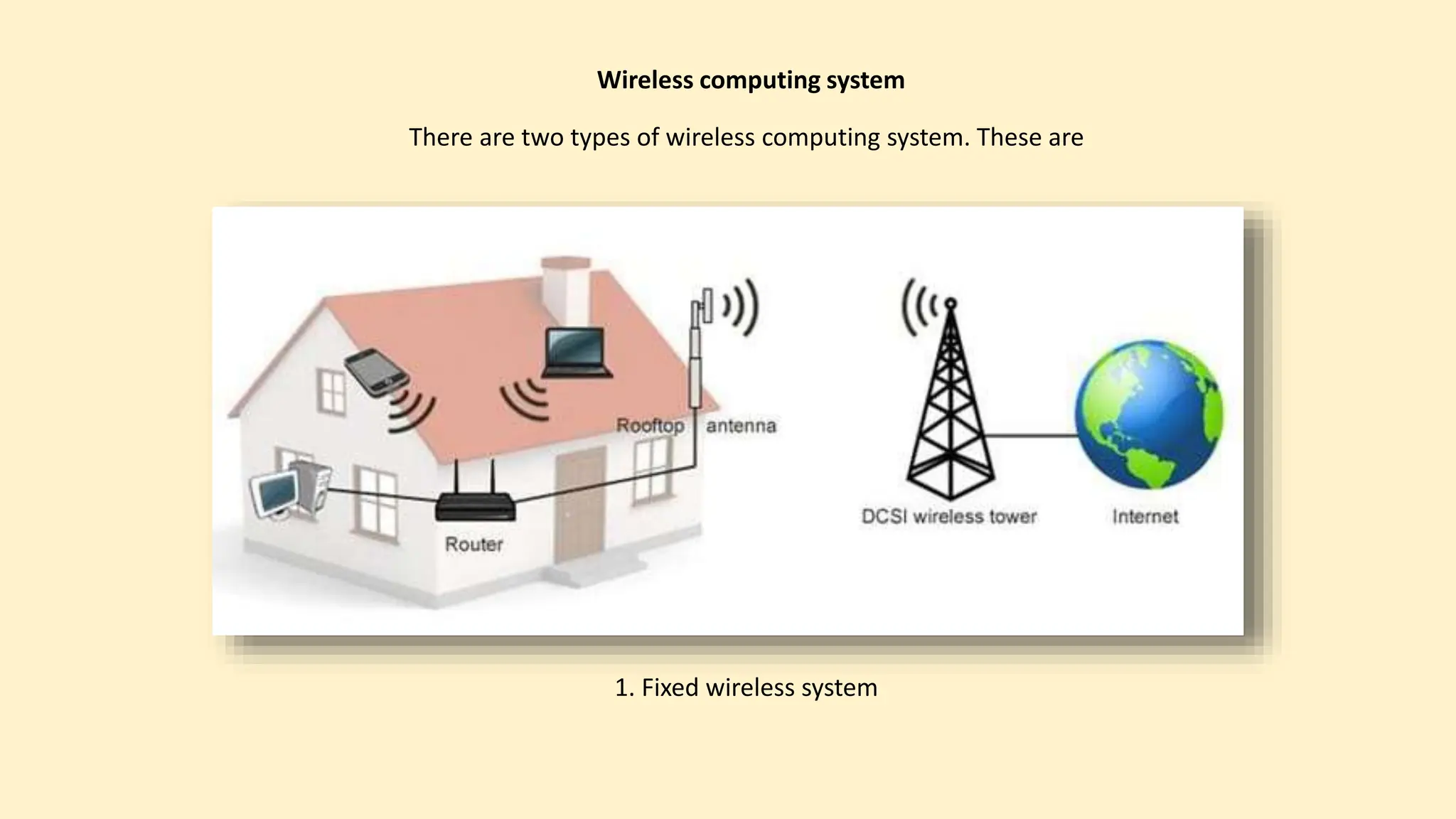
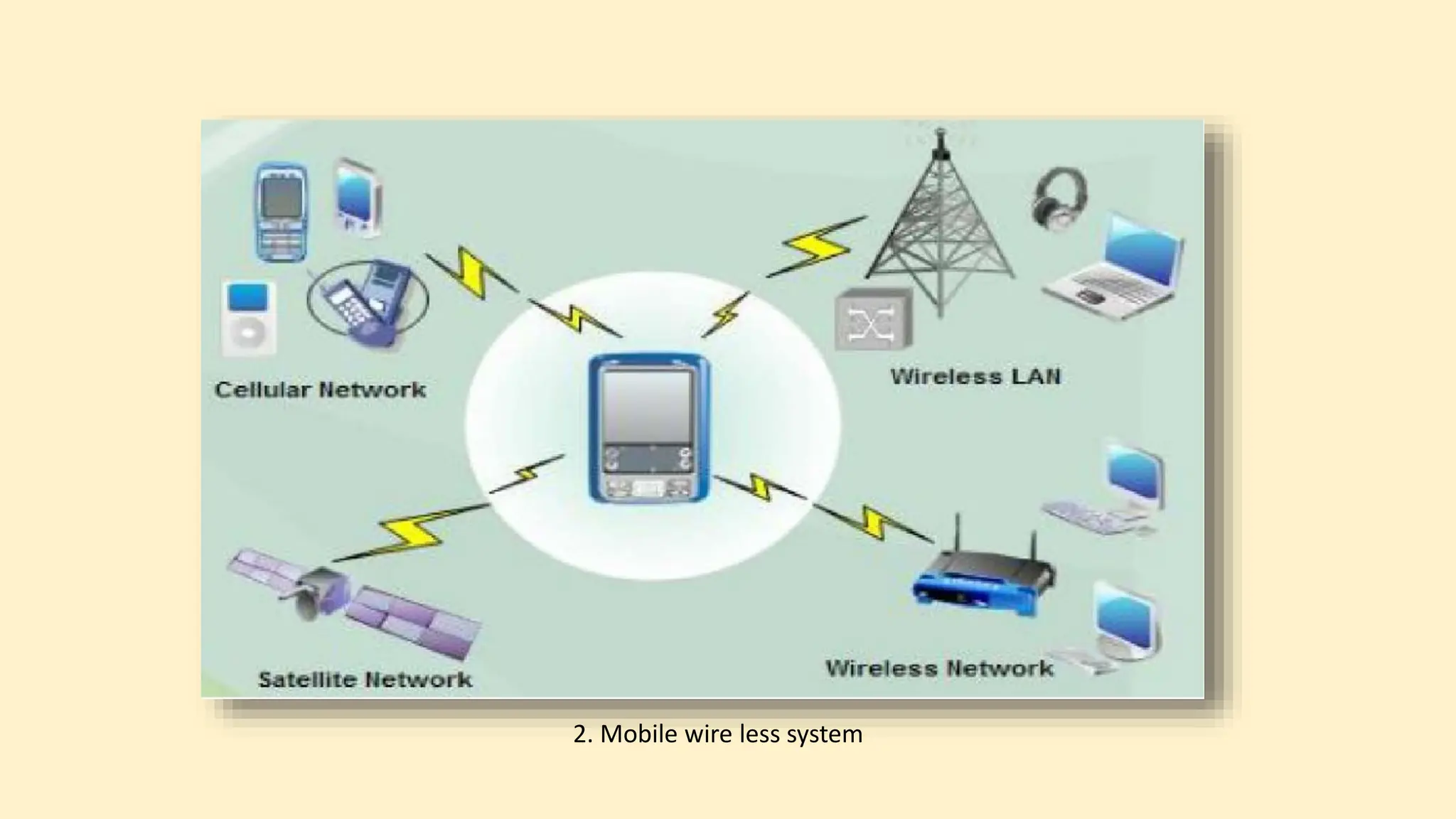
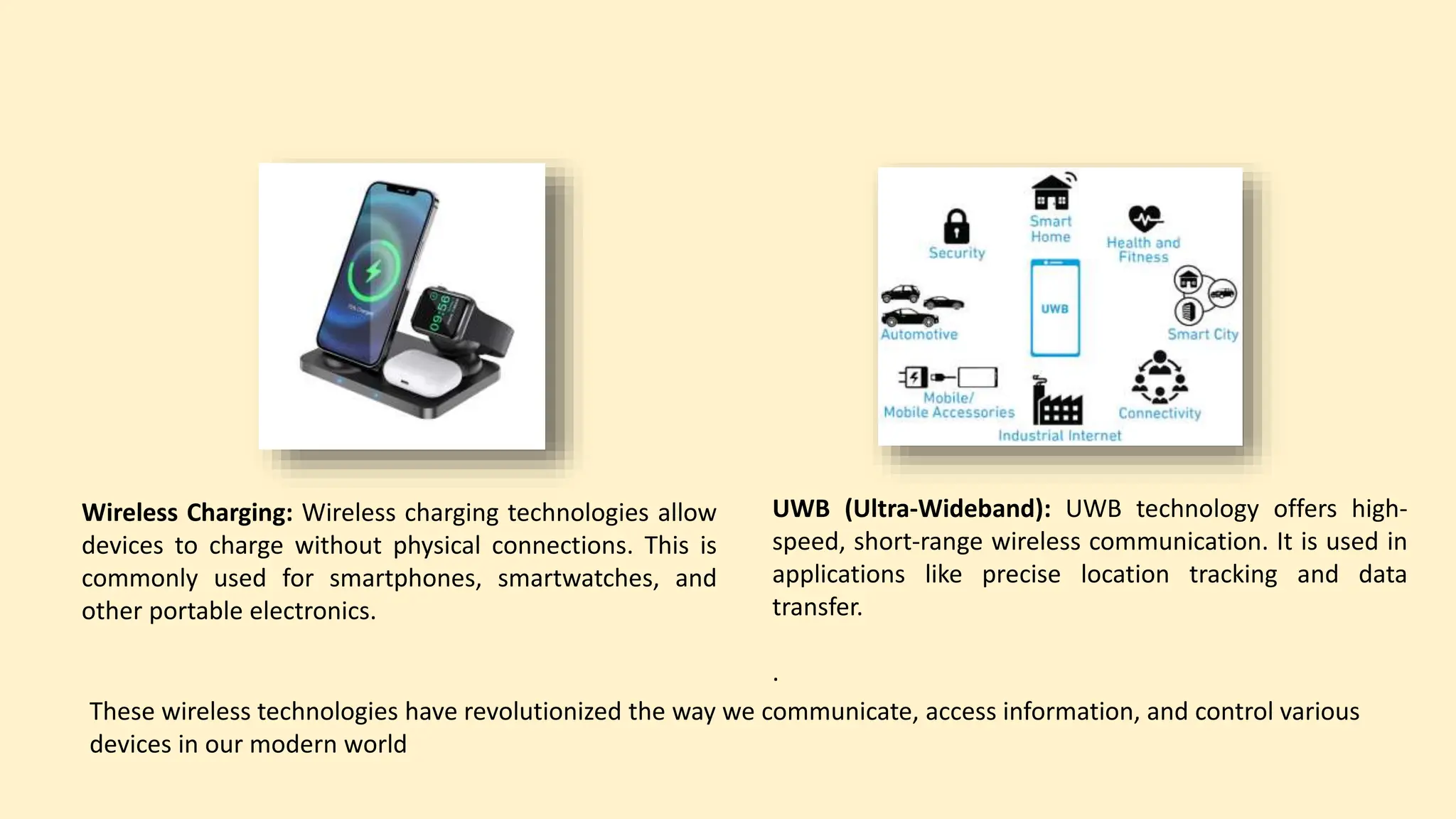
