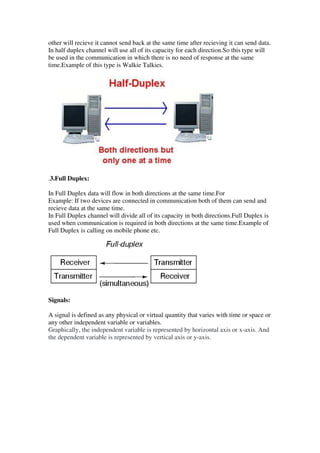
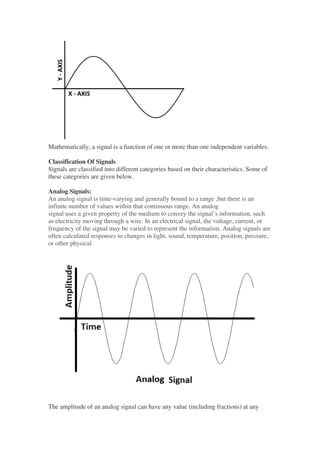
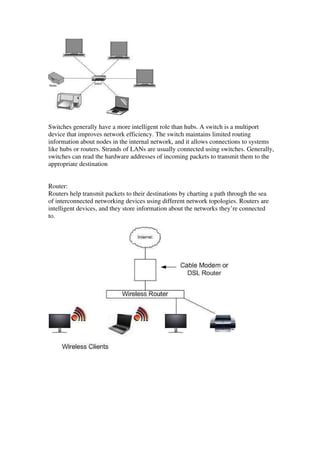
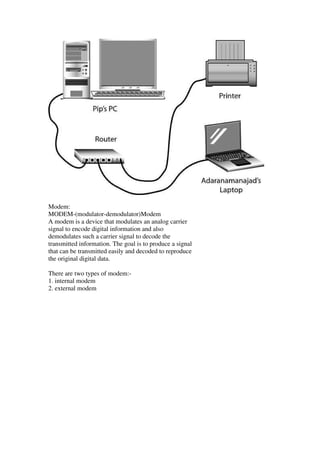
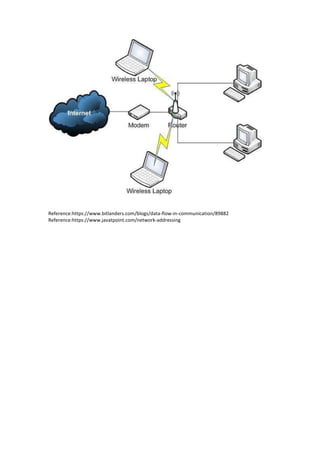
This document provides an overview of data communication, including the different types of data flow (simplex, half duplex, and full duplex), network addressing, and network devices. It defines simplex as one-way data flow, half duplex as two-way data flow but not simultaneously, and full duplex as two-way simultaneous data flow. The document also discusses analog and digital signals, classful IP addressing, the internet vs intranet, types of computer networks (LAN, MAN, WAN), and common network devices like hubs and switches.