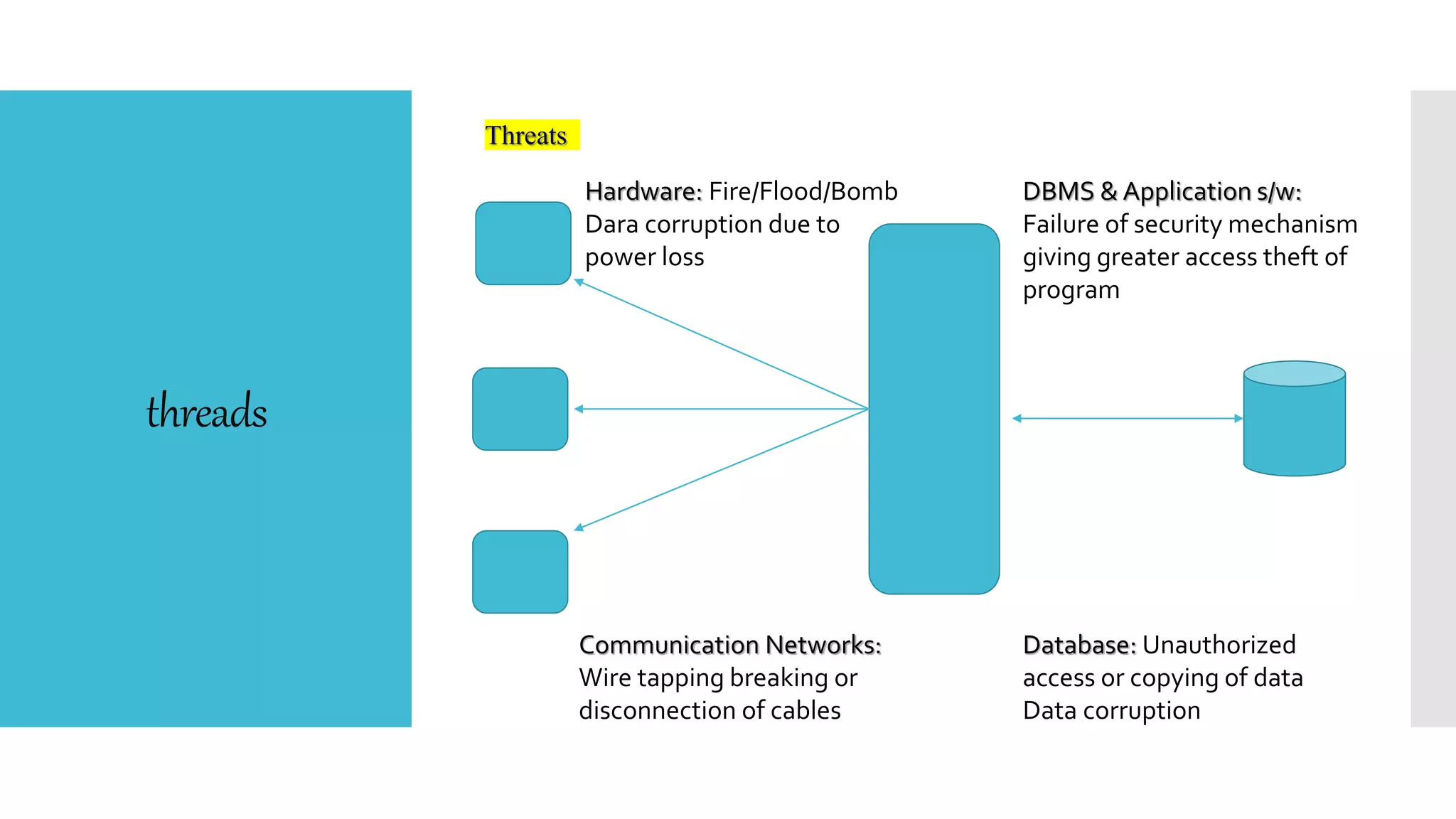
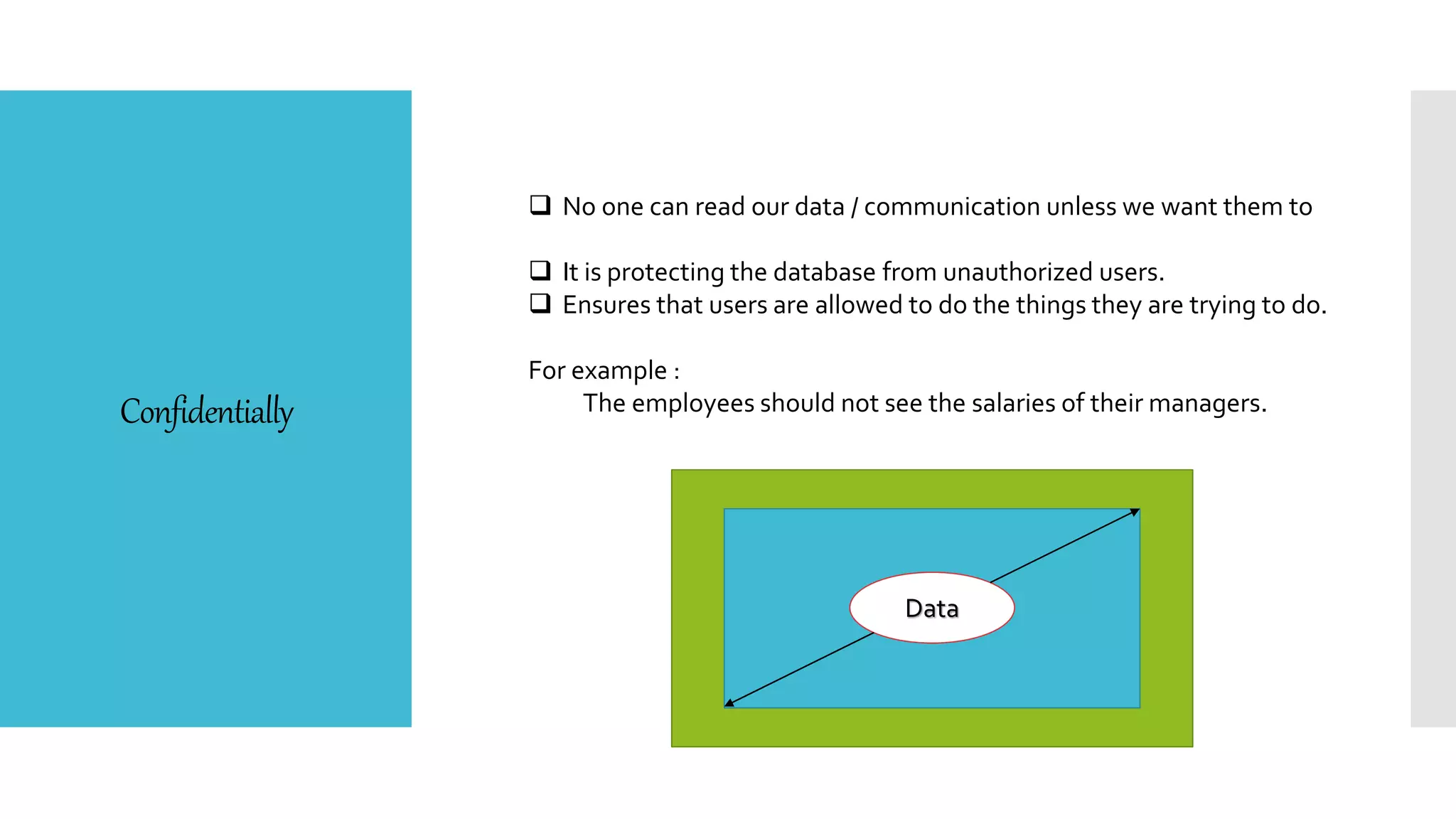
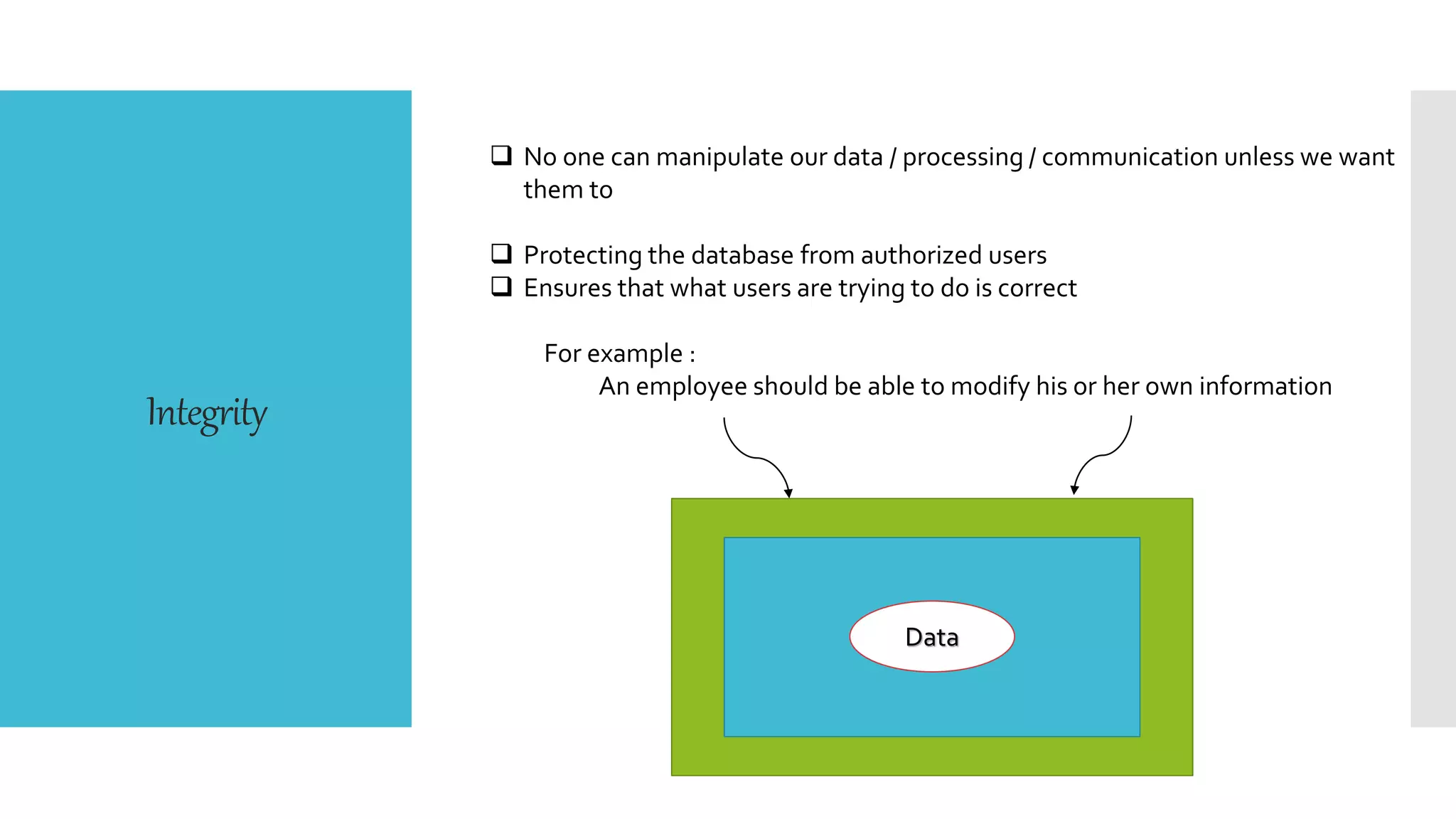
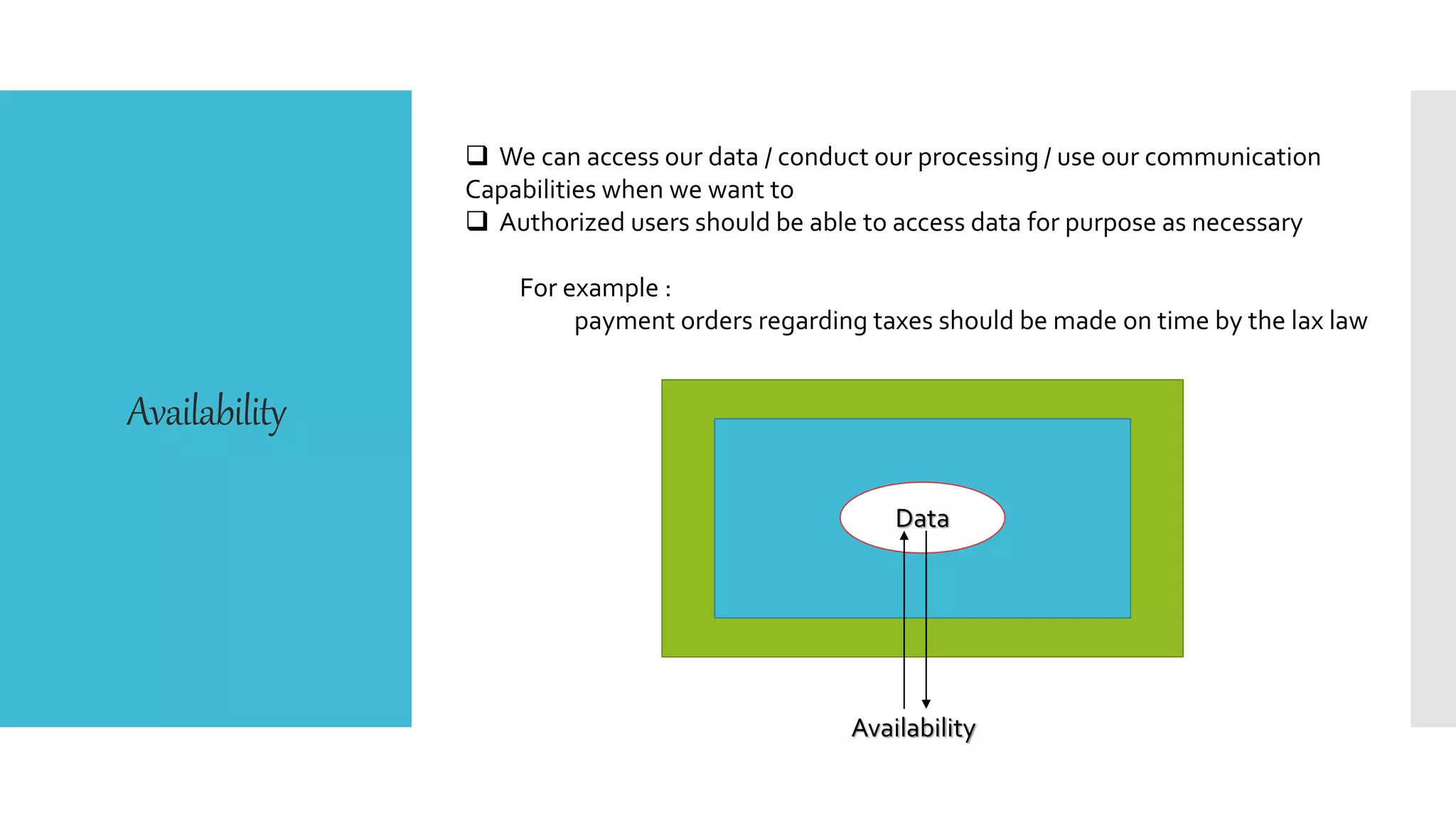