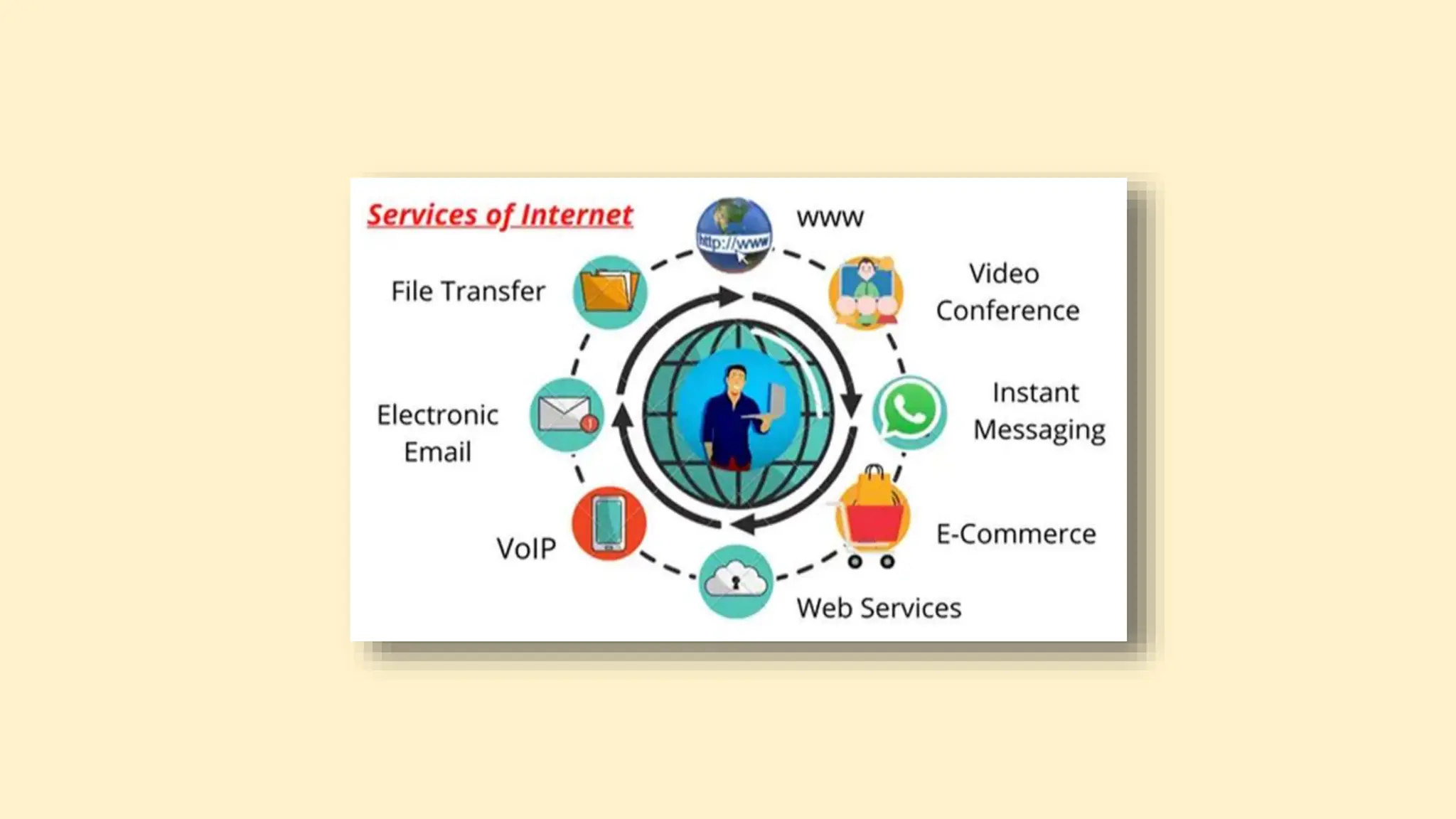
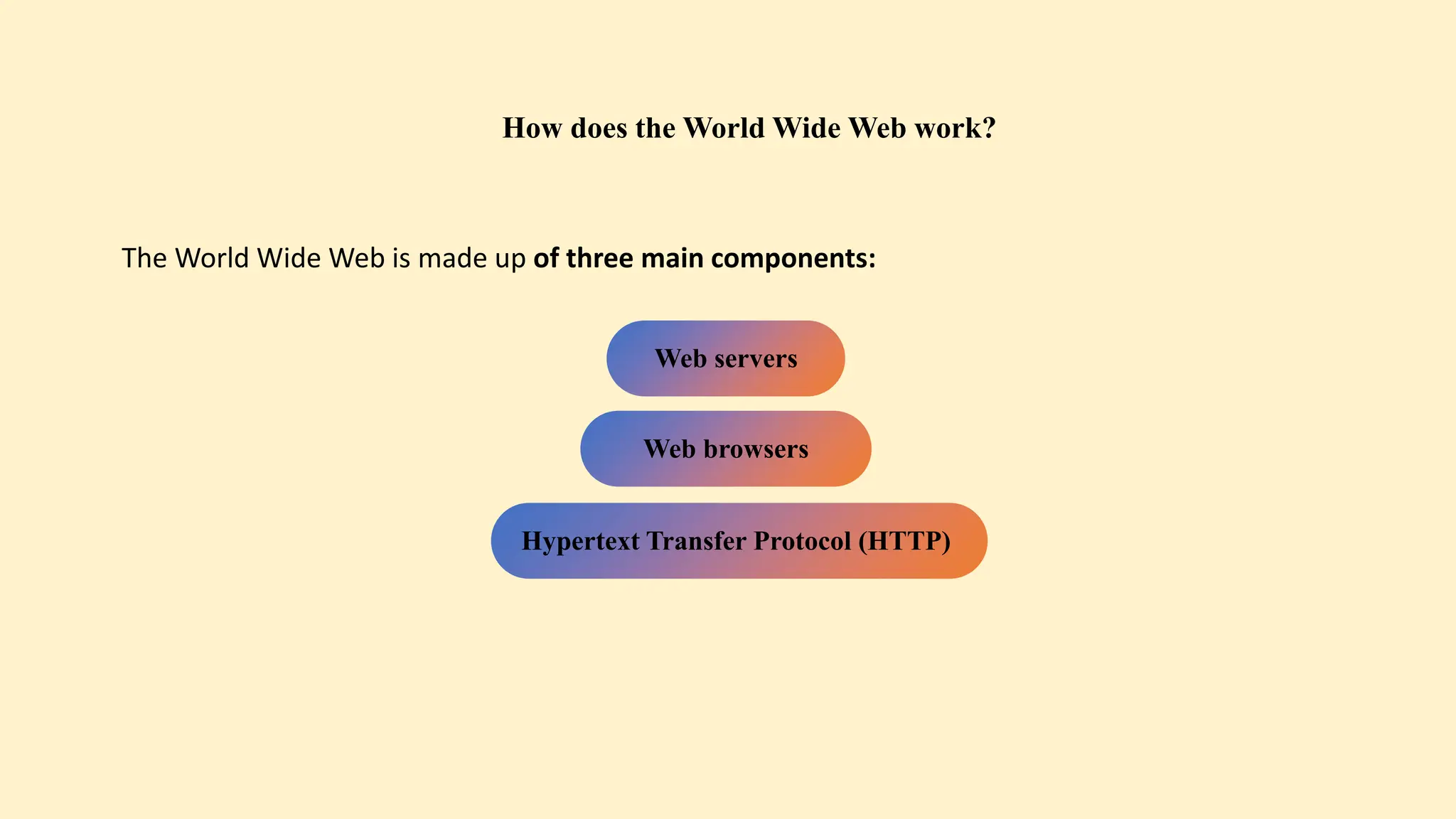
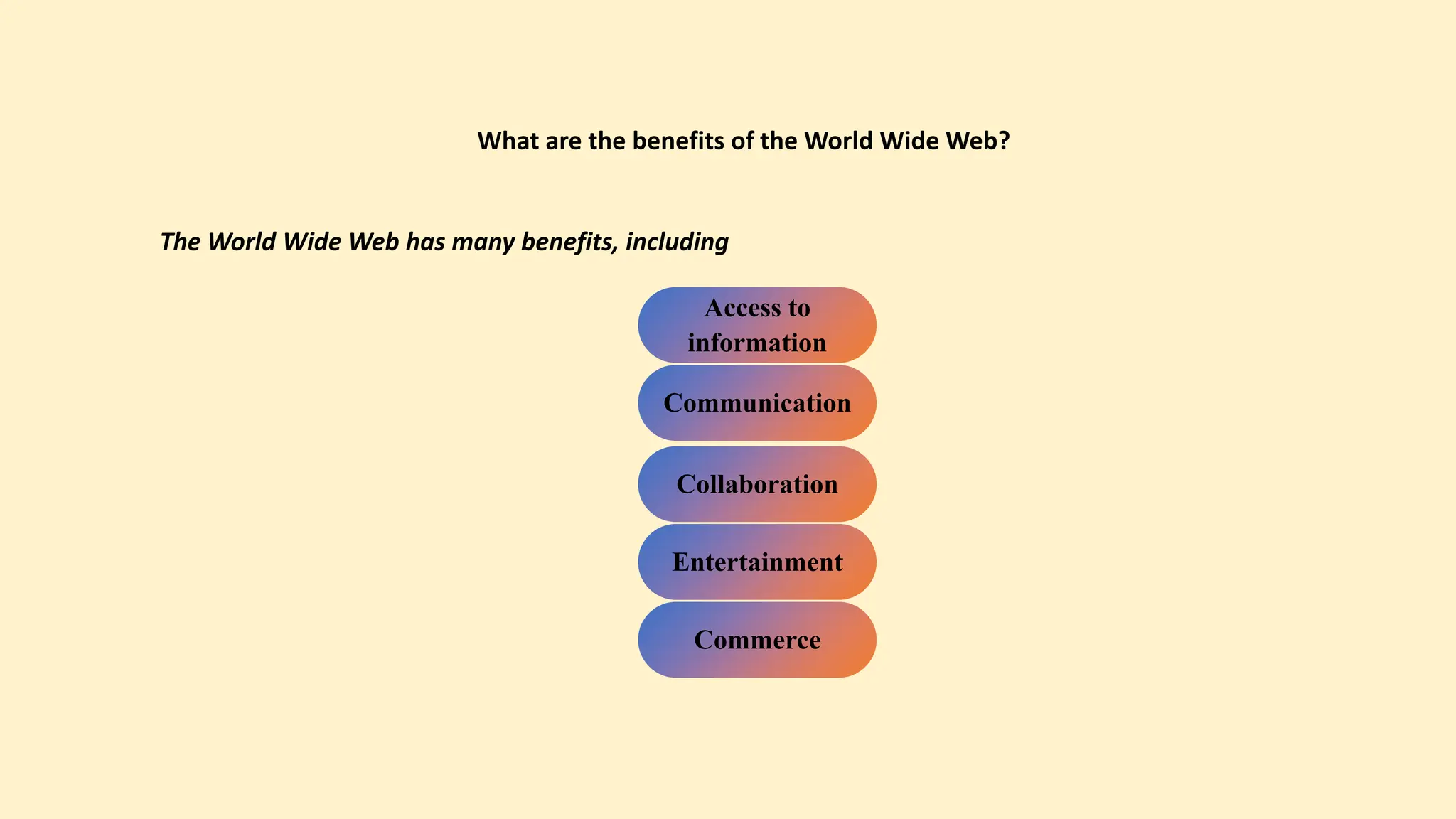
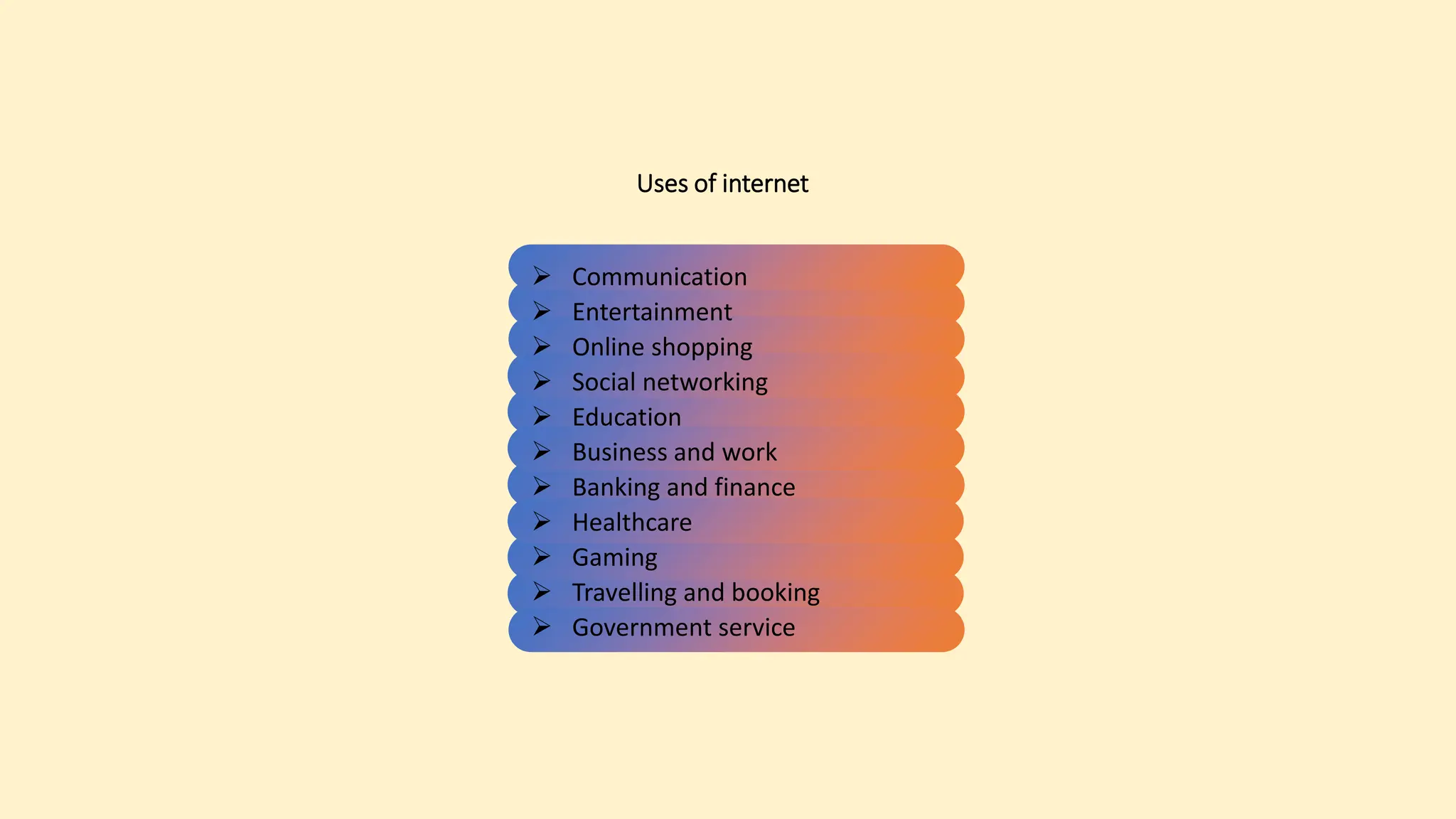
The document discusses various topics related to data communication and computer networks. It provides details about the group members working on the project. It then discusses basic elements of a communication system including a sender, medium, and receiver. It explains different data transmission models such as simplex, half-duplex, and full-duplex. It also discusses data transmission speed and different categories based on bandwidth. The document covers additional topics such as data transmission media, digital and analog transmission, network topologies, types of networks, roles of communication protocols, wireless technologies and issues, elements of internet search engines, and uses of the internet.