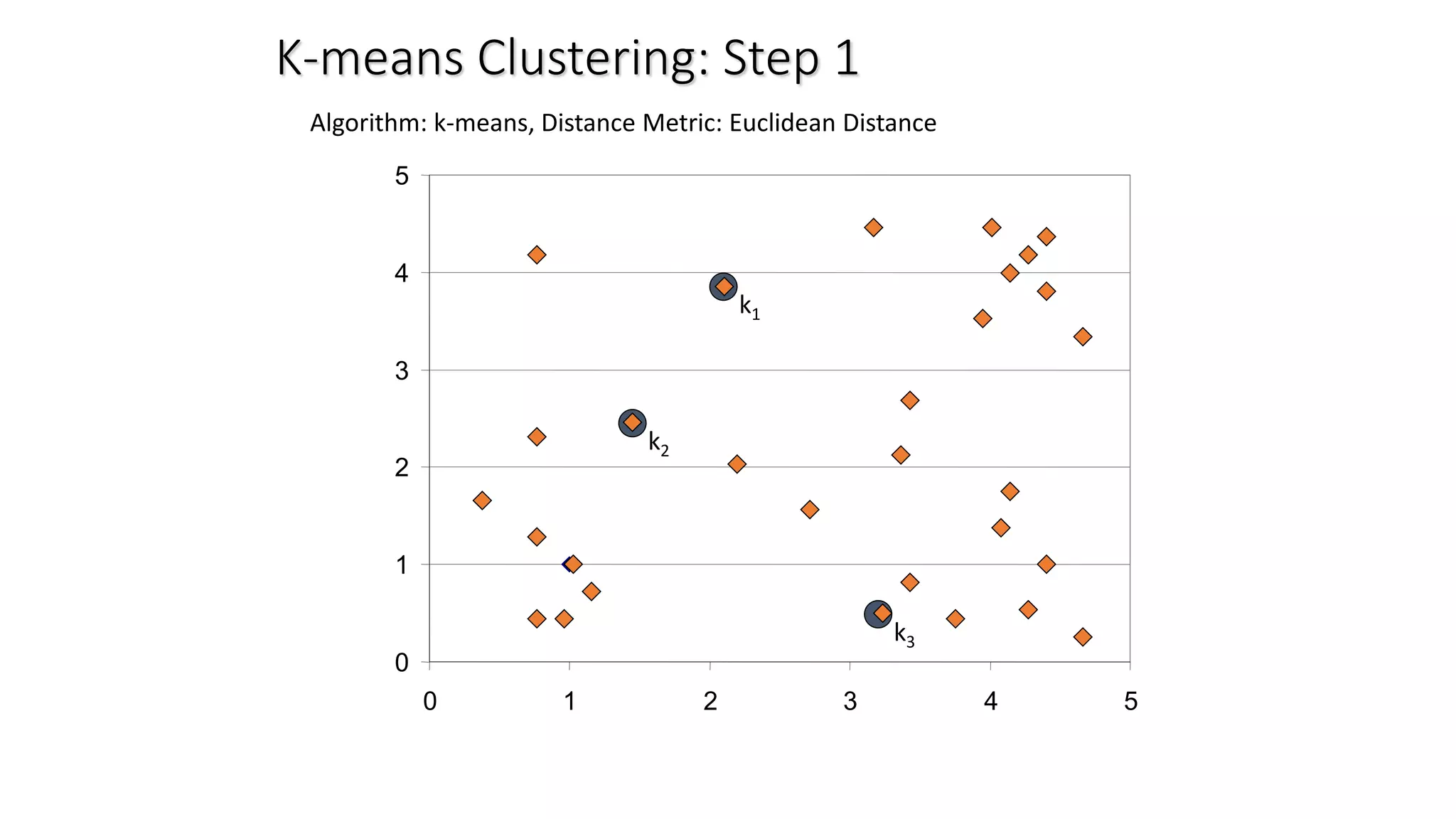
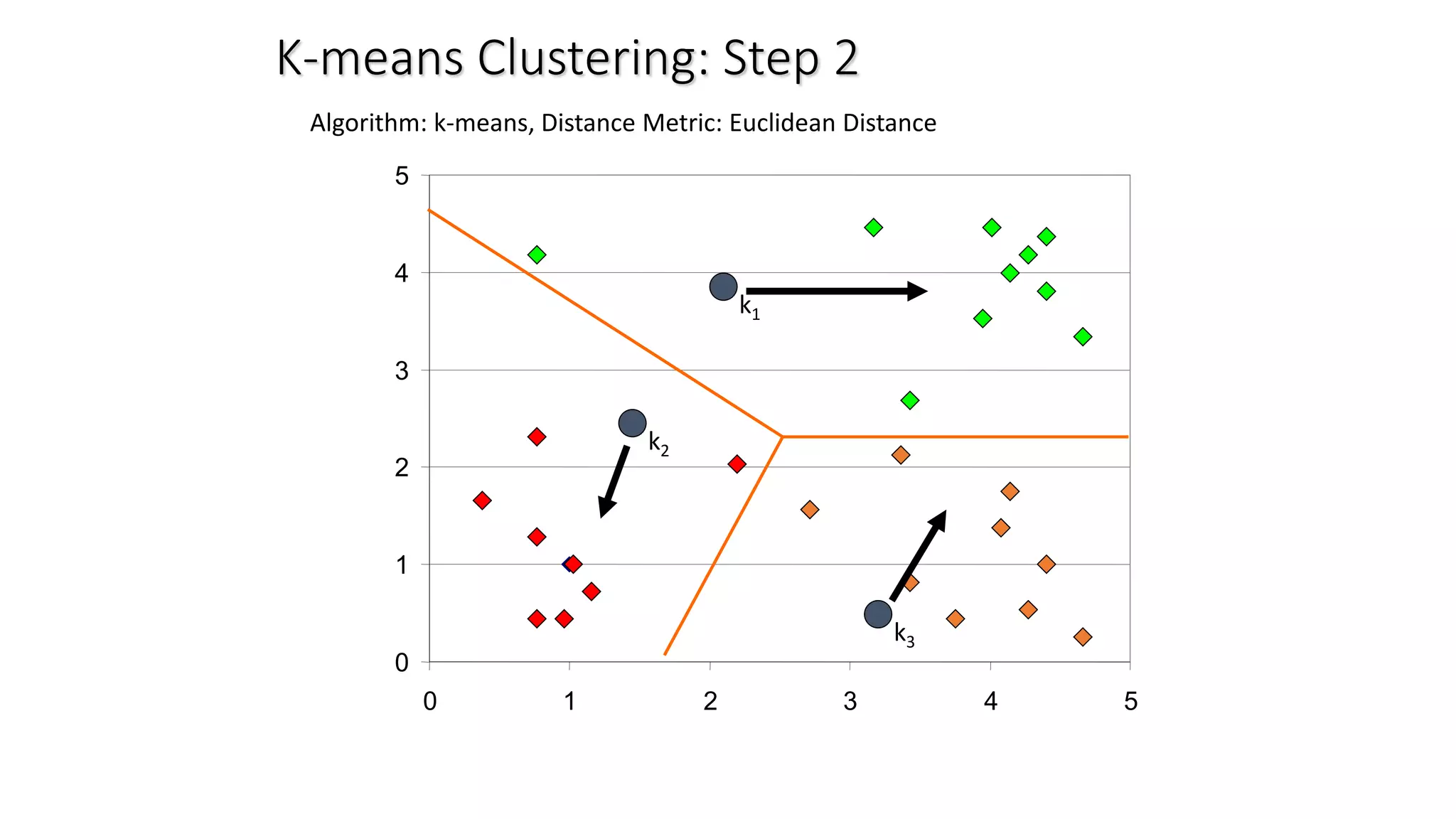
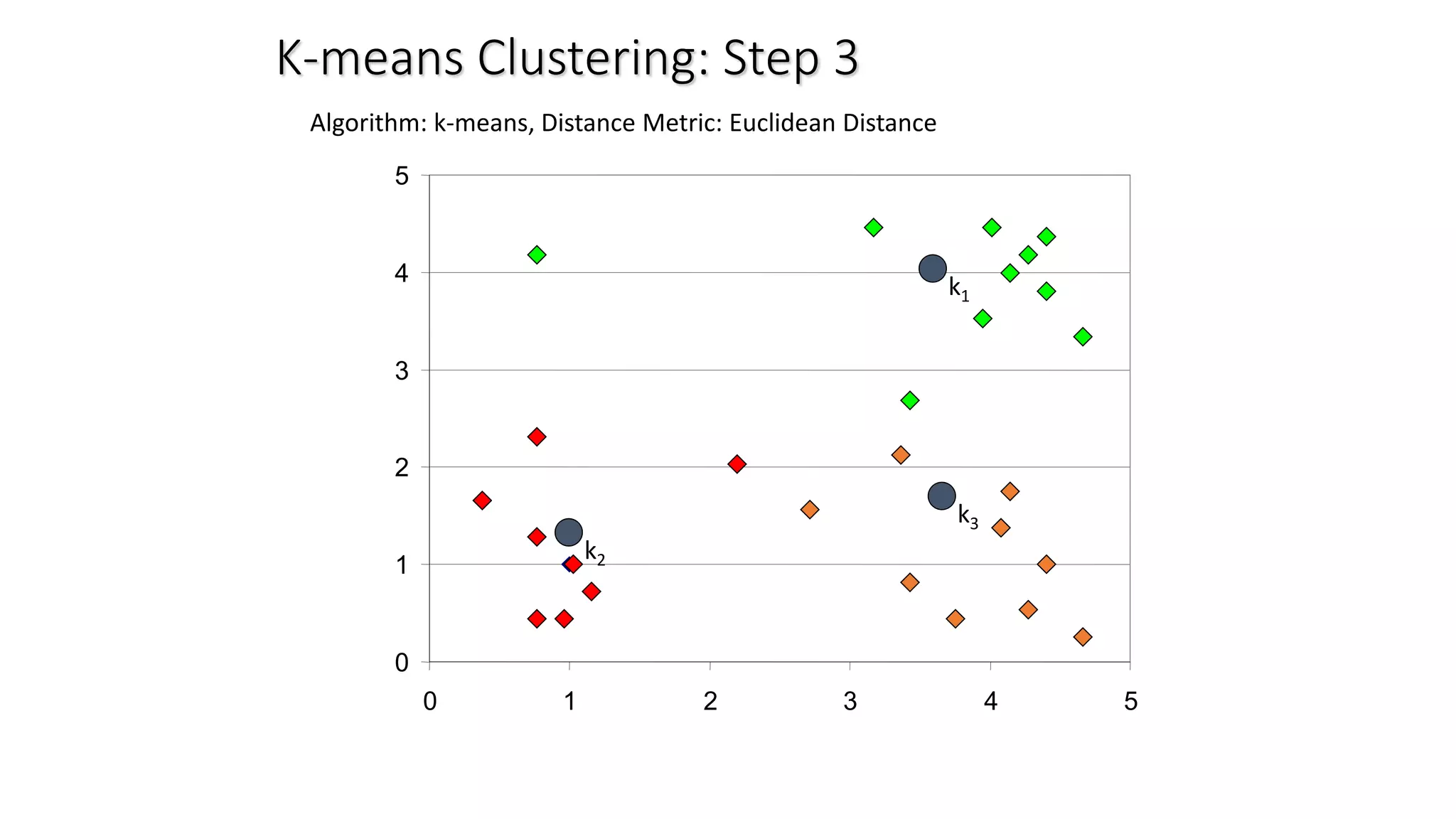
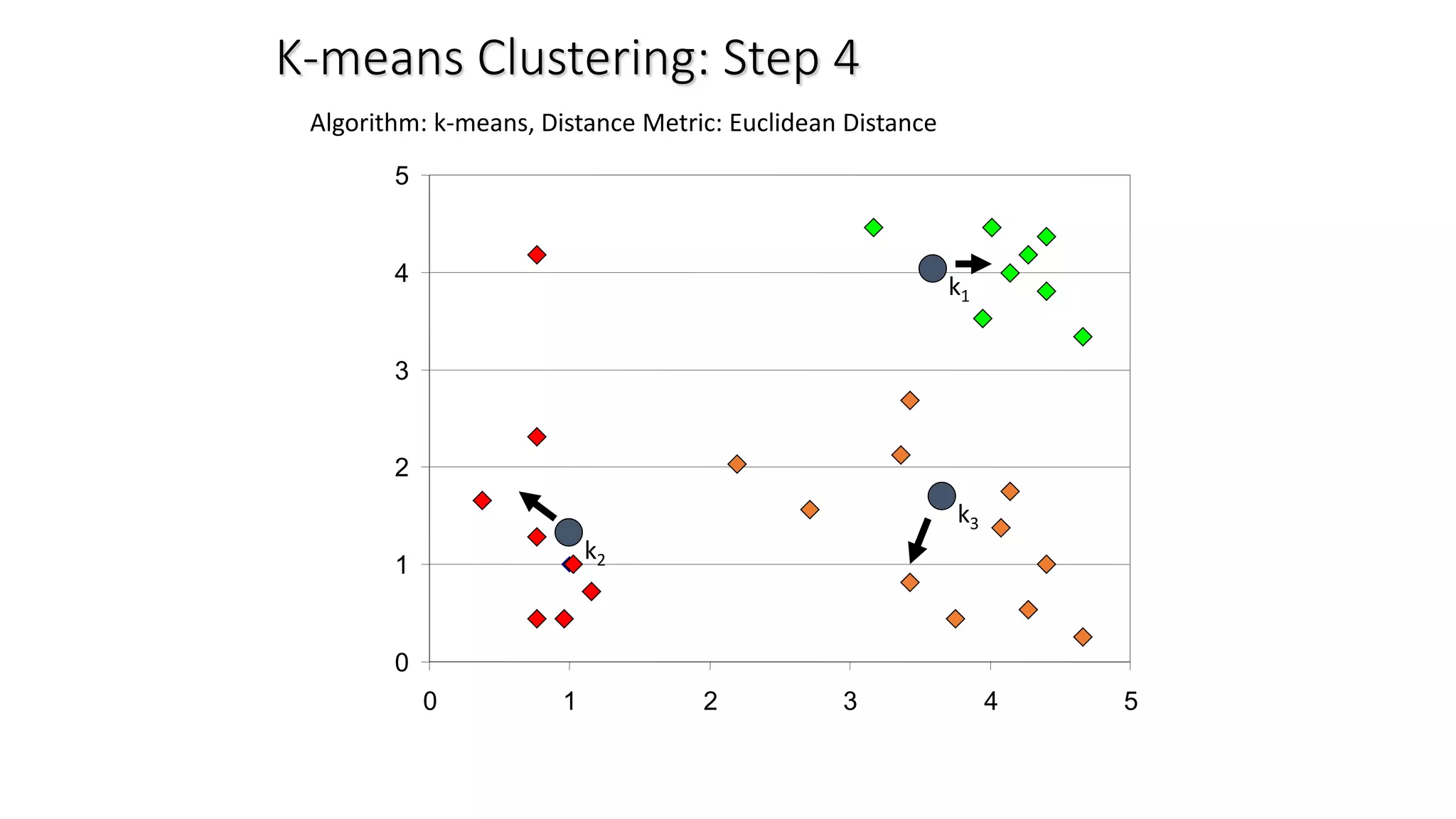