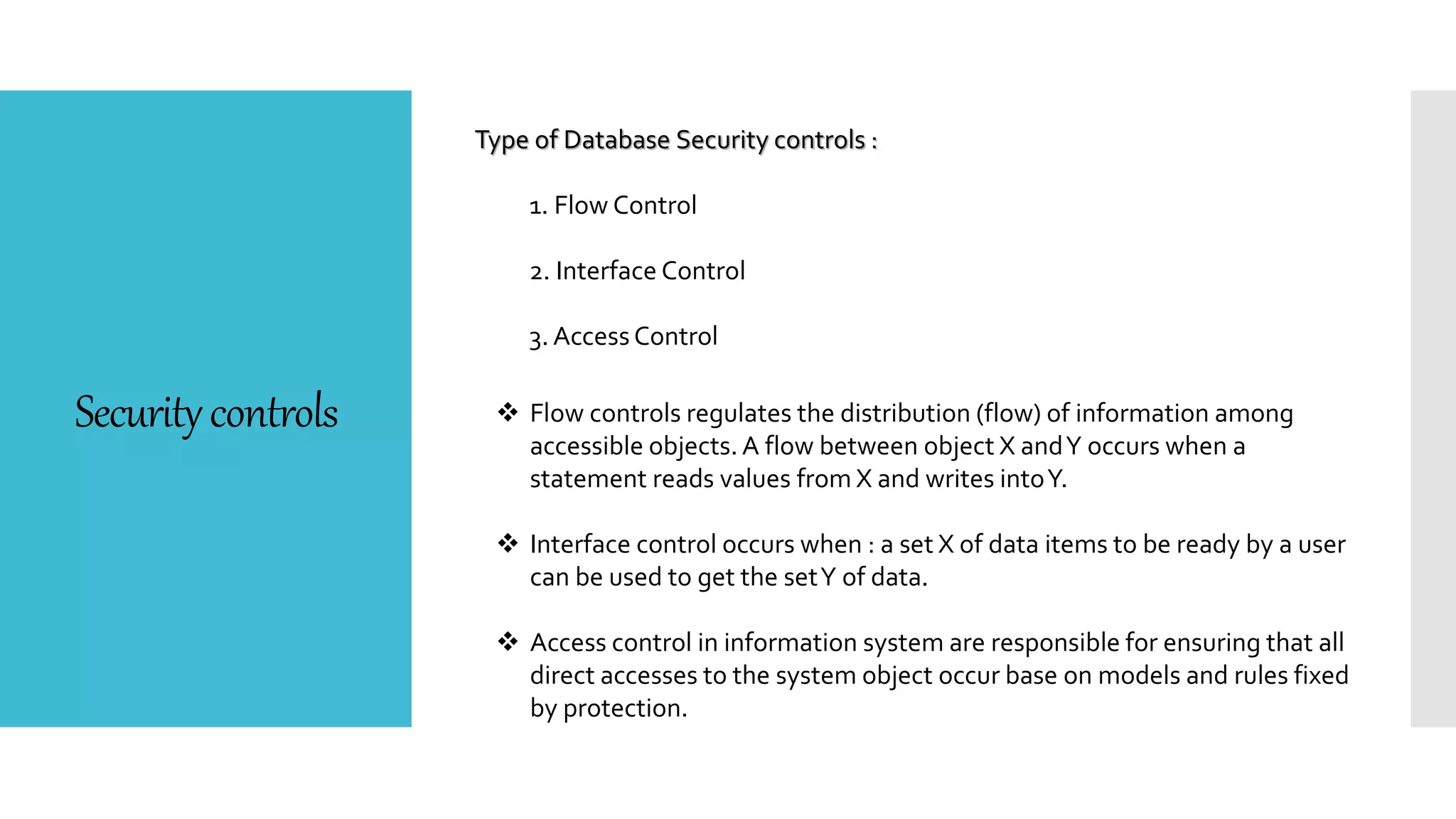
This document discusses database security. It defines database security and outlines some common security risks to databases like banks. It describes threats to databases from hardware failures, software bugs, and network issues. It explains the concepts of confidentiality, integrity, and availability in database security. It also outlines some common methods to secure databases like authorization, encryption, and authentication. Finally, it discusses different types of database security controls like flow control, interface control, and access control.