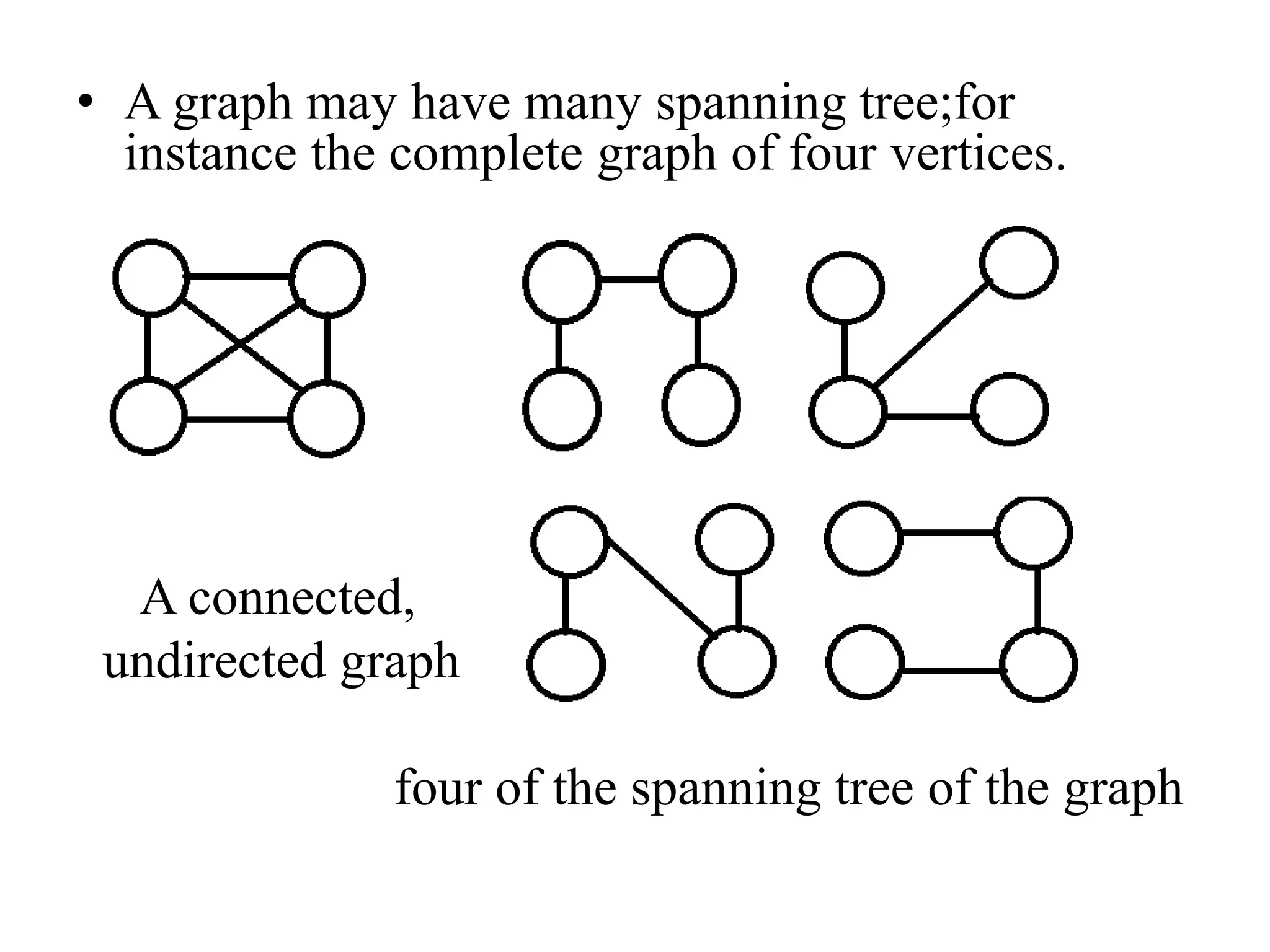
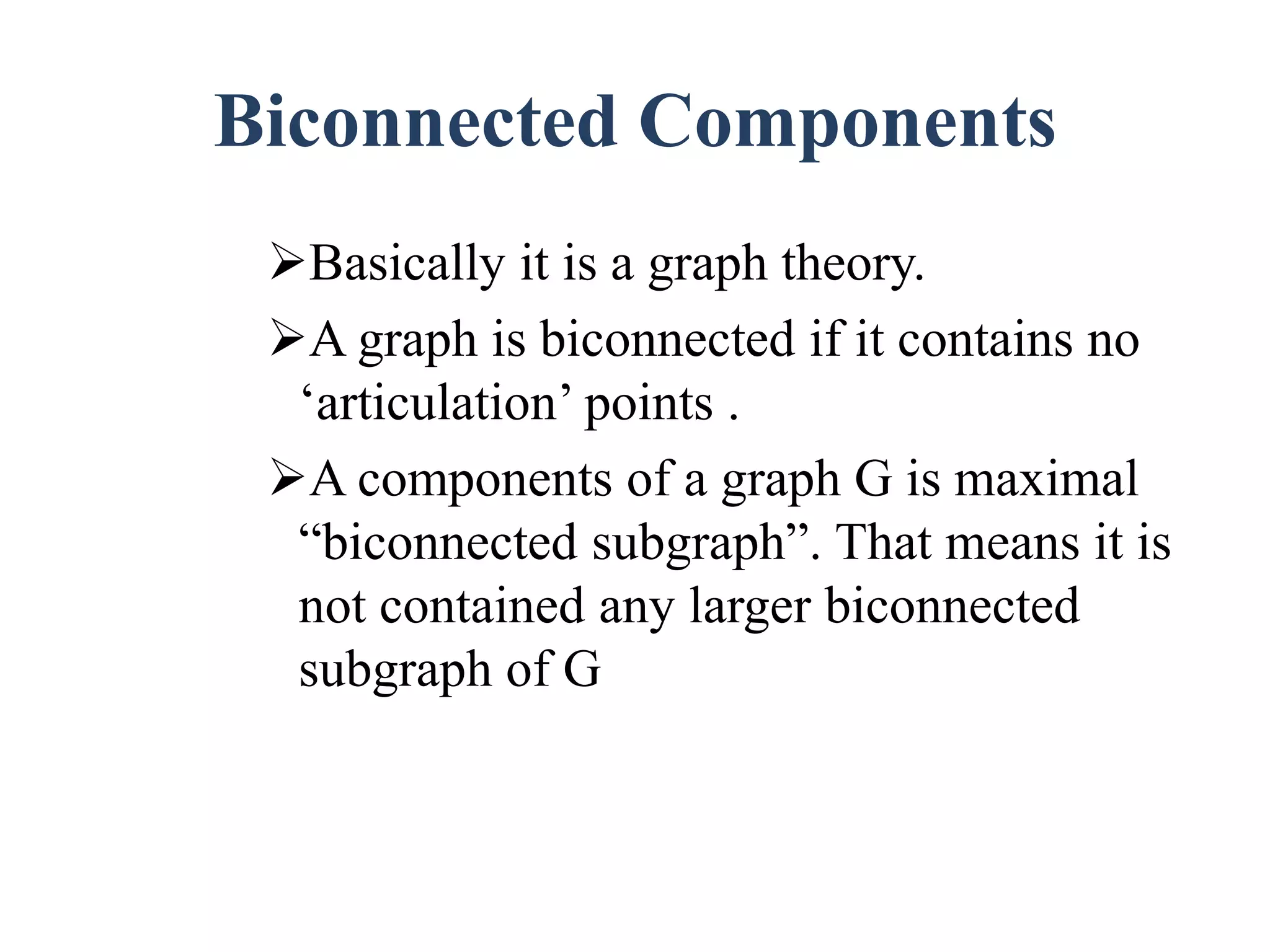
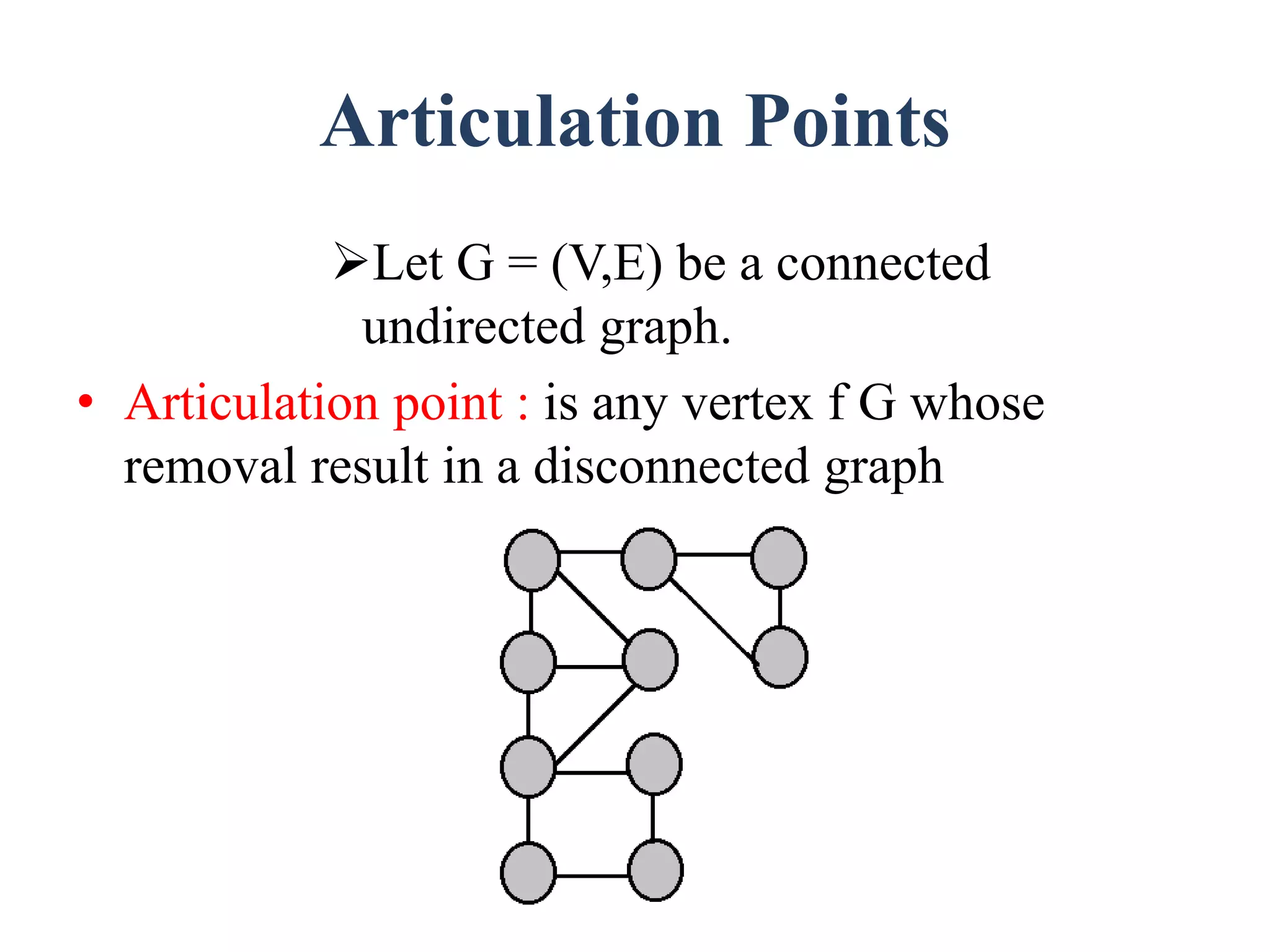
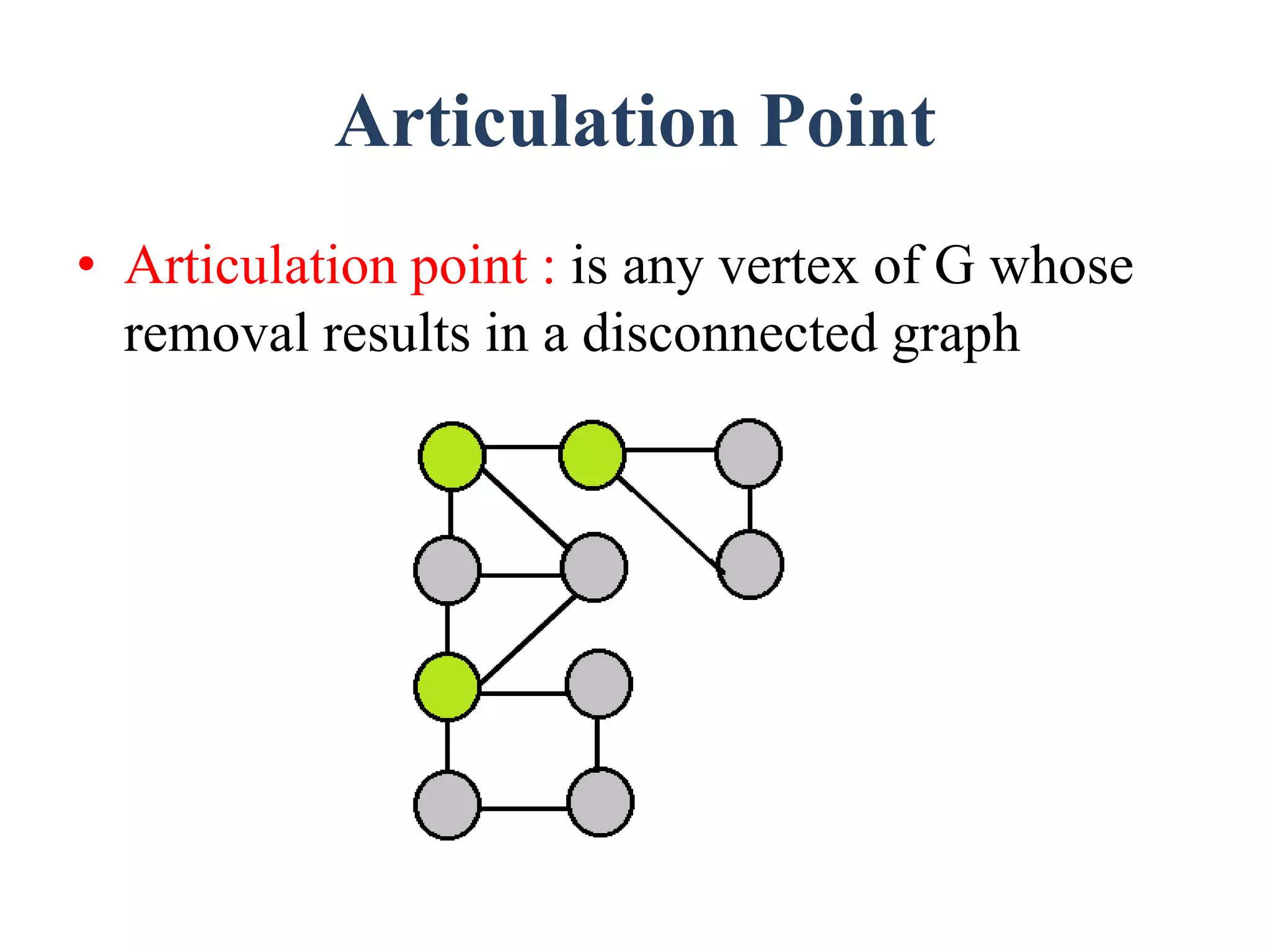
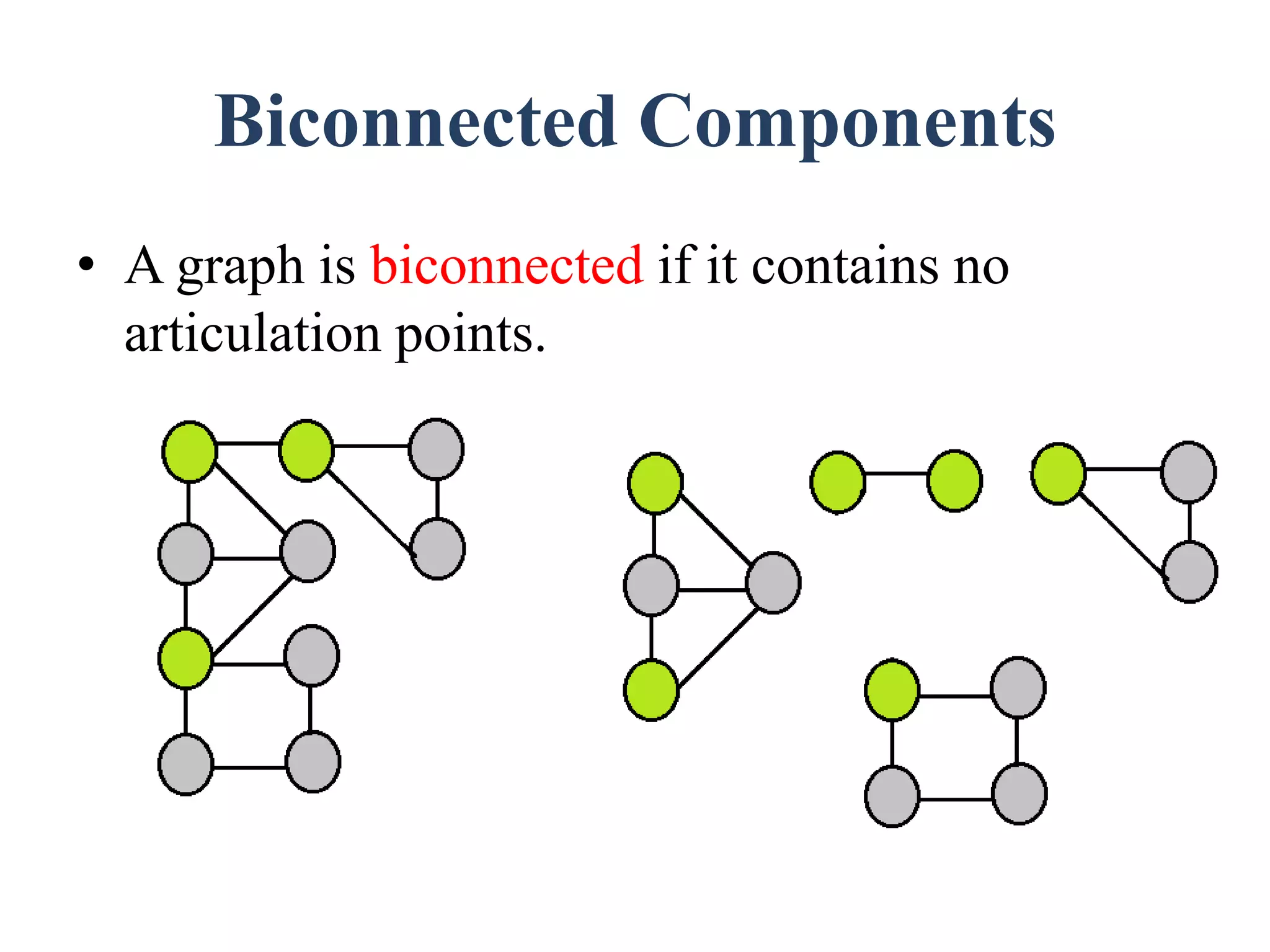
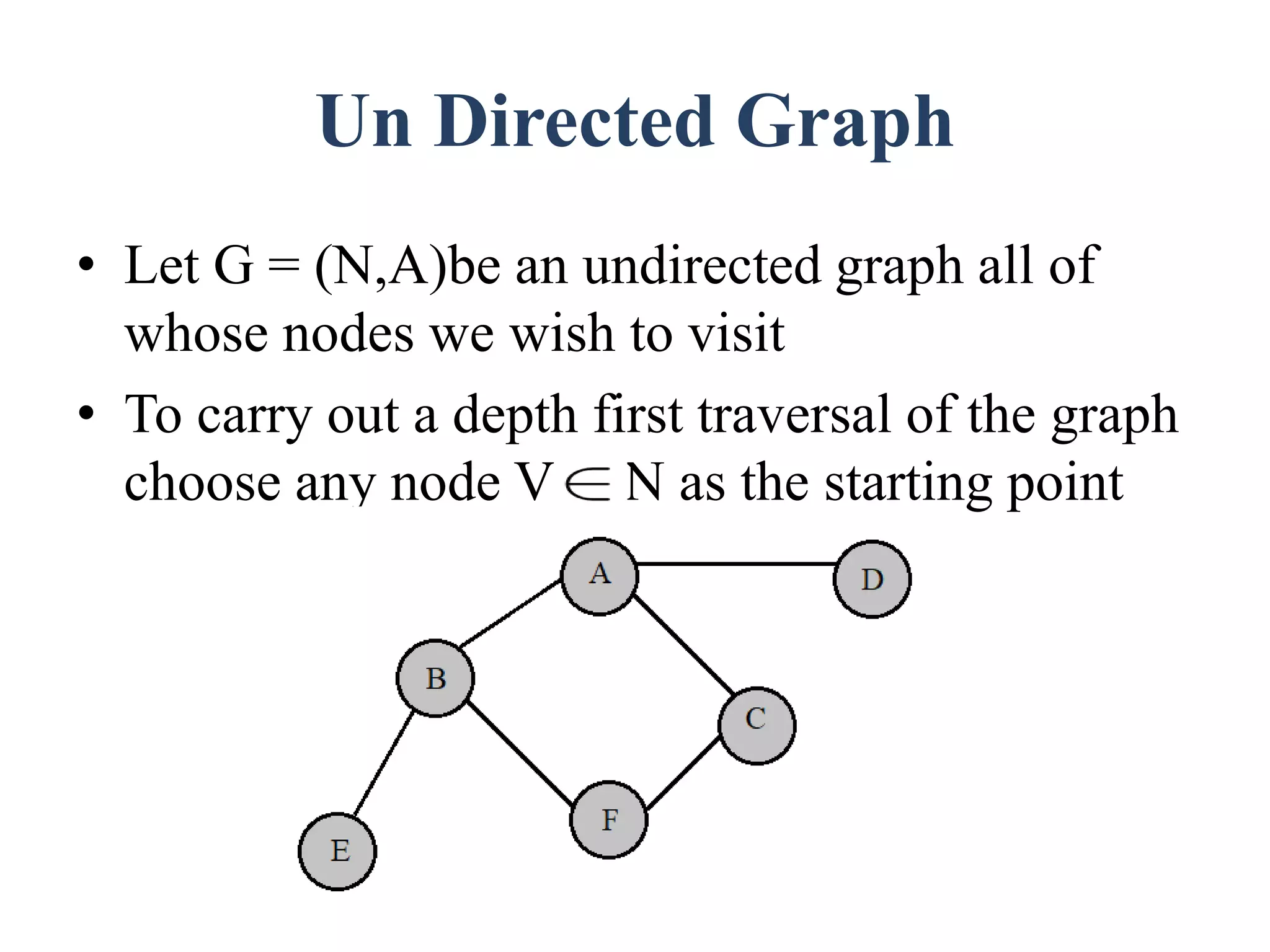
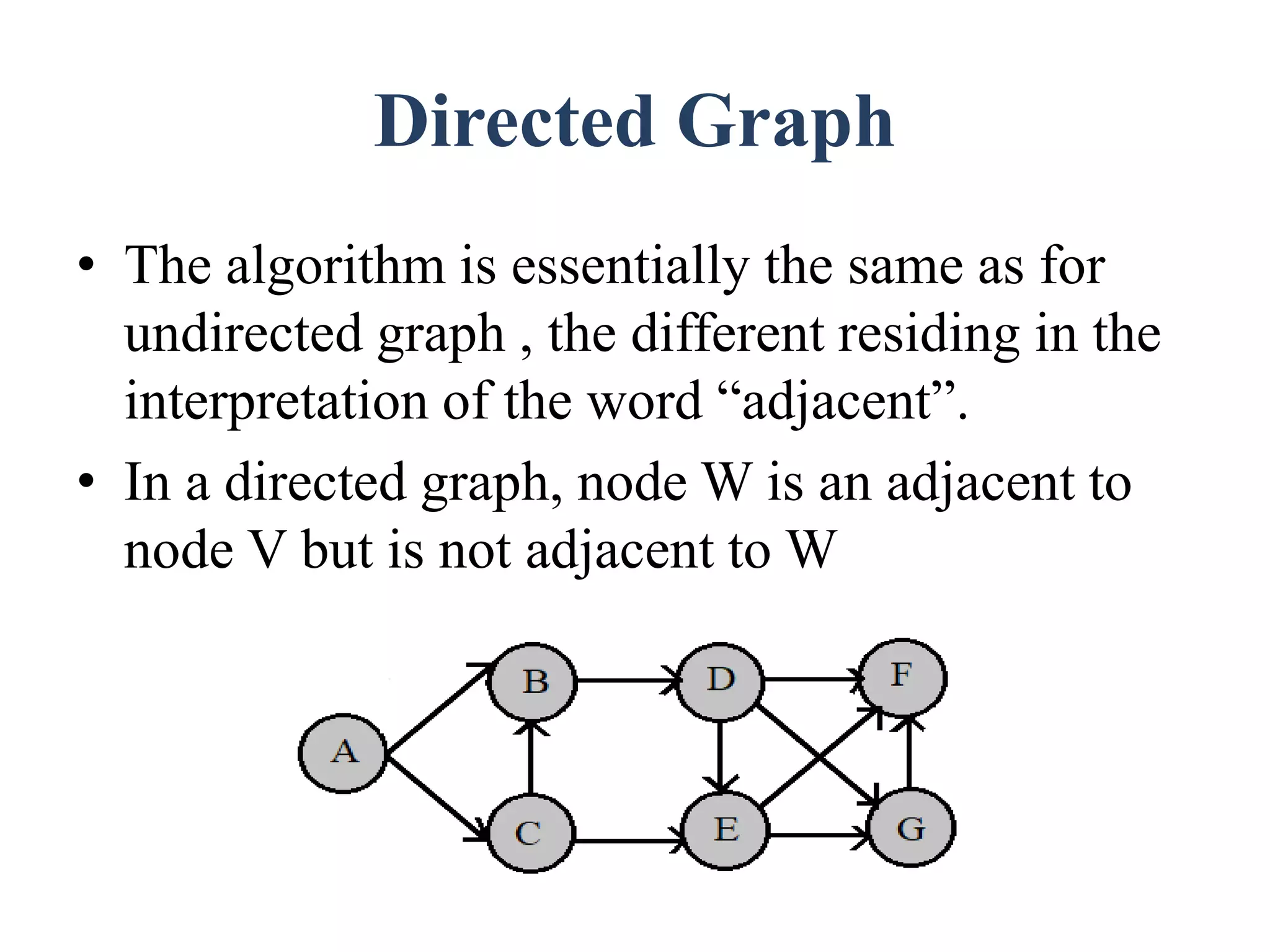
The document discusses graph theory concepts such as connected components, spanning trees, and biconnected components, with a focus on traversal and search techniques. It describes algorithms for depth-first search (DFS) and breadth-first search (BFS), as well as definitions of articulation points and the characteristics of spanning trees. Key points include how to identify connected components and implement traversal techniques effectively.
![Basic Traversal And Search
Techniques
Presented by
S.Vijayalakshmi I-MSC[IT]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsappt-220202134932/75/Basic-Traversal-and-Search-Techniques-1-2048.jpg)




![Determining Connected
Components
void Graph::Components()
{
visited = new Boolean[n];
for(int i=0 ; i<n ; i++)
visited[i]= False;
for(i=0 ; i<n ; i++)
if(!visited[i])
{
DFS(i);
OutputNewComponent();
}
delete[]vivited;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsappt-220202134932/75/Basic-Traversal-and-Search-Techniques-6-2048.jpg)