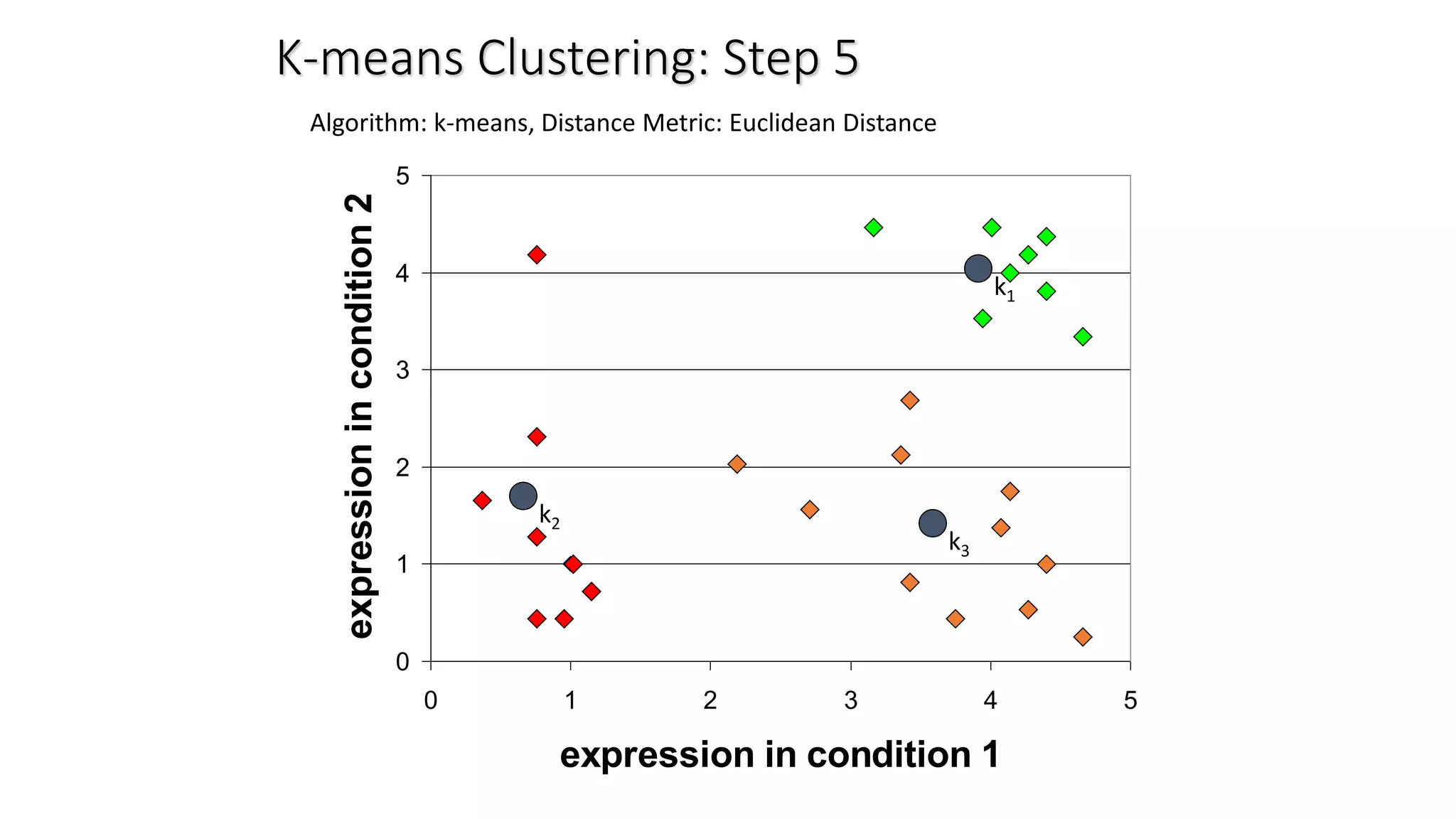
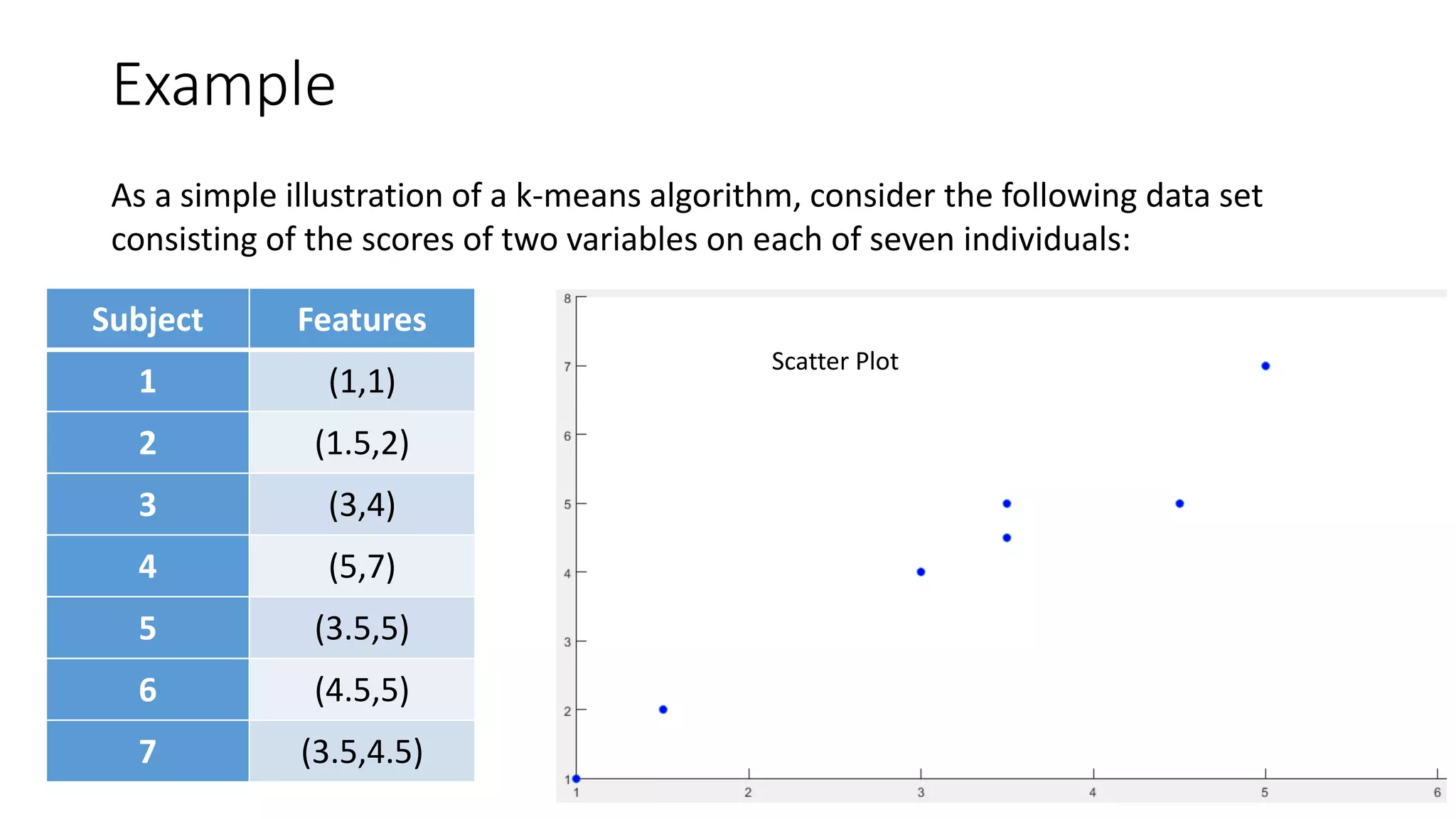
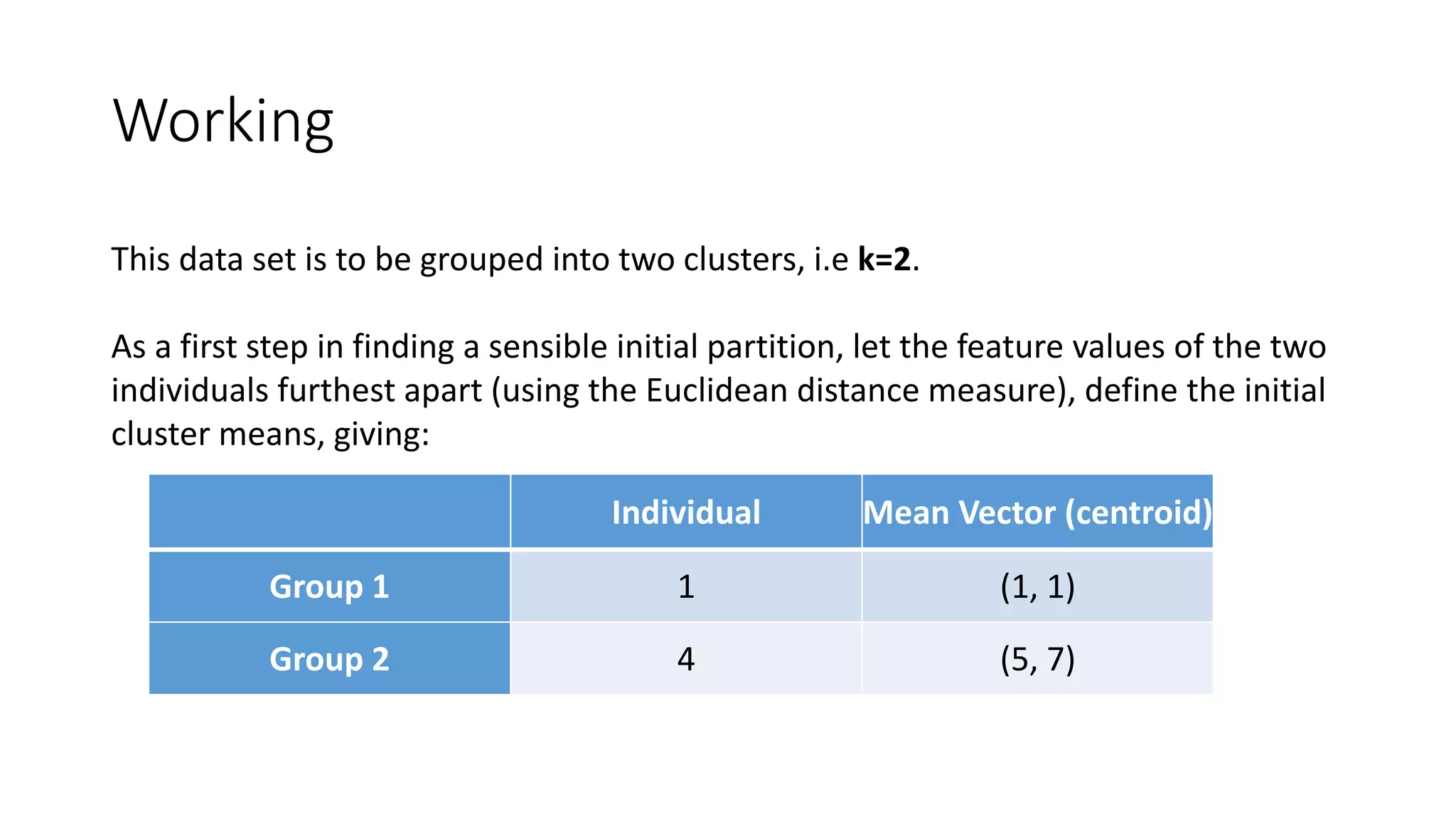
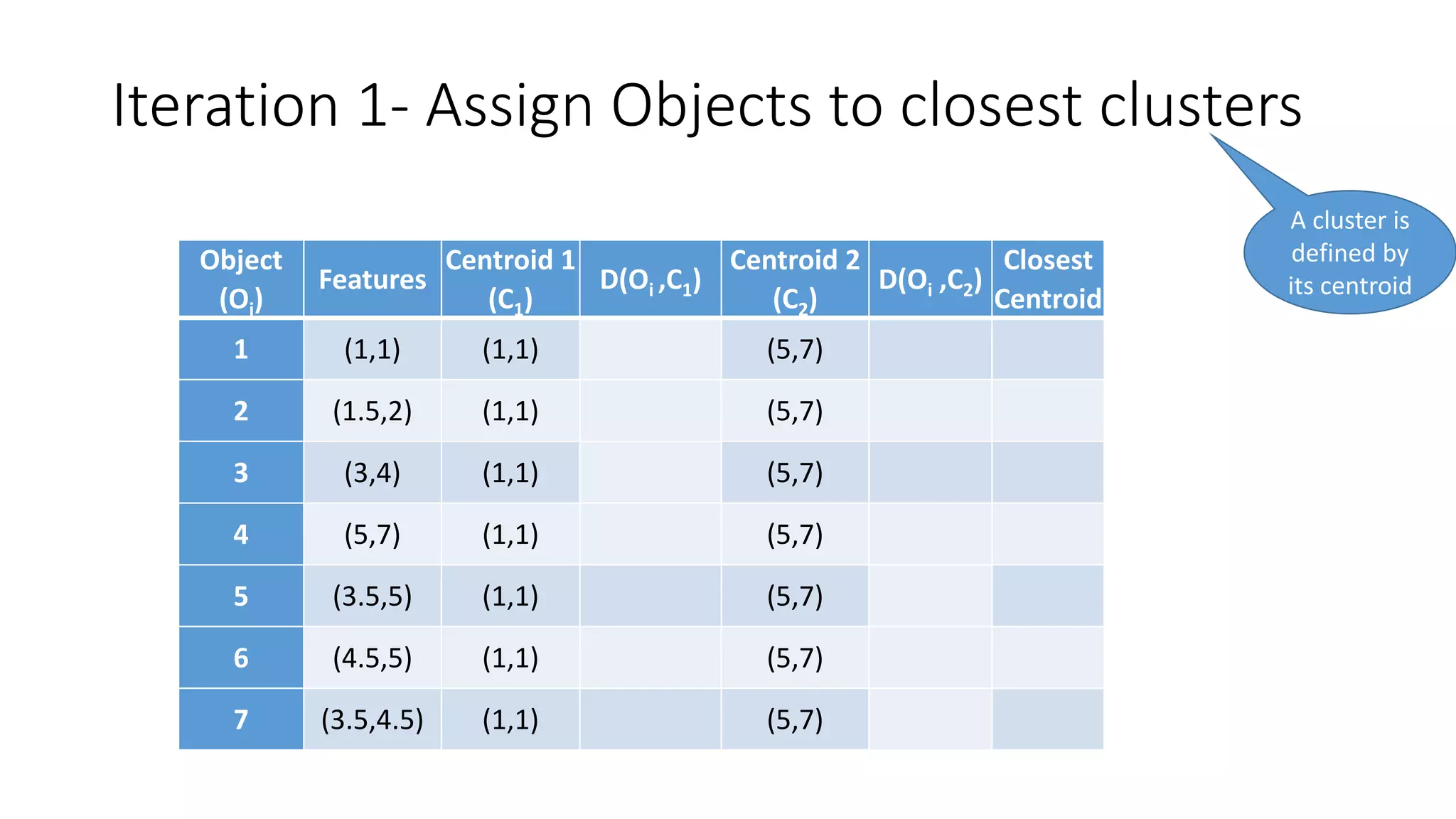
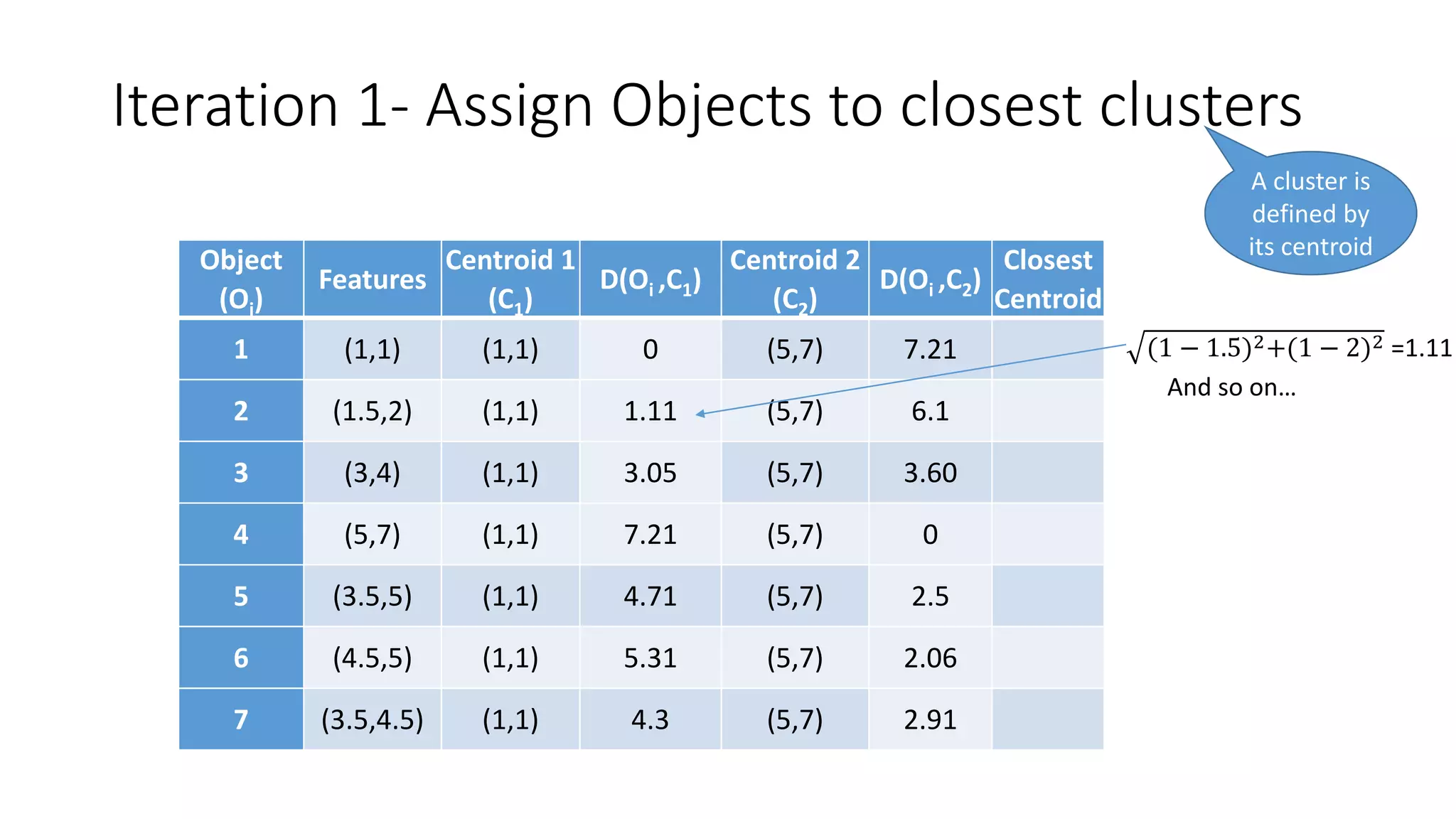
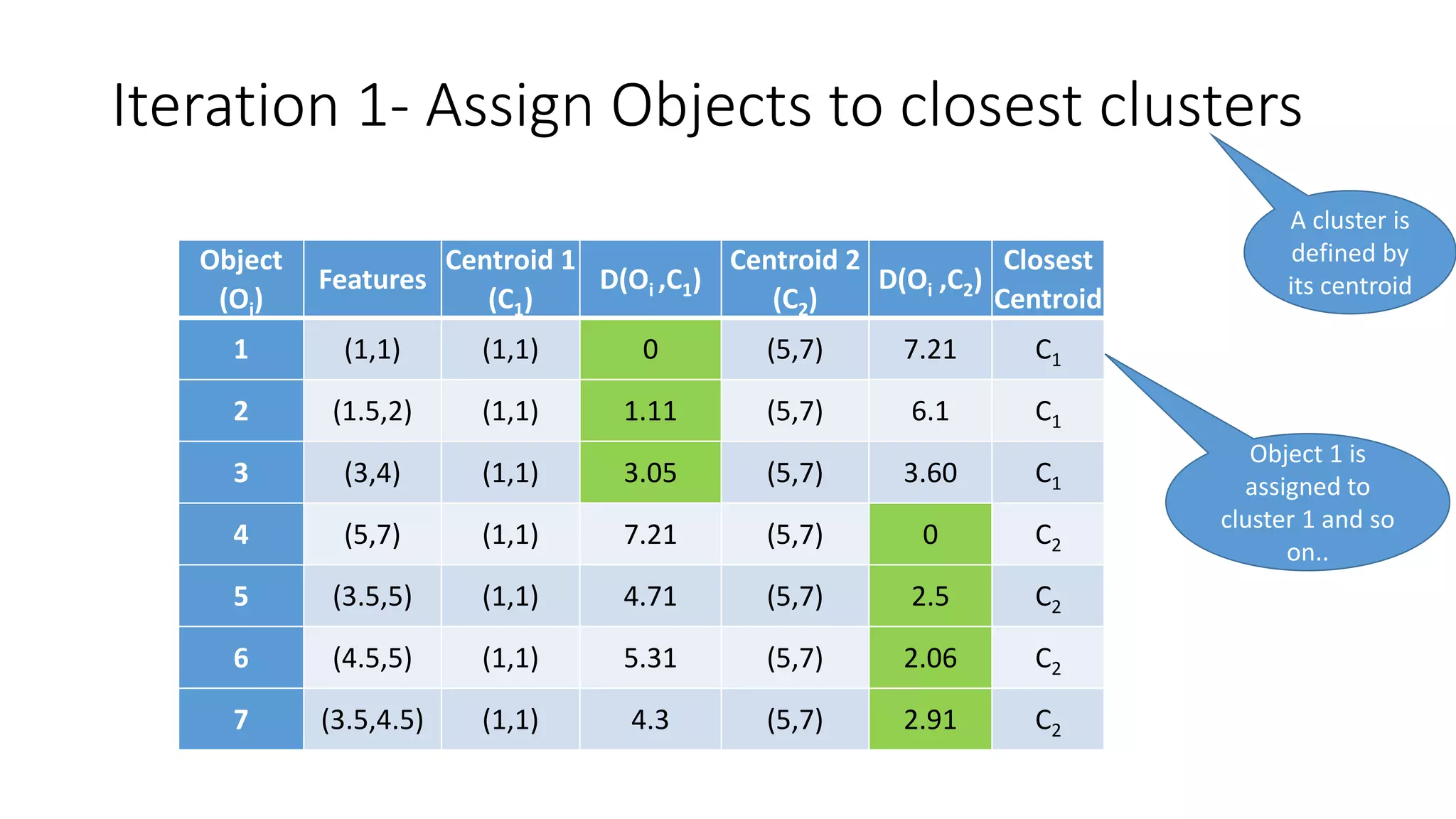
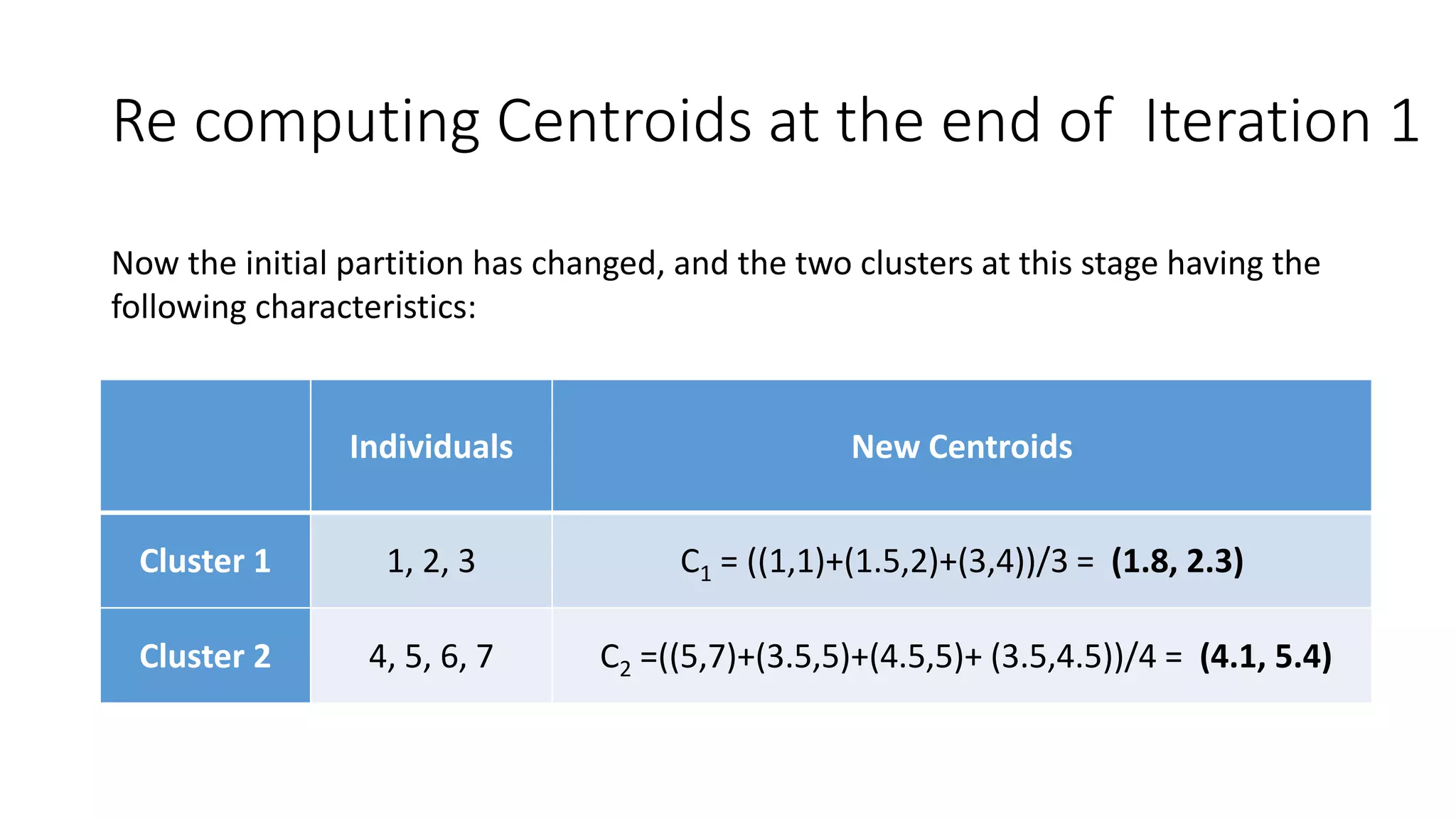
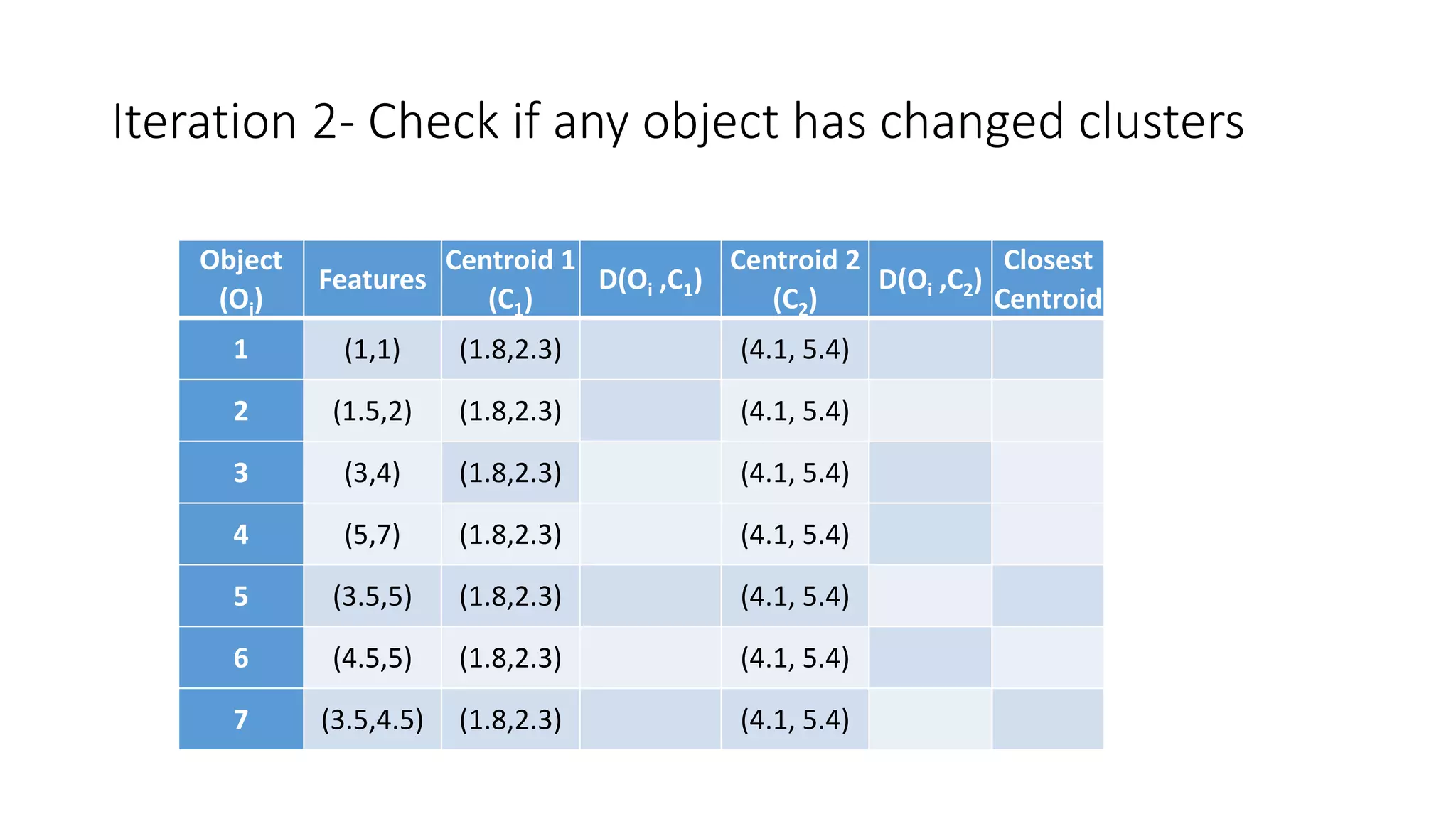
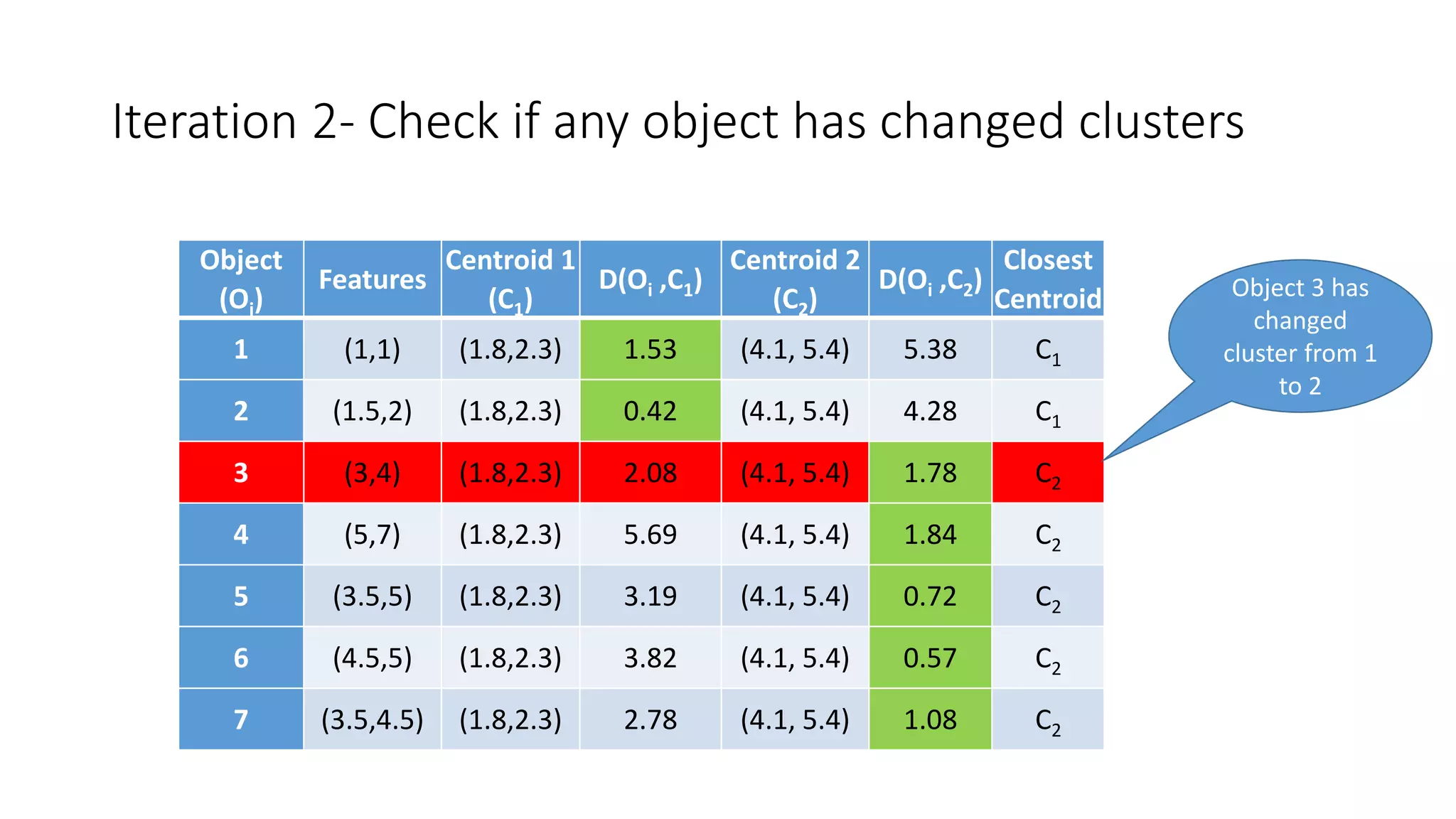
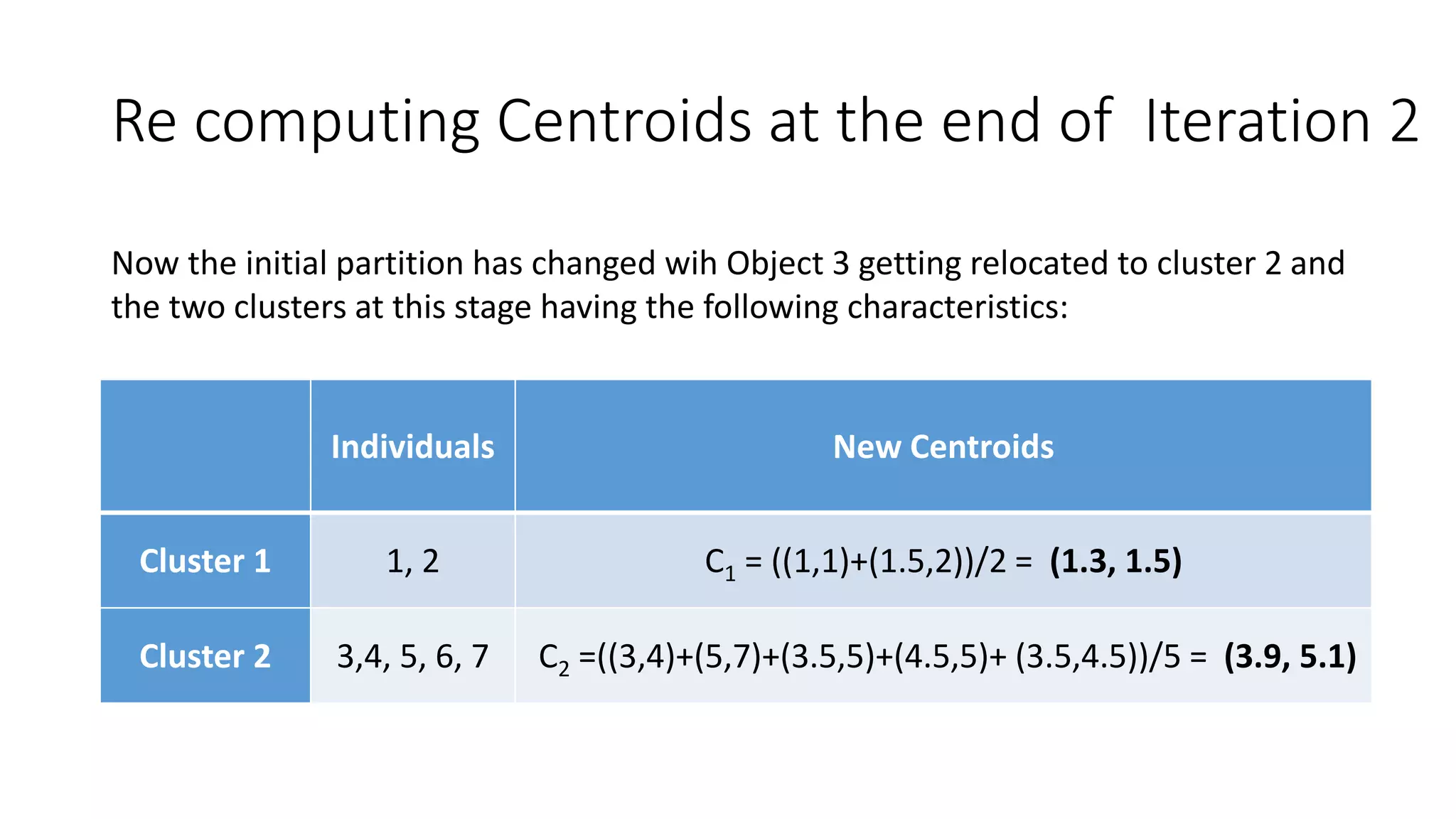
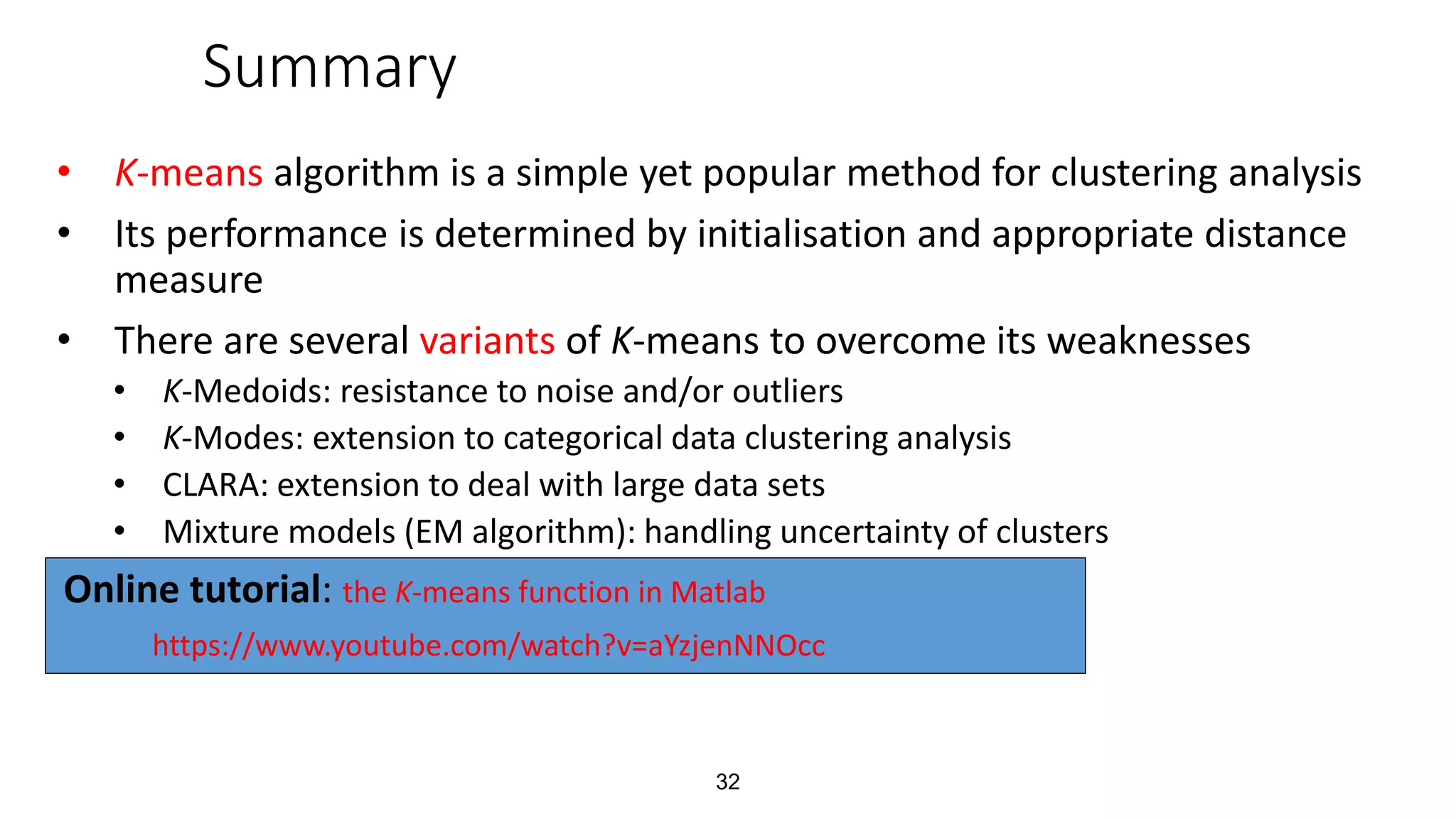
This document discusses clustering and the k-means clustering algorithm. It defines clustering as grouping a set of data objects into clusters so that objects within the same cluster are similar to each other but dissimilar to objects in other clusters. The k-means algorithm is described as an iterative process that assigns each object to one of k predefined clusters based on the object's distance from the cluster's centroid, then recalculates the centroid, repeating until cluster assignments no longer change. A worked example demonstrates how k-means partitions 7 objects into 2 clusters over 3 iterations. The k-means algorithm is noted to be efficient but requires specifying k and can be impacted by outliers, noise, and non-convex cluster shapes